Disability in patients with end-stage liver disease: Results from the functional assessment in liver transplantation study
- PMID: 27884053
- PMCID: PMC5325797
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.24684
Disability in patients with end-stage liver disease: Results from the functional assessment in liver transplantation study
Abstract
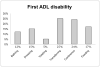
Cirrhosis leads to sarcopenia and functional decline that can severely impact one's ability to function at home and in society. Self-reported disability scales to quantify disability-Activities of Daily Living (ADL) and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL)-are validated to predict mortality in older adults. To evaluate disability in liver transplantation (LT) candidates and quantify its impact on outcomes, consecutive outpatients ≥18 years listed for LT with laboratory Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores of ≥12 at a single high-volume US LT center were assessed for ADLs and IADLs during clinic visits. Multivariate competing risk models explored the effect of disabilities on wait-list mortality (death or delisting for illness). Of 458 patients, 36% were women, median (interquartile range [IQR]) age was 60 years (IQR, 54-64 years), and initial Model for End-Stage Liver Disease-Sodium (MELD-Na) was 17 (IQR 14-20). At first visit, 31% had lost ≥ 1 ADL, and 40% had lost ≥ 1 IADL. The most prevalent ADL deficits lost were continence (22%), dressing (12%), and transferring (11%); the most prevalent IADLs lost were shopping (28%), food preparation (23%), and medication management (22%). After adjustment for age, MELD-Na, and encephalopathy, dressing (subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR], 1.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-2.8; P = 0.04), toileting (SHR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.5; P = 0.03), transferring (SHR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.0; P = 0.009), housekeeping (SHR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.2-3.0; P = 0.009), and laundry (SHR, 2.2; 95% CI, 1.3-3.5; P = 0.002) remained independent predictors of wait-list mortality. In conclusion, ADL/IADL deficits are common in LT candidates. LT candidates would benefit from chronic disease management programs developed to address the impact of cirrhosis on their daily lives. Liver Transplantation 23 292-298 2017 AASLD.
© 2016 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio correlates with proinflammatory neutrophils and predicts death in low model for end-stage liver disease patients with cirrhosis.Liver Transpl. 2017 Feb;23(2):155-165. doi: 10.1002/lt.24702. Liver Transpl. 2017. PMID: 28006875 Free PMC article.
-
MELD scores with incorporation of serum sodium and death prediction in cirrhotic patients on the waiting list for liver transplantation: a single center experience in southern Brazil.Clin Transplant. 2012 Jul-Aug;26(4):E395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2012.01688.x. Clin Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22882694 Clinical Trial.
-
Low serum testosterone is associated with adverse outcome in men with cirrhosis independent of the model for end-stage liver disease score.Liver Transpl. 2016 Nov;22(11):1482-1490. doi: 10.1002/lt.24607. Liver Transpl. 2016. PMID: 27542090
-
Physical exercise in cirrhotic patients: Towards prehabilitation on waiting list for liver transplantation. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun;42(3):205-215. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29162460
-
Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Impact on Outcomes.Liver Transpl. 2019 Sep;25(9):1422-1438. doi: 10.1002/lt.25591. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Liver Transpl. 2019. PMID: 31242345 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of cancer rehabilitation on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Mar;19(3):2355-2367. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11345. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32194735 Free PMC article.
-
Frailty in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Cirrhosis: A Comparison with Alcoholic Cirrhosis, Risk Patterns, and Impact on Prognosis.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May 21;2021:5576531. doi: 10.1155/2021/5576531. eCollection 2021. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34095016 Free PMC article.
-
The Liver Frailty Index Improves Mortality Prediction of the Subjective Clinician Assessment in Patients With Cirrhosis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2018 Feb;113(2):235-242. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.443. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29231189 Free PMC article.
-
Liver transplantation in the patient with physical frailty.J Hepatol. 2023 Jun;78(6):1105-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.025. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37208097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malnutrition, Frailty, and Sarcopenia in Patients With Cirrhosis: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.Hepatology. 2021 Sep;74(3):1611-1644. doi: 10.1002/hep.32049. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34233031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Asplund K, Gustafson Y, Jacobsson C, Bucht G, Wahlin A, Peterson J, et al. Geriatric-based versus general wards for older acute medical patients: a randomized comparison of outcomes and use of resources. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000 Nov;48(11):1381–8. - PubMed
-
- Doughty RN, Wright SP, Pearl A, Walsh HJ, Muncaster S, Whalley GA, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of integrated heart failure management: The Auckland Heart Failure Management Study. Eur Heart J. 2002 Jan;23(2):139–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical