Effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on vascular function and skeletal muscle microvascular deoxygenation
- PMID: 27884955
- PMCID: PMC5358004
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13032
Effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on vascular function and skeletal muscle microvascular deoxygenation
Abstract
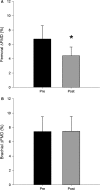
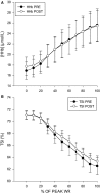
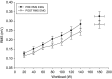
This paper investigated the effects of unaccustomed eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) on macro- and microvascular function. We tested the hypotheses that resting local and systemic endothelial-dependent flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and microvascular reactivity would decrease, V˙O2max would be altered, and that during ramp exercise, peripheral O2 extraction, evaluated via near-infrared-derived spectroscopy (NIRS) derived deoxygenated hemoglobin + myoglobin ([HHb]), would be distorted following EIMD In 13 participants, measurements were performed prior to (Pre) and 48 h after a bout of knee extensor eccentric exercise designed to elicit localized muscle damage (Post). Flow-mediated dilation and postocclusive reactive hyperemic responses measured in the superficial femoral artery served as a measurement of local vascular function relative to the damaged tissue, while the brachial artery served as an index of nonlocal, systemic, vascular function. During ramp-incremental exercise on a cycle ergometer, [HHb] and tissue saturation (TSI%) in the m. vastus lateralis were measured. Superficial femoral artery FMD significantly decreased following EIMD (pre 6.75 ± 3.89%; post 4.01 ± 2.90%; P < 0.05), while brachial artery FMD showed no change. The [HHb] and TSI% amplitudes were not different following EIMD ([HHb]: pre, 16.9 ± 4.7; post 17.7 ± 4.9; TSI%: pre, 71.0 ± 19.7; post 71.0 ± 19.7; all P > 0.05). At each progressive increase in workload (i.e., 0-100% peak), the [HHb] and TOI% responses were similar pre- and 48 h post-EIMD (P > 0.05). Additionally, V˙O2max was similar at pre- (3.0 ± 0.67 L min-1) to 48 h post (2.96 ± 0.60 L min-1)-EIMD (P > 0.05). Results suggest that moderate eccentric muscle damage leads to impaired local, but not systemic, macrovascular dysfunction.
Keywords: Flow‐mediated dilation; muscle damage; near‐infrared spectroscopy; vascular function.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Spatial Distribution of Absolute Skeletal Muscle Deoxygenation During Ramp-Incremental Exercise Is Not Influenced by Hypoxia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;876:19-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3023-4_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26782190
-
Changes in whole tissue heme concentration dissociates muscle deoxygenation from muscle oxygen extraction during passive head-up tilt.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 May 1;118(9):1091-9. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00918.2014. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25678700
-
Which is the best indicator of muscle oxygen extraction during exercise using NIRS?: Evidence that HHb is not the candidate.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;789:163-169. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7411-1_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23852491
-
Muscle Oxygen Dynamics Measured by NIRS.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1463:347-351. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-67458-7_56. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39400846 Review.
-
Appropriateness of indirect markers of muscle damage following lower limbs eccentric-biased exercises: A systematic review with meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 14;17(7):e0271233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271233. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35834532 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Downhill Running: What Are The Effects and How Can We Adapt? A Narrative Review.Sports Med. 2020 Dec;50(12):2083-2110. doi: 10.1007/s40279-020-01355-z. Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 33037592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of acute grape seed extract supplementation on muscle damage after eccentric exercise: A randomized, controlled clinical trial.J Exerc Sci Fit. 2019 Jan 20;17(2):77-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jesf.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2019. PMID: 30992707 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of heat pre-conditioning on recovery following exercise-induced muscle damage.Curr Res Physiol. 2021 Jun 7;4:155-162. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2021.06.002. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34746835 Free PMC article.
-
Peak Eccentric Cycling Exercise and Cardiorespiratory Responses to Normobaric Hypoxia Versus Normobaric Normoxia in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 11;14(4):1151. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041151. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004681 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between hemoglobin and : A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0292835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292835. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, T. J. , Charbonneau F., Title L. M., Buithieu J., Rose M. S., Conradson H., et al. 2011. Microvascular function predicts cardiovascular events in primary prevention: long‐term results from the Firefighters and Their Endothelium (FATE) study. Circulation 123:163–169. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, J. N. , Trombold J. R., Dhindsa M., Lin H. F., and Tanaka H.. 2010. Arterial stiffening following eccentric exercise‐induced muscle damage. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 109:1102–1108. - PubMed
-
- Beck, T. W. , Housh T. J., Johnson G. O., Weir J. P., Cramer J. T., Coburn J. W., et al. 2005. The effects of interelectrode distance on electromyographic amplitude and mean power frequency during isokinetic and isometric muscle actions of the biceps brachii. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 15:482–495. - PubMed
-
- Bellotti, C. , Calabria E., Capelli C., and Pogliaghi S.. 2013. Determination of maximal lactate steady state in healthy adults: can NIRS help? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 45:1208–1216. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

