Effects in dogs with behavioural disorders of a commercial nutraceutical diet on stress and neuroendocrine parameters
- PMID: 27885066
- PMCID: PMC5284471
- DOI: 10.1136/vr.103865
Effects in dogs with behavioural disorders of a commercial nutraceutical diet on stress and neuroendocrine parameters
Abstract
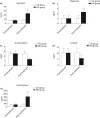
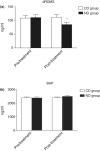
The well-being of dogs can be affected by changes in human lifestyle, eating habits and increased stressors that lead to behavioural disorders including fear, hyperactivity and anxiety, followed by negative affective moods and poor welfare. This randomised, controlled clinical evaluation involved 69 dogs, 38 males and 31 females, of different breeds, with behavioural disorders related to anxiety and chronic stress. They were fed a control diet or a nutraceutical diet (ND group) for 45 days. Neuroendocrine (serotonin, dopamine, β-endorphins, noradrenaline and cortisol) and stress (derivatives of reactive oxygen metabolites (dROMs) and biological antioxidant potential (BAP)) parameters related to behavioural disorders were evaluated at the beginning and end of the study period. Results showed a significant increase in serotonin, dopamine and β-endorphins plasma concentrations (*P<0.05, *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, respectively) and a significant decrease in noradrenaline and cortisol plasma concentrations in the ND group (*P<0.05). dROMs significantly decreased in the ND group (*P<0.05) while BAP was not affected. This study demonstrated for the first time that a specific diet significantly and positively affected neuroendocrine parameters and dROMs. These results open significant perspectives concerning the use of diet and nutraceuticals in the treatment of behavioural disorders.
Keywords: Neuroendocrine parameters; anxiety; behavioral disorders; chronic stress; nutraceutical diet; stress parameters.
British Veterinary Association.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was performed in collaboration with some scientists from the Division of Research and Development, Sanypet SpA, Padua, Italy (as indicated in the author's affiliation) according to scientific and ethical principles of the scientific community.
Figures
Comment in
-
Possible effect of diet on stress and neuroendocrine parameters in dogs with behavioural disorders.Vet Rec. 2017 May 13;180(19):476-477. doi: 10.1136/vr.j2254. Vet Rec. 2017. PMID: 28500157 No abstract available.
-
Possible effect of diet on stress and neuroendocrine parameters in dogs with behavioural disorders.Vet Rec. 2017 May 13;180(19):476. doi: 10.1136/vr.j2256. Vet Rec. 2017. PMID: 28500158 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Clinical evaluation of an antiinflammatory and antioxidant diet effect in 30 dogs affected by chronic otitis externa: preliminary results.Vet Res Commun. 2016 Mar;40(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s11259-015-9651-4. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Vet Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26743397 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical evaluation of a nutraceutical diet as an adjuvant to pharmacological treatment in dogs affected by Keratoconjunctivitis sicca.BMC Vet Res. 2016 Sep 22;12(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0841-2. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27658509 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and food supplementation with antioxidants in therapy dogs.Can J Vet Res. 2017 Jul;81(3):206-216. Can J Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28725111 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Managing behavioural problems in human-dog interactions.Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2011;47(4):378-83. doi: 10.4415/ANN_11_04_09. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2011. PMID: 22194072 Review.
-
Nutritional psychiatry: the present state of the evidence.Proc Nutr Soc. 2017 Nov;76(4):427-436. doi: 10.1017/S0029665117002026. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Proc Nutr Soc. 2017. PMID: 28942748 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of a Novel Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strain (LP815TM) in Reducing Canine Aggression and Anxiety: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial with Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 4;15(15):2280. doi: 10.3390/ani15152280. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805070 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Study on the Interplay between the Serum Levels of Neurotransmitters and Thyroid Hormones for the Evaluation of the Behavioral Phenotype of Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;13(3):411. doi: 10.3390/ani13030411. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766302 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional needs and health outcomes of ageing cats and dogs: is it time for updated nutrient guidelines?Anim Front. 2024 Jun 20;14(3):5-16. doi: 10.1093/af/vfae008. eCollection 2024 Jun. Anim Front. 2024. PMID: 38910950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Changes in Plasma Metabolites Concentrations in Obese Dogs Supplemented With Anti-oxidant Compound.Front Nutr. 2018 Sep 7;5:74. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00074. eCollection 2018. Front Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30246011 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the effects of shrimp hydrolysate as a dietary ingredient in healthy adult Beagle dogs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae280. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae280. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39292957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ANESINI C., WERNER S. & BORDA E. (1999) Effect of Tilia cordata Mill. flowers on lymphocyte proliferation: participation of peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites. Fitoterapia 70, 361–367 10.1016/S0367-326X(99)00049-0 - DOI
-
- BADINO P., ODORE R., OSELLA M. C., BERGAMASCO L., FRANCONE P., GIRARDI C. & RE G. (2004) Modifications of serotonergic and adrenergic receptor concentrations in the brain of aggressive Canis familiaris. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 139, 343–350 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

