Fundamental Role of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase 677 C → T Genotype and Flavin Compounds in Biochemical Phenotypes for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis
- PMID: 27881965
- PMCID: PMC5102045
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00172
Fundamental Role of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase 677 C → T Genotype and Flavin Compounds in Biochemical Phenotypes for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis
Abstract
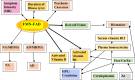
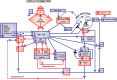
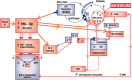
The Mental Health Biomarker Project (2010-2016) explored variables for psychosis in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Blood samples from 67, highly characterized symptomatic cases and 67 gender and age matched control participants were analyzed for methyl tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) 677C → T gene variants and for vitamin B6, B12 and D, folate, unbound copper, zinc cofactors for enzymes in the methylation cycle, and related catecholamine pathways. Urine samples were analyzed for indole-catecholamines, their metabolites, and oxidative-stress marker, hydroxylpyrolline-2-one (HPL). Rating scales were Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, Global Assessment of Function scale, Clinical Global Impression (CGI) score, and Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale (SOFAS). Analysis used Spearman's correlates, receiver operating characteristics and structural equation modeling (SEM). The correlative pattern of variables in the overall participant sample strongly implicated monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme inactivity so the significant role of MAO's cofactor flavin adenine nucleotide and its precursor flavin adenine mononucleotide (FMN) within the biochemical pathways was investigated and confirmed as 71% on SEM of the total sample. Splitting the data sets for MTHFR 677C → T polymorphism variants coding for the MTHFR enzyme, discovered that biochemistry variables relating to the wild-type enzyme differed markedly in pattern from those coded by the homozygous variant and that the hereozygous-variant pattern resembled the wild-type-coded pattern. The MTHFR 677C → T-wild and -heterozygous gene variants have a pattern of depleted vitamin cofactors characteristic of flavin insufficiency with under-methylation and severe oxidative stress. The second homozygous MTHFR 677TT pattern related to elevated copper:zinc ratio and a vitamin pattern related to flavin sufficiency and risk of over-methylation. The two gene variants and their different biochemical phenotypes govern findings in relationship to case-identification, illness severity, duration of illness, and functional disability in schizophrenia and schizoaffective psychosis, and establish a basis for trials of gene-guided precision treatment for the management of psychosis.
Keywords: MTHFR 677C → T polymorphisms; copper; psychosis; riboflavin; schizophrenia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanism Biomarkers Predict Diagnosis in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis, with Implications for Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15845. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115845. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958826 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Provide a Landscape for Biomarker Selection for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15296. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Variant Related Neurological and Molecular Biomarkers Predict Psychosis Progression, with Potential for Monitoring and Prevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13348. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413348. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769114 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker Case-Detection and Prediction with Potential for Functional Psychosis Screening: Development and Validation of a Model Related to Biochemistry, Sensory Neural Timing and End Organ Performance.Front Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 14;7:48. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00048. eCollection 2016. Front Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27148083 Free PMC article.
-
The biochemical structure and function of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase provide the rationale to interpret the epidemiological results on the risk for infants with Down syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2008 Jun 1;146A(11):1477-82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32308. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. PMID: 18446861 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin B₆ and Its Role in Cell Metabolism and Physiology.Cells. 2018 Jul 22;7(7):84. doi: 10.3390/cells7070084. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30037155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MTHFR c.665C>T and c.1298A>C Polymorphisms in Tailoring Personalized Anti-TNF-α Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 18;24(4):4110. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044110. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835522 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism Biomarkers Predict Diagnosis in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis, with Implications for Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15845. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115845. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958826 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting outliers in case-control cohorts for improving deep learning networks on Schizophrenia prediction.J Integr Bioinform. 2024 Jul 15;21(2):20230042. doi: 10.1515/jib-2023-0042. eCollection 2024 Jun 1. J Integr Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39004922 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Provide a Landscape for Biomarker Selection for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15296. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fryar-Williams S, Strobel J. Biomarker case-detection and prediction with potential for functional psychosis screening: development and validation of a model elated to biochemistry, sensory neural timing and end organ performance. Front Psychiatry (2016) 7:48.10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00048 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Irvine DG. Hydroxy-haemopyrrolenone, not kryptopyrrole, in the urine of schizophrenics and porphyrics. Clin Chem (1978) 24(11):2069–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

