Circuit Mechanisms of Sensorimotor Learning
- PMID: 27883902
- PMCID: PMC5131723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.029
Circuit Mechanisms of Sensorimotor Learning
Abstract
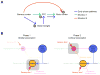
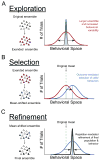
The relationship between the brain and the environment is flexible, forming the foundation for our ability to learn. Here we review the current state of our understanding of the modifications in the sensorimotor pathway related to sensorimotor learning. We divide the process into three hierarchical levels with distinct goals: (1) sensory perceptual learning, (2) sensorimotor associative learning, and (3) motor skill learning. Perceptual learning optimizes the representations of important sensory stimuli. Associative learning and the initial phase of motor skill learning are ensured by feedback-based mechanisms that permit trial-and-error learning. The later phase of motor skill learning may primarily involve feedback-independent mechanisms operating under the classic Hebbian rule. With these changes under distinct constraints and mechanisms, sensorimotor learning establishes dedicated circuitry for the reproduction of stereotyped neural activity patterns and behavior.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Perception as a Route for Motor Skill Learning: Perspectives from Neuroscience.Neuroscience. 2018 Jul 1;382:144-153. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29694916 Review.
-
Bayesian integration in sensorimotor learning.Nature. 2004 Jan 15;427(6971):244-7. doi: 10.1038/nature02169. Nature. 2004. PMID: 14724638
-
Neural Variability Limits Adolescent Skill Learning.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 10;39(15):2889-2902. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2878-18.2019. Epub 2019 Feb 12. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30755494 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from learning: what can visuomotor adaptations tell us about the neuronal representation of movement?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;629:221-42. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77064-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19227502 Review.
-
Neural basis of sensorimotor learning: modifying internal models.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Dec;18(6):573-81. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.11.003. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 19054663 Review.
Cited by
-
The learning-relative hemodynamic modulation of cortical plasticity induced by a force-control motor training.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 8;16:922725. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.922725. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36161184 Free PMC article.
-
Active perceptual learning involves motor exploration and adaptation of predictive sensory integration.iScience. 2023 Dec 1;27(1):108604. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108604. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38155781 Free PMC article.
-
[Procyanidin B2 protects neurons from cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress through the P13K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Aug 20;41(8):1158-1164. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.08.05. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34549705 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
EEG connectivity and BDNF correlates of fast motor learning in laparoscopic surgery.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 3;15(1):7399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89261-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40032953 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of BDNF Expression in Layer II/III and Layer V Neurons of the Motor Cortex Is Essential for Motor Learning.J Neurosci. 2020 Aug 12;40(33):6289-6308. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0288-20.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32651187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asaad WF, Rainer G, Miller EK. Neural Activity in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex during Associative Learning. Neuron. 1998;21:1399–1407. - PubMed
-
- Averbeck BB, Latham PE, Pouget A. Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Bathellier B, Ushakova L, Rumpel S. Discrete neocortical dynamics predict behavioral categorization of sounds. Neuron. 2012;76:435–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

