Activity-dependent redistribution of Kv2.1 ion channels on rat spinal motoneurons
- PMID: 27884958
- PMCID: PMC5358001
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13039
Activity-dependent redistribution of Kv2.1 ion channels on rat spinal motoneurons
Abstract
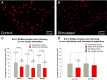
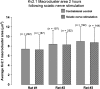
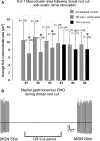
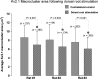
Homeostatic plasticity occurs through diverse cellular and synaptic mechanisms, and extensive investigations over the preceding decade have established Kv2.1 ion channels as key homeostatic regulatory elements in several central neuronal systems. As in these cellular systems, Kv2.1 channels in spinal motoneurons (MNs) localize within large somatic membrane clusters. However, their role in regulating motoneuron activity is not fully established in vivo. We have previously demonstrated marked Kv2.1 channel redistribution in MNs following in vitro glutamate application and in vivo peripheral nerve injury (Romer et al., 2014, Brain Research, 1547:1-15). Here, we extend these findings through the novel use of a fully intact, in vivo rat preparation to show that Kv2.1 ion channels in lumbar MNs rapidly and reversibly redistribute throughout the somatic membrane following 10 min of electrophysiological sensory and/or motor nerve stimulation. These data establish that Kv2.1 channels are remarkably responsive in vivo to electrically evoked and synaptically driven action potentials in MNs, and strongly implicate motoneuron Kv2.1 channels in the rapid homeostatic response to altered neuronal activity.
Keywords: C‐boutons; Kv2.1; voltage‐gated ion channels, activity dependent; α‐motoneuron.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kv2 channels create endoplasmic reticulum / plasma membrane junctions: a brief history of Kv2 channel subcellular localization.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):88-101. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1568824. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 30712450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A molecular rheostat: Kv2.1 currents maintain or suppress repetitive firing in motoneurons.J Physiol. 2019 Jul;597(14):3769-3786. doi: 10.1113/JP277833. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31145471
-
Redistribution of Kv2.1 ion channels on spinal motoneurons following peripheral nerve injury.Brain Res. 2014 Feb 14;1547:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24355600 Free PMC article.
-
Focal aggregation of voltage-gated, Kv2.1 subunit-containing, potassium channels at synaptic sites in rat spinal motoneurones.J Physiol. 2004 Feb 1;554(Pt 3):673-85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.056192. Epub 2003 Nov 7. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14608003 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of the voltage-gated Kv2.1 potassium channel by multisite phosphorylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1064-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0351064. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956280 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic mechanisms underlying modulation of locomotor-related motoneuron output by premotor cholinergic interneurons.Elife. 2020 Feb 21;9:e54170. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54170. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32081133 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in motor behavior and lumbar motoneuron morphology following repeated chlorpyrifos exposure in rats.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 14;19(6):e0305173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305173. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38875300 Free PMC article.
-
Kv2 channels create endoplasmic reticulum / plasma membrane junctions: a brief history of Kv2 channel subcellular localization.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):88-101. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1568824. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 30712450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical Ion Channel Behaviour in Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 15;20(18):4572. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184572. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31540178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic control of neuronal activity enhances axonal growth only on permissive substrates.Mol Med. 2022 Aug 17;28(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00524-2. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35978278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anneser, J. M. , Borasio G. D., Berthele A., Zieglgansberger W., and Tolle T. R.. 1999. Differential expression of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat spinal cord somatic and autonomic motoneurons: possible implications for the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 6:140–147. - PubMed
-
- Anneser, J. M. , Berthele A., Borasio G. D., Castro‐Lopes J. M., Zieglgansberger W., and Tolle T. R.. 2000. Axotomy of the sciatic nerve differentially affects expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA in adult rat motoneurons. Brain Res. 868:215–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

