Inhibition of antiviral drug cidofovir on proliferation of human papillomavirus-infected cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 27882102
- PMCID: PMC5103731
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3718
Inhibition of antiviral drug cidofovir on proliferation of human papillomavirus-infected cervical cancer cells
Abstract
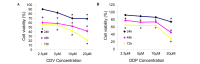
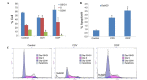
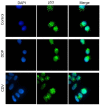
In order to evaluate the potential application value of cidofovir (CDV) in the prevention of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and treatment of cervical cancer, the inhibitory effect of CDV on the proliferation of HPV 18-positive HeLa cells in cervical cancer was preliminarily investigated, using cisplatin (DDP) as a positive control. An MTT assay was used to analyze the effects of CDV and DDP on HeLa cell proliferation. In addition, clone formation assay and Giemsa staining were used to examine the extent of HeLa cell apoptosis caused by CDV and DDP. Flow cytometry was also used to detect the shape and size of apoptotic cells following propidium iodide staining, while western blot analysis identified the expression levels of of E6 and p53 proteins in HeLa cells. A cell climbing immunofluorescence technique was used to locate the subcellular position of p53 in HeLa cells. The results demonstrated that CDV and DDP inhibited the proliferation of HeLa cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometry showed that CDV and DDP treatments resulted in cell arrest in the S-phase, and triggered programmed cell death. Furthermore, western blot analysis revealed that CDV and DDP inhibited E6 protein expression and activated p53 expression in HeLa cells. Finally, the immunofluorescence results indicated that CDV and DDP inhibited the nuclear export of p53 by E6 protein, which is required for degradation of endogenous p53 by MDM2 and human papilloma virus E6. In conclusion, CDV and DDP inhibited HeLa cell proliferation in a concentration- and time-dependent manner, reduced the expression of E6 protein, and reinstated p53 protein activity. Thus, CDV regulates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and may be a potential cervical cancer therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: HeLa cells; apoptosis; cervical cancer; cidofovir; cisplatin; human papillomavirus.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhanced antiproliferative effects of alkoxyalkyl esters of cidofovir in human cervical cancer cells in vitro.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Jan;5(1):156-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0200. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16432174
-
Cidofovir selectivity is based on the different response of normal and cancer cells to DNA damage.BMC Med Genomics. 2013 May 23;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-18. BMC Med Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23702334 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide induces cervical cancer apoptosis, but specifically targets human papillomavirus-infected cell populations.Anticancer Drugs. 2012 Mar;23(3):280-7. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32834f1fd3. Anticancer Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22245994
-
Cidofovir in the treatment of HPV-associated lesions.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(2):93-120, discussion 120-2. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11436421 Review.
-
Proteasome inhibitor MG132 sensitizes HPV-positive human cervical cancer cells to rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis.Int J Cancer. 2006 Apr 15;118(8):1892-900. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21580. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16287099
Cited by
-
Identification of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus DNA, p16, and E6/E7 Oncoproteins in Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Viruses. 2021 May 27;13(6):1008. doi: 10.3390/v13061008. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34072187 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Prostaglandin E2 Signaling in Carcinogenesis: A Focus on Cervical Cancer Therapeutics.Cells. 2022 Aug 15;11(16):2528. doi: 10.3390/cells11162528. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic and Stemness Signatures of the High-Risk HCMV Strains in Breast Cancer Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 1;14(17):4271. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174271. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077806 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the p16 and p53 Tumor Suppressor Proteins and Viral HPV16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in the Assessment of Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Cancers Associated with Human Papillomavirus Infections.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 11;15(10):2722. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102722. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345059 Free PMC article.
-
Novel directions of precision oncology: circulating microbial DNA emerging in cancer-microbiome areas.Precis Clin Med. 2022 Feb 3;5(1):pbac005. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbac005. eCollection 2022 Mar. Precis Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35692444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cox JT. Epidemiology and natural history of HPV. J Fam Pract Suppl. 2006:3–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
