Modulatory effects of feeding pregnant and lactating mice Rhodiola kirilowii extracts on the immune system of offspring
- PMID: 27882178
- PMCID: PMC5103842
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3759
Modulatory effects of feeding pregnant and lactating mice Rhodiola kirilowii extracts on the immune system of offspring
Abstract
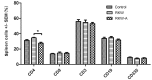
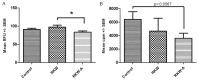
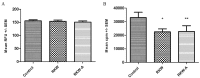
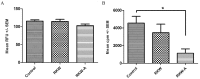
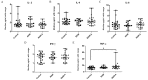
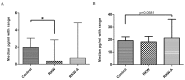
Plants of Rhodiola genus are medicinal herbs that have a number of therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activity. The present study aimed to determine whether the use Rhodiola kirilowii as an immunostimulant during pregnancy has an adverse effect on the development of the offspring immune system. Following mating, pregnant mice were placed in three groups that were fed during pregnancy and lactation with R. kirilowii aqueous extract (RKW; 20 mg/kg), R. kirilowii 50% hydro-alcoholic extract (RKW-A; 20 mg/kg) or water (control group), receiving water. Following birth, offspring were given six weeks to develop prior to evaluation of their immune system. Morphometric and morphological examination of the spleen did not reveal any abnormalities or differences between the experimental and control groups. However, both RKW and RKW-A splenic lymphocytes presented a diminished proliferative response to concanavalin A. RKW spleen lymphocytes demonstrated increased metabolic activity following phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulation, which was associated with a higher percentage of cluster of differentiation 4 positive spleen cells and lower interleukin-17a (IL-17a) serum concentration. The RKW-A group exhibited a diminished proliferative response of spleen lymphocytes to PHA and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and increased serum concentrations of IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). The progeny of mice fed with RKW-A extract demonstrated a significantly lower level of anti-SRBC antibody following immunization compared with progeny of the control (P=0.0305) and RKW (P=0.0331) groups. In conclusion, caution is recommended in the use of RKW and RKW-A extracts as immunostimulants in pregnancy.
Keywords: Rhodiola kirilowii; immune response; mice; pregnancy; progeny.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Administration of Rhodiola kirilowii Extracts during Mouse Pregnancy and Lactation Stimulates Innate but Not Adaptive Immunity of the Offspring.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8081642. doi: 10.1155/2017/8081642. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29214185 Free PMC article.
-
Morphofunctional Renal Alterations in Progeny of Mice Fed Rhodiola kirilowii Extracts or Epigallocatechin During Pregnancy and Lactation.J Med Food. 2017 Jan;20(1):86-92. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.0126. Epub 2016 Dec 9. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 27935764
-
The influence of aqueous and hydro-alcoholic extracts of roots and rhizomes of Rhodiola kirilowii on the course of pregnancy in mice.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2014;39(4):471-5. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2014.47731. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 26155165 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches of Rhodiola kirilowii and Rhodiola rosea field cultivation in Poland and their potential health benefits.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2015;22(2):281-5. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1152081. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2015. PMID: 26094524 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of three species of Rhodiola L. in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1139239. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1139239. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Administration of Rhodiola kirilowii Extracts during Mouse Pregnancy and Lactation Stimulates Innate but Not Adaptive Immunity of the Offspring.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8081642. doi: 10.1155/2017/8081642. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29214185 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of feeding mice during gestation and nursing with Rhodiola kirilowii extracts or epigallocatechin on CD4 and CD8 cells number and distribution in the spleen of their progeny.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2017;42(1):10-16. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2017.67313. Epub 2017 May 8. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28680326 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of Plants with Immunomodulatory Properties during Pregnancy and Lactation-Maternal and Offspring Health Effects.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 20;11(8):1958. doi: 10.3390/nu11081958. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31434310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang S, Gao W, Xu K, Guo Y, Lin S, Xue X, Lu G, Li N, Liu H, Liu W. Early use of Chinese drug rhodiola compound for patients with post-trauma and inflammation in prevention of ALI/ARDS. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1999;37:238–240. (In Chinese) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
