Biosimilars for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Systematic Review of Published Evidence
- PMID: 27885553
- PMCID: PMC5126192
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-016-0201-6
Biosimilars for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Systematic Review of Published Evidence
Abstract
Background: Clinicians are required to assimilate, critically evaluate, and extrapolate information to support appropriate use of biosimilars across indications.
Objectives: The objective of this study was to systematically collate all published data in order to assess the weight (quantity and quality) of available evidence for each molecule and inform and support healthcare decision-making in chronic inflammatory diseases.
Methods: MEDLINE®, EMBASE®, and ISI Web of Science® were searched to September 2015. Selected conference proceedings were searched from 2012 to July 2015. Studies disclosing biosimilars with unique identifiers were categorized by originator, study type, and indication. Risk of bias assessments were performed. Intended copies were differentiated as commercially available agents without evidence of rigorous comparative biosimilarity evaluations.
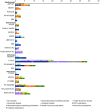
Results: Proposed biosimilars for adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, and rituximab are reported in the published literature. Across indications, approved biosimilars infliximab CT-P13, SB2, and etanercept SB4 have published studies involving the largest number of patients or healthy subjects (n = 1405, 743, and 734, respectively), mostly in rheumatoid arthritis. At data cut-off, only CT-P13 had published data in ankylosing spondylitis (n = 250; randomized control trial) and ulcerative colitis/Crohn's disease (n = 336; observational studies). Published data were not available for ongoing studies in psoriasis patients. Four intended copies were identified in published studies (total: n = 1430; n = 1372 in observational studies). Thematic analysis of non-empirical publications showed that indication extrapolation remains an issue, particularly for gastroenterologists.
Conclusions: While most agents display a moderate to high degree of similarity to their originator in the published studies identified, large discrepancies persist in the overall amount and type of data available in the public domain. Significant gaps exist particularly for intended copies, reinforcing the need to maintain a clear differentiation between these molecules and true biosimilars.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical Standards Author Contributions All authors were involved in drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript submitted for publication. Conflict of interest IJ, DP and KLS are full-time employees and shareholders of Pfizer. LI was a full-time employee of Pfizer Inc. at the time the study was conducted. SL is a full-time employee of Envision Pharma Group, who were paid consultants to Pfizer in connection with the development of the SLR report that forms the basis of this manuscript. He was not compensated for his role in the development of this manuscript. Funding The SLR to support this manuscript was sponsored by Pfizer Inc.
Figures

References
-
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on similar biological medicinal products containing biotechnology-derived proteins as active substance: non-clinical and clinical issues. 2014 Dec 8. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guidelin.... Accessed 21 Jun 2016.
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. Guidelines on evaluation of similar biotherapeutic products (SBPs). 2009 Oct 19–23. http://www.who.int/biologicals/areas/biological_therapeutics/BIOTHERAPEU.... Accessed 21 Jun 2016.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Biosimilars: questions and answers regarding implementation of the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009: guidance for industry. 2015 Apr. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformati.... Accessed 28 Jul 2016.
-
- Taylor L. Over 700 biosimilars now in development worldwide: report. 2014 Sep 30. http://www.pharmatimes.com/article/14-09-30/over_700_biosimilars_now_in_.... Accessed 19 Jul 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

