Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants
- PMID: 27885658
- PMCID: PMC6464366
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003519.pub4
Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants
Abstract
Background: Mother-infant separation post birth is common. In standard hospital care, newborn infants are held wrapped or dressed in their mother's arms, placed in open cribs or under radiant warmers. Skin-to-skin contact (SSC) begins ideally at birth and should last continually until the end of the first breastfeeding. SSC involves placing the dried, naked baby prone on the mother's bare chest, often covered with a warm blanket. According to mammalian neuroscience, the intimate contact inherent in this place (habitat) evokes neuro-behaviors ensuring fulfillment of basic biological needs. This time frame immediately post birth may represent a 'sensitive period' for programming future physiology and behavior.
Objectives: To assess the effects of immediate or early SSC for healthy newborn infants compared to standard contact on establishment and maintenance of breastfeeding and infant physiology.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (17 December 2015), made personal contact with trialists, consulted the bibliography on kangaroo mother care (KMC) maintained by Dr Susan Ludington, and reviewed reference lists of retrieved studies.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials that compared immediate or early SSC with usual hospital care.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trials for inclusion and risk of bias, extracted data and checked them for accuracy. Quality of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach.
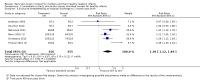
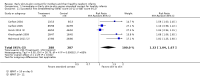
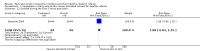
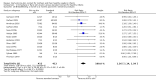
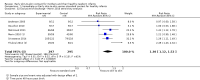
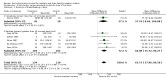
Main results: We included 46 trials with 3850 women and their infants; 38 trials with 3472 women and infants contributed data to our analyses. Trials took place in 21 countries, and most recruited small samples (just 12 trials randomized more than 100 women). Eight trials included women who had SSC after cesarean birth. All infants recruited to trials were healthy, and the majority were full term. Six trials studied late preterm infants (greater than 35 weeks' gestation). No included trial met all criteria for good quality with respect to methodology and reporting; no trial was successfully blinded, and all analyses were imprecise due to small sample size. Many analyses had statistical heterogeneity due to considerable differences between SSC and standard care control groups. Results for womenSSC women were more likely than women with standard contact to be breastfeeding at one to four months post birth, though there was some uncertainty in this estimate due to risks of bias in included trials (average risk ratio (RR) 1.24, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.07 to 1.43; participants = 887; studies = 14; I² = 41%; GRADE: moderate quality). SSC women also breast fed their infants longer, though data were limited (mean difference (MD) 64 days, 95% CI 37.96 to 89.50; participants = 264; studies = six; GRADE:low quality); this result was from a sensitivity analysis excluding one trial contributing all of the heterogeneity in the primary analysis. SSC women were probably more likely to exclusively breast feed from hospital discharge to one month post birth and from six weeks to six months post birth, though both analyses had substantial heterogeneity (from discharge average RR 1.30, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.49; participants = 711; studies = six; I² = 44%; GRADE: moderate quality; from six weeks average RR 1.50, 95% CI 1.18 to 1.90; participants = 640; studies = seven; I² = 62%; GRADE: moderate quality).Women in the SCC group had higher mean scores for breastfeeding effectiveness, with moderate heterogeneity (IBFAT (Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool) score MD 2.28, 95% CI 1.41 to 3.15; participants = 384; studies = four; I² = 41%). SSC infants were more likely to breast feed successfully during their first feed, with high heterogeneity (average RR 1.32, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.67; participants = 575; studies = five; I² = 85%). Results for infantsSSC infants had higher SCRIP (stability of the cardio-respiratory system) scores overall, suggesting better stabilization on three physiological parameters. However, there were few infants, and the clinical significance of the test was unclear because trialists reported averages of multiple time points (standardized mean difference (SMD) 1.24, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.72; participants = 81; studies = two; GRADE low quality). SSC infants had higher blood glucose levels (MD 10.49, 95% CI 8.39 to 12.59; participants = 144; studies = three; GRADE: low quality), but similar temperature to infants in standard care (MD 0.30 degree Celcius (°C) 95% CI 0.13 °C to 0.47 °C; participants = 558; studies = six; I² = 88%; GRADE: low quality). Women and infants after cesarean birthWomen practicing SSC after cesarean birth were probably more likely to breast feed one to four months post birth and to breast feed successfully (IBFAT score), but analyses were based on just two trials and few women. Evidence was insufficient to determine whether SSC could improve breastfeeding at other times after cesarean. Single trials contributed to infant respiratory rate, maternal pain and maternal state anxiety with no power to detect group differences. SubgroupsWe found no differences for any outcome when we compared times of initiation (immediate less than 10 minutes post birth versus early 10 minutes or more post birth) or lengths of contact time (60 minutes or less contact versus more than 60 minutes contact).
Authors' conclusions: Evidence supports the use of SSC to promote breastfeeding. Studies with larger sample sizes are necessary to confirm physiological benefit for infants during transition to extra-uterine life and to establish possible dose-response effects and optimal initiation time. Methodological quality of trials remains problematic, and small trials reporting different outcomes with different scales and limited data limit our confidence in the benefits of SSC for infants. Our review included only healthy infants, which limits the range of physiological parameters observed and makes their interpretation difficult.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Anderson, Dr Bergman and Dr Moore have conducted trials that have been included in this review.
Anderson 2003 was conducted by Dr Anderson. Chwo 1999, Punthmatharith 2001, Shiau 1997 and Syfrett 1993 were conducted by students of Dr Anderson’s at Case Western Reserve University. Risk of bias for all these trials was assessed by T Dowswell, Research Associate, Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth, Dr Moore and Dr Bergman.
Dr Bergman conducted Bergman 2004 and was a consultant for Luong 2015. T Dowswell, Dr Anderson and Dr Moore evaluated Bergman 2004 for Risk of Bias and N Medley, Research Associate, Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth, Dr Anderson and Dr Moore evaluated Luong 2015 for risk of bias. Dr Bergman has received lecture fees for teaching and demonstrating on Skin‐to‐Skin Contact theory and techniques, and produces promotional products for sale. Further, he has participated on a South African patent in the name of the University of Cape Town for a neonatal autonomic nervous system monitoring device. He is an active trialist working on skin‐to‐skin contact for low birth weight newborns.
Dr Moore conducted Moore 2005 while a student of Dr Anderson’s at Vanderbilt University. Moore 2005 was evaluated for risk of bias by T Dowswell and Dr Bergman.
Nancy Medley's work was financially supported by the University of Liverpool's Harris‐Wellbeing of Women Preterm Birth Centre research award and by a grant to University of Liverpool from the World Health Organization.
Figures















































Update of
-
Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;5(5):CD003519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003519.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 25;11:CD003519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003519.pub4. PMID: 22592691 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Anderson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Anderson GC, Chiu SH, Dombrowski MA, Swinth JY, Albert JM, Wada N. Mother‐newborn contact in a randomized trial of kangaroo (skin‐to‐skin) care. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 2003;32(5):604‐11. - PubMed
-
- Hake‐Brooks SJ, Anderson GC. Kangaroo care and breastfeeding of mother‐preterm infant dyads 0‐18 months: a randomized, controlled trial. Neonatal Network 2008;27(3):151‐9. - PubMed
Armbrust 2016 {published data only}
-
- Armbrust R, Hinkson L, Weizsacker K, Henrich W. The Charite cesarean birth: a family orientated approach of cesarean section. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2016;29(1):163‐8. - PubMed
Beiranvand 2014 {published data only}
Bergman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bergman N. Kangaroo mother care from birth compared to conventional incubator care. 22nd Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in South Africa; 2003 March 11‐14; Free State, South Africa. 2003.
-
- Bergman NJ, Linley LL, Fawcus SR. Randomized controlled trial of skin‐to‐skin contact from birth versus conventional incubator for physiological stabilization. Acta Paediatrica 2004;93(6):779‐85. - PubMed
-
- Bigelow A, Littlejohn M, Bergman N, McDonald C. The relation between early mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact and later maternal sensitivity in South African mothers of low birth weight infants. Infant Mental Health Journal 2010;31(3):358‐77. - PubMed
Bystrova 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bystrova K, Ivanova V, Edhborg M, Matthiesen AS, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Mukhamedrakhimov R, et al. Early contact versus separation: effects on mother‐infant interaction one year later. Birth 2009;36(2):97‐109. - PubMed
-
- Bystrova K, Matthiesen AS, Vorontsov I, Widstrom AM, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Uvnas‐Moberg K. Maternal axillar and breast temperature after giving birth: effects of delivery ward practices and relation to infant temperature. Birth 2007;34(4):291‐300. - PubMed
-
- Bystrova K, Matthiesen AS, Widstrom AM, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Welles‐Nystrom B, Vorontsov I, et al. The effect of Russian maternity home routines on breastfeeding and neonatal weight loss with special reference to swaddling. Early Human Development 2007;83(1):29‐39. - PubMed
-
- Bystrova K, Widstrom AM, Matthiesen AS, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Welles‐Nystrom B, Vorontsov I, et al. Early lactation performance in primiparous and multiparous women in relation to different maternity home practices. A randomised trial in St. Petersburg. International Breastfeeding Journal 2007;2(1):9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bystrova K, Widstrom AM, Matthiesen AS, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Welles‐Nystrom B, Wassberg C, et al. Skin‐to‐skin contact may reduce negative consequences of "the stress of being born": a study on temperature in newborn infants, subjected to different ward routines in St. Petersburg. Acta Paediatrica 2003;92(3):320‐6. - PubMed
Carfoot 2004 {published data only}
-
- Carfoot S, Williamson PR, Dickson R. The value of a pilot study in breast‐feeding research. Midwifery 2004;20(2):188‐93. - PubMed
Carfoot 2005 {published data only}
-
- Carfoot S, Williamson P, Dickson R. A randomised controlled trial in the north of England examining the effects of skin‐to‐skin care on breast feeding. Midwifery 2005;21(1):71‐9. - PubMed
Carlsson 1978 {published data only}
-
- Carlsson SG, Fagerberg H, Horneman G, Hwang CP, Larsson K, Rodholm M. Effects of various amounts of contact between mother and child on the mother's nursing behavior: a follow‐up study. Infant Behaviour and Development 1979;2:209‐14. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson SG, Fagerberg H, Horneman G, Hwang CP, Larsson K, Rodholm M, et al. Effects of amount of contact between mother and child on the mother's nursing behavior. Developmental Psychobiology 1978;11:143‐50. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson SG, Larsson K, Schaller, J. Early mother‐child contact and nursing. Reproduction, Nutrition and Development 1980;20:881‐9. - PubMed
-
- Hwang CP. Aspects of the mother‐infant relationship during nursing 1 and 6 weeks after early and extended postpartum contact. Early Human Development 1981;5:279‐87. - PubMed
-
- Schaller J, Carlsson SG, Larsson K. Effects of extended post‐partum mother‐child contact on the mother's behavior during nursing. Infant Behavior and Development 1979;2:319‐24.
Christensson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Christensson K, Siles C, Moreno L, Belaustequi A, Fuente P, Lagercrantz H, et al. Temperature, metabolic adaptation and crying in healthy full‐term newborns cared for skin‐to‐skin or in a cot. Acta Paediatrica 1992;81:488‐93. - PubMed
Christensson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Christensson K, Cabrera T, Christensson E, Uvnas Moberg K, Winberg J. Separation distress call in the human neonate in the absence of maternal body contact. Acta Paediatrica 1995;84(5):468‐73. - PubMed
-
- Michelsson K, Christensson K, Rothganger H, Winberg J. Crying in separated and non‐separated newborns: sound spectrographic analysis. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85:471‐5. - PubMed
Chwo 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chwo MJ. Early kangaroo care for 34‐36 week preterm infants: effects on temperature, weight, cortisol, and behavior [dissertation]. Cleveland (OH): Case Western Reserve University, 1999.
-
- Chwo MJ, Anderson GC, Good M, Dowling DA, Shiau SH, Chu DM. A randomized controlled trial of early kangaroo care for preterm infants: effects on temperature, weight, behavior, and acuity. Journal of Nursing Research 2002;10(2):129‐42. - PubMed
Craig 1982 {published data only}
-
- Craig S, Tyson JE, Samson J, Lasky RE. The effect of early contact on maternal perception of infant behavior. Early Human Development 1982;6:197‐204. - PubMed
Curry 1982 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Curry MA. The effect of skin‐to‐skin contact between mother and infant during the first hour following delivery on the mother's maternal attachment behavior and self concept [dissertation]. San Francisco (CA): University of California, 1979.
-
- Curry MA. Maternal attachment behaviour and the mother's self‐concept: the effect of early skin‐to‐skin contact. Nursing Research 1982;31:73‐8. - PubMed
-
- Curry MAH. Contact during the first hour with the wrapped or naked newborn: effect on maternal attachment behaviors at 36 hours and three months. Birth and the Family Journal 1979;6:227‐35.
De Chateau 1977 {published data only}
-
- Chateau P. Early post‐partum contact and later attitudes. International Journal of Behavioral Development 1980;3:273‐86.
-
- Chateau P. The first hour after delivery ‐ its impact on synchrony of the parent‐infant relationship. Paediatrician 1980;9:151‐68. - PubMed
-
- Chateau P. The influence of early contact on maternal and infant behaviour in primiparae. Birth and the Family Journal 1976;3:149‐55.
-
- Chateau P, Holmberg H, Jakobsson K, Winberg J. A study of factors promoting and inhibiting lactation. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1977;19:575‐84. - PubMed
-
- Chateau P, Wiberg B. Long‐term effect on mother‐infant behaviour of extra contact during the first hour post partum. I. First observations at 36 hours. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1977;66:137‐43. - PubMed
Fardig 1980 {published data only}
-
- Fardig JA. A comparison of skin‐to‐skin contact and radiant heaters in promoting neonatal thermoregulation. Journal of Nurse‐Midwifery 1980;25:19‐28. - PubMed
Ferber 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ferber SG, Makhoul IR. The effect of skin‐to‐skin contact (kangaroo care) shortly after birth on the neurobehavioral responses of the term newborn: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2004;113(4):858‐65. - PubMed
Girish 2013 {published data only}
-
- Girish M, Mujawar N, Gotmare P, Paul N, Punia S, Pandey P. Impact and feasibility of breast crawl in a tertiary care hospital. Journal of Perinatology 2013;33(4):288‐91. - PubMed
Gouchon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gouchon S, Gregori D, Picotto A, Patrucco G, Nangeroni M, Di GiulioP. Skin‐to‐skin contact after cesarean delivery: an experimental study. Nursing Research 2010;59(2):78‐84. - PubMed
Hales 1977 {published data only}
-
- Hales DJ, Lozoff B, Sosa R, Kennell JH. Defining the limits of the maternal sensitive period. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1977;19:454‐61. - PubMed
Huang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Huang YY, Huang CY, Lin SM, Wu SC. Effect of very early kangaroo care on extrauterine temperature adaptation in newborn infants with hypothermia problem. Hu Li Za Zhi 2006;53(4):41‐8. - PubMed
Kastner 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kastner R, Gingelmaier A, Langer B, Grubert TA, Hartl K, Stauber M. Mother‐child relationship before, during and after birth [Die Mutter‐Kind‐Beziehung pranatal, unter der Geburt und postnatal]. Gynakologische Praxis 2005;29(1):109‐14.
-
- Kastner R, Gingelmaier A, Langer B, Grubert TA, Hartl K, Stauber M. Mother‐child relationship before, during and after birth [Die Mutter‐Kind‐Beziehung pranatal, unter der Geburt und postnatal]. Padiatrische Praxis 2005‐2006;67(1):13‐8.
Khadivzadeh 2009 {published data only}
-
- Karimi A, Bagheri S, Khadivzadeh T, Najmabadi KM. The effect of an interventional program, based on the theory of ethology, on breastfeeding competence in infants. Iranian Journal of Neonatology 2014;5(3):5.
-
- Karimi A, Kadivzadeh T. The effects of immediate and continuous mother‐infant skin to skin contact on breastfeeding self‐efficacy among primiparous mothers. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S801.
-
- Karimi A, Khadivzadeh T. The effects of mother‐infant skin to skin contact on breastfeeding experience. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S753.
-
- Karimi A, Khadivzadeh T, Bagheri S. Effect of immediate and continuous mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact on breastfeeding self‐efficacy of primiparous women: A randomised control trial. Women & Birth 2014;27(1):37‐40. - PubMed
-
- Karimi A, Khadivzadeh T, Tara F. The effect of mother‐infant skin to skin contact on mother's attachment. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S668.
Luong 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Luong KC, Nguyen TL, Thi DHH, Carrara HPO, Bergman NJ. Newly born low birthweight infants stabilise better in skin‐to‐skin contact than when separated from their mothers: a randomised controlled trial. Acta Paediatrica 2015. - PubMed
Mahmood 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mahmood I, Jamal M, Khan N. Effect of mother‐infant early skin‐to‐skin contact on breastfeeding status: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2011;21(10):601‐5. - PubMed
Marin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gabriel MAM, Martin IL, Escobar AL, Villalba EF, Blanco IR, Pol PT. Randomized controlled trial of early skin‐to‐skin contact: effects on the mother and the newborn. Acta Paediatrica 2010;99(11):1630‐4. - PubMed
-
- Marin Gabriel MA, Llana Martin I, Lopez Escobar A, Fernandez Villalba E, Romero Blanco I, Touza Pol P. Randomized controlled trial of early skin‐to‐skin contact: effects on the mother and the newborn. Acta Paediatrica 2010;99(11):1630‐4. - PubMed
Mazurek 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mazurek T, Mikiel‐Kostyra K, Mazur J, Wieczorek P, Radwanska B, Pachuta‐Wegier L. Influence of immediate newborn care on infant adaptation to the environment [Wplyw postepowania z noworodkiem bezposrednio po porodzie na cechy jego adaptacji do srodowiska]. Medycyna Wieku Rozwojowego 1999;3(2):215‐24. - PubMed
McClellan 1980 {published data only}
-
- McClellan MS, Cabianca WA. Effects of early mother‐infant contact following cesarean birth. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1980;56:52‐5. - PubMed
Mizuno 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mizuno K, Mizuno N, Shinohara T, Noda M. Mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact after delivery results in early recognition of own mother's milk odour. Acta Paediatrica 2004;93(12):1640‐5. - PubMed
Moore 2005 {published data only}
-
- Moore E. Randomized controlled trial of early mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact and breastfeeding success [dissertation]. Nashville (TN): Vanderbilt University, 2005.
-
- Moore ER, Anderson GC. Randomized controlled trial of very early mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact and breastfeeding status. Journal of Midwifery and Women's Health 2007; Vol. 52, issue 2:116‐24. - PubMed
-
- Moore ER, Anderson GC. Randomized controlled trial or early mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact and breastfeeding success. Journal of Human Lactation 2005;21(4):488‐9.
Nahidi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nahidi F, Dorri F, Ravari M, Akbarzade A. Effect of early skin‐ to‐ skin contact of mother and newborn on mother's satisfaction. Journal of Nursing & Midwifery 2011;20(4):1‐5.
Nasehi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nasehi MM, Farhadi R, Ghaffari V, Ghaffari‐Charati M. The effect of early breastfeeding after cesarean section on the success of exclusive breastfeeding. HealthMED 2012;6(11):3597‐601.
Nimbalkar 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nimbalkar SM, Patel DV, Patel DN, Patel VK, Nimbalkar AS, Phatak AG. Infant and young child feeding practices in infants receiving skin to skin care at birth: A follow up of randomised cohort. Pediatric Academic Socieities Annual Meeting; 2015 April 25‐28; San Diego, California, USA. 2015. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nimbalkar SM, Patel VK, Patel DV, Nimbalkar AS, Sethi A, Phatak A. Effect of early skin‐to‐skin contact following normal delivery on incidence of hypothermia in neonates more than 1800 g: randomized control trial. Journal of Perinatology 2014;34(5):364‐8. - PubMed
Nolan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nolan A, Lawrence C. A pilot study of a nursing intervention protocol to minimize maternal‐infant separation after Cesarean birth. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing 2009;38(4):430‐42. - PubMed
Norouzi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Norouzi F, Keshavarz M, SeyedFatemi N, Montazeri A. The impact of kangaroo care and music on maternal state anxiety. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 2013;21(5):468‐72. - PubMed
Punthmatharith 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Punthmatharith B. Randomized Controlled Trial of early Kangaroo Care (Skin‐to‐Skin) Care: Effects on Maternal Feelings, Maternal‐Infant Interaction and Breastfeeding Success in Thailand [dissertation]. Cleveland (OH): Case Western Reserve University, 2001.
Shiau 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiau S‐HH. Randomized Controlled Trial of Kangaroo Care with Full‐Term Infants: Effects on Maternal Anxiety, Breast‐Milk Maturation, Breast Engorgement, and Breastfeeding Status [Dissertation]. Cleveland (OH): Case Western Reserve University, 1997.
-
- Shiau S‐HH. Randomized controlled trial of kangaroo care with full term infants: effects on breastmilk maturation, breast engorgement, and breastfeeding status. International Breastfeeding Conference, Australia's Breastfeeding Association; 1997 October; Sydney, Australia. 1997.
Sosa 1976a {published data only}
-
- Sosa R, Kennell, JH, Klaus M, Urrutia JJ. The effect of early mother‐infant contact on breastfeeding, infection and growth. In: Elliott K, Fitzsimons DW editor(s). Breastfeeding and the Mother: Ciba Foundation Symposium. Vol. 45, New York: Elsevier Excerpta Medica, 1976:179‐93. - PubMed
Sosa 1976b {published data only}
-
- Sosa R, Kennell, JH, Klaus M, Urrutia JJ. The effect of early mother‐infant contact on breastfeeding, infection and growth. In: Elliott K, Fitzsimons DW editor(s). Breastfeeding and the Mother: Ciba Foundation Symposium. Vol. 45, New York: Elsevier Excerpta Medica, 1976:179‐93. - PubMed
Sosa 1976c {published data only}
-
- Sosa R, Kennell, JH, Klaus M, Urrutia JJ. The effect of early mother‐infant contact on breastfeeding, infection and growth. In: Elliott K, Fitzsimons DW editor(s). Breastfeeding and the Mother: Ciba Foundation Symposium. Vol. 45, New York: Elsevier Excerpta Medica, 1976:179‐93. - PubMed
Srivastava 2014 {published data only}
-
- Srivastava S, Gupta A, Bhatnagar A, Dutta S. Effect of very early skin to skin contact on success at breastfeeding and preventing early hypothermia in neonates. Indian Journal of Public Health 2014;58(1):22‐6. - PubMed
Svejda 1980 {published data only}
-
- Svejda MJ, Campos JJ, Emde RN. Mother‐infant bonding: failure to generalize. Child Development 1980;51:775‐9. - PubMed
Syfrett 1993 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Syfrett EB. Very Early and Virtually Continuous Kangaroo Care for 34‐36 week Gestation Preterm Infants: Effects on Temperature, Breastfeeding, Supplementation and Weight [thesis]. Gainesville (FL): University of Florida, 1993.
-
- Syfrett EB, Anderson GC. Very early kangaroo care beginning at birth for healthy preterm infants and mothers who choose to breastfeed: effect on outcome. A Workshop on the Kangaroo‐Mother Method for Low Birthweight Infants. World Health Organization; 1996 October; Trieste, Italy. 1996.
Thomson 1979 {published data only}
Thukral 2012 {published data only}
-
- Thukral A, Sankar MJ, Agarwal R, Gupta N, Deorari AK, Paul VK. Early skin‐to‐skin contact and breast‐feeding behavior in term neonates: a randomized controlled trial. Neonatology 2012;102(2):114‐9. - PubMed
Vaidya 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vaidya K, Sharma A, Dhungel S. Effect of early mother‐baby close contact over the duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Nepal Medical College Journal: NMCJ 2005;7:138‐40. - PubMed
Villalon 1992 {published data only}
-
- Villalon HU, Alvarez PC. Short term effects of early skin‐to‐skin contact (kangaroo care) on breastfeeding in healthy full‐term newborns [Efecto a corto plazo del contacto precoz piel a piel sobre la lactancia materna en recien nacidos de termino sanos]. Revista Chilena de Pediatria 1993;64(2):124‐8.
-
- Villalon HU, Alvarez PC, Barria EH, Caneleo DH, Carrillo LM, Duran SG. Effect of early skin‐to‐skin contact on temperature regulation, heart rate, and respiratory rate in healthy, full‐term newborns [Contacto precoz piel a piel: efecto sobre los parametros fisiologicos en las cuatro horas posteriores al parto en recien nacidos de termino sanos]. Revista Chilena de Pediatria 1992;63(3):140‐4.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdel Razek 2009 {published data only}
-
- Abdel Razek A, Az El‐Dein N. Effect of breast‐feeding on pain relief during infant immunization injections. International Journal of Nursing Practice 2009;15(2):99‐104. - PubMed
Ali 1981 {published data only}
-
- Ali Z, Lowry M. Early maternal‐child contact: effects on later behavior. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1981;23:337‐45. - PubMed
Anisfeld 1983 {published data only}
-
- Anisfeld E, Lipper E. Early contact, social support, and mother‐infant bonding. Pediatrics 1983;72:79‐83. - PubMed
Arnon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Arnon S, Diamant C, Bauer S, Regev R, Sirota G, Litmanovitz I. Maternal singing during kangaroo care led to autonomic stability in preterm infants and reduced maternal anxiety. Acta Paediatrica 2014;103(10):1039‐44. - PubMed
Bigelow 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bigelow A, Power M, MacLellan‐Peters J, Alex M, McDonald C. Effect of mother/infant skin‐to‐skin contact on postpartum depressive symptoms and maternal physiological stress. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing : JOGNN 2012;41(3):369‐82. - PubMed
-
- Bigelow AE, Power M, Gillis DE, Maclellan‐Peters J, Alex M, McDonald C. Breastfeeding, skin‐to‐skin contact, and mother‐infant interactions over infants' first three months. Infant Mental Health Journal 2014;35(1):51‐62. - PubMed
Castral 2008 {published data only}
-
- Castral TC, Warnock F, Leite AM, Haas VJ, Scochi CG. The effects of skin‐to‐skin contact during acute pain in preterm newborns. European Journal of Pain 2008;12(4):464‐71. - PubMed
Cattaneo 1998 {published data only}
-
- Cattaneo A, Davanzo R, Worku B, Surjono A, Echeverria M, Bedri A, et al. Kangaroo mother care for low birthweight infants: a randomized controlled trial in different settings. Acta Paediatrica 1998;87(9):976‐85. - PubMed
Christensson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Christensson K, Bhat GJ, Amadi BC. Randomised study of skin‐to‐skin versus incubator care for rewarming low‐risk hypothermic neonates. Lancet 1998;352:1115. - PubMed
Darmstadt 2006 {published data only}
-
- Darmstadt GL, Kumar V, Yadav R, Singh V, Singh P, Mohanty S, et al. Introduction of community‐based skin‐to‐skin care in rural Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Perinatology 2006;26(10):597‐604. - PubMed
de Ocampo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ocampo FS, Uy HG, Uy MEV. A randomized controlled trial of kangaroo mother care versus conventional care in increasing the rate of weight gain among low birth weight neonates. Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting; 2013 May 4‐7; Washington DC, USA. 2013.
Durand 1997 {published data only}
-
- Durand R, Hodges S, LaRock S, Lund L, Schmid S, Swick D, et al. The effect of skin‐to‐skin breastfeeding in the immediate recovery period on newborn thermoregulation and blood glucose values. Neonatal Intensive Care 1997;3/4:23‐9.
Erlandsson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Erlandsson K, Dsilna A, Fagerberg I, Christensson K. Skin‐to‐skin care with the father after cesarean birth and its effect on newborn crying and prefeeding behavior. Birth 2007;34(2):105‐14. - PubMed
Feldman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Feldman R, Weller A, Sirota L, Eidelman AI. Testing a family intervention hypothesis: the contribution of mother‐infant skin‐to‐skin contact (kangaroo care) to family interaction, proximity, and touch. Journal of Family Psychology 2003;17(1):94‐107. - PubMed
Ferber 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ferber SG, Makhoul IR. Neurobehavioural assessment of skin‐to‐skin effects on reaction to pain in preterm infants: a randomized, controlled within‐subject trial. Acta Paediatrica 2008;97(2):171‐6. - PubMed
Filho 2015 {published data only}
-
- Filho FL, Sousa SH, Freitas IJ, Lamy ZC, Simoes VM, Silva AA, et al. Effect of maternal skin‐to‐skin contact on decolonization of Methicillin‐Oxacillin‐Resistant Staphylococcus in neonatal intensive care units: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2015;15(1):63. - PMC - PubMed
Gardner 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gardner S. The mother as incubator‐after delivery. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1979;8(3):174‐6. - PubMed
Gathwala 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gathwala G, Singh B, Balhara B. KMC facilitates mother baby attachment in low birth weight infants. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2008;75(1):43‐7. - PubMed
-
- Gathwala G, Singh B, Singh J. Effect of Kangaroo Mother Care on physical growth, breastfeeding and its acceptability. Tropical Doctor 2010;40(4):199‐202. - PubMed
Gomes‐Pedro 1984 {published data only}
-
- Gomes‐Pedro J, Bento de Almeida J, Silveira da Costa C, Barbosa A. Influence of early mother‐infant contact on dyadic behaviour during the first month of life. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1984;26:657‐64. - PubMed
Gray 2000 {published data only}
-
- Gray L, Watt L, Blass EM. Skin‐to‐skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 2000;105(1):e14. - PubMed
Gray 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gray L, Miller LW, Philipp BL, Blass EM. Breastfeeding is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 2002;109:590‐3. - PubMed
Grossman 1981 {published data only}
-
- Grossman K, Thane K, Grossman KE. Maternal tactual contact of the newborn after various postpartum conditions of mother‐infant contact. Developmental Psychobiology 1981;17:158‐69.
Hill 1979 {published data only}
-
- Hill ST, Shronk LK. The effect of early parent‐infant contact on newborn body temperature. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1979;8(5):287‐90. - PubMed
Holditch‐Davis 2014 {published data only}
Horn 2014 {published data only}
-
- Horn EP, Bein B, Steinfath M, Ramaker K, Buchloh B, Hocker J. The incidence and prevention of hypothermia in newborn bonding after cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2014;118(5):997‐1002. - PubMed
Ibe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ibe OE, Austin T, Sullivan K, Fabanwo O, Disu E, Costello AM. A comparison of kangaroo mother care and conventional incubator care for thermal regulation of infants <2000g in Nigeria using continuous ambulatory temperature monitoring. Annals of Tropical Pediatrics 2004;24:245‐51. - PubMed
Ignacio 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ignacio RP, Uy MEV. Kangaroo care transport versus transport incubator in transporting stable preterm neonates: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting; 2013 May 4‐7; Washington DC, USA. 2013.
Johanson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Johanson RB, Malla DS, Rolfe P, Spencer A. The effect of postdelivery care on neonatal body temperature. Early Human Development 1990;21:132‐3.
-
- Johanson RB, Spencer SA, Rolfe P, Jones P, Malla DS. Effect of post‐delivery care on neonatal body temperature. Acta Paediatrica 1992;81:859‐63. - PubMed
Johnson 1976 {published data only}
-
- Johnson NW. Breast‐feeding at one hour of age. American Journal of Maternal‐Child Nursing 1976;1:12‐6. - PubMed
Kadam 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kadam S, Binoy S, Kanbur W, Mondkar JA, Fernandez A. Feasibility of kangaroo mother care in Mumbai. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2005;72(1):35‐8. - PubMed
Karlsson 1996 {published data only}
Keshavarz 2010a {published data only}
-
- Keshavarz M, Haghighi NB. Effects of kangaroo contact on some physiological parameters in term neonates and pain score in mothers with cesarean section. Koomesh 2010;11(2):91‐9.
Klaus 1972 {published data only}
-
- Kennell JH, Jerauld R, Wolfe H, Chesler D, Kreger NC, McAlpine W. Maternal behavior one year after early and extended post‐partum contact. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1974;16:172‐9. - PubMed
-
- Kennell JH, Trause MA, Klaus MH. Evidence for a sensitive period in the human mother. Parent infant interaction. CIBA Foundation Symposium 1975; Vol. 33:87‐101. - PubMed
-
- Klaus M, Jerauld R, Kreger N, McAlpine W, Steffa M, Kennell J. Maternal attachment: importance of the first postpartum days. New England Journal of Medicine 1972;286:460‐3. - PubMed
-
- Ringler N, Kennell JH, Klaus MH, Navojosky B. Mother to child speech at two years: the effects of increased post‐natal contact. Pediatric Research 1974;8:345.
-
- Ringler N, Trause MA, Klaus MH, Kennell JH. The effects of extra postpartum contact and maternal speech patterns on children's IQs, speech and language comprehension at five. Child Development 1978;49:862‐5.
Kontos 1978 {published data only}
-
- Kontos D. A study of the effects of extended mother‐infant contact on maternal behavior at one and three months. Birth and the Family Journal 1978;5(3):133‐40.
Limrattamorn 2013 {published data only}
-
- Limrattamorn P, Kaewkiattikun K. The effect of early mother‐infant skin to skin contact and suckling on duration of exclusive breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial. Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013;21:101‐9.
Lindenberg 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lindenberg CS, Artola RC, Jimenez V. The effect of early postpartum mother‐infant contact and breastfeeding promotion on the incidence and continuation of breastfeeding. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1990;27:179‐86. - PubMed
Ludington‐Hoe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ludington‐Hoe SM, Anderson GC, Swinth JY, Thompson C, Hadeed AJ. Randomized controlled trial of kangaroo care: cardiorespiratory and thermal effects on healthy preterm infants. Neonatal Network ‐ Journal of Neonatal Nursing 2004;23(3):39‐48. - PubMed
Ludington‐Hoe 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ludington‐Hoe SM, Johnson MW, Morgan K, Lewis T, Gutman J, Wilson PD, et al. Neurophysiologic assessment of neonatal sleep organization: preliminary results of a randomized, controlled trial of skin contact with preterm infants. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):e909‐23. - PubMed
Mikiel‐Kostyra 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mikiel‐Kostyra K, Boltruszko I, Mazur J. Skin‐to‐skin contact after birth as a factor determining breastfeeding duration [Kontakt skora‐do‐skory po porodzie jako czynnik warunkujacy czas trwania karmienia piersia]. Medycyna Wieku Rozwojowego 2001;5(2):179‐89. - PubMed
-
- Mikiel‐Kostyra K, Mazur J, Boltruszko I. Effect of early skin‐to‐skin contact after delivery on duration of breastfeeding: a prospective cohort study. Acta Paediatrica 2002;91(12):1301‐6. - PubMed
Miles 2006 {published data only}
-
- Miles R, Cowan F, Glover V, Stevenson J, Modi N. A controlled trial of skin‐to‐skin contact in extremely preterm infants. Early Human Development 2006;82(7):447‐55. - PubMed
Morelius 2015 {published data only}
-
- Morelius E, Ortenstrand A, Theodorsson E, Frostell A. A randomised trial of continuous skin‐to‐skin contact after preterm birth and the effects on salivary cortisol, parental stress, depression, and breastfeeding. Early Human Development 2015;91(1):63‐70. - PubMed
Nagai 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nagai S, Andrianarimanana D, Rabesandratana N, Yonemoto N, Nakayama T, Mori R. Earlier versus later continuous Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC) for stable low‐birth‐weight infants: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Paediatrica 2010;99(6):827‐35. - PubMed
Neu 2010 {published data only}
Ohgi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ohgi S, Fukuda M, Moriuchi H, Kusumoto T, Akiyama T, Nugent JK, et al. Comparison of kangaroo care and standard care: behavioral organization, development, and temperament in healthy, low‐birth‐weight infants through 1 year. Journal of Perinatology 2002;22(5):374‐9. - PubMed
Okan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Okan F, Ozdil A, Bulbul A, Yapici Z, Nuhoglu A. Analgesic effects of skin‐to‐skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2010;30(2):119‐28. - PubMed
Ottaviano 1979 {published data only}
-
- Ottaviano CM, Campbell SBG, Taylor PM. The effects of extra postpartum contact on infant‐mother attachment at one year. Pediatric Research 1979;13:336.
Raguindin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Raguindin PF, Uy ME, Dumalag JA. Prolactin level and breast milk volume among mothers of low birth weight infants admitted to level II neonatal intensive care unit who underwent Kangaroo Mother Care. Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(Suppl 1):S‐4.
Ramanathan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ramanathan K, Paul VK, Deorari AK, Taneja U, George G. Kangaroo mother care in very low birth weight infants. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2001;68(11):1019‐23. - PubMed
Roberts 2000 {published data only}
-
- Roberts KL, Paynter C, McEwan B. A comparison of kangaroo mother care and conventional cuddling care. Neonatal Network ‐ Journal of Neonatal Nursing 2000;19(4):31‐5. - PubMed
Rojas 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rojas MA, Kaplan M, Mayes L, Quevedo ME, Foster LB, Sherwonit E, et al. Traditional holding (TH) and skin‐to‐skin care (SSC) for newborn infants <= 1500 grams. A randomized controlled trial [abstract]. Pediatric Research 2001;49(4):360A.
Ruiz 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz JG, Charpak N, Castillo M. Randomized controlled trial on kangaroo mother care in Bogata: cost‐utility analysis. Pediatric Academic Societies and Asian Society for Pediatric Research Joint Meeting; 2014 May 3‐6; Vancouver, Canada. 2014:Abstract no: 3845.684.
Saatsaz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Saatsaz S, Rezaei R, Sharifnia SH, Kheirkhah F, Moulookzadeh M, Haji Hosseini F. Effect of mother and newborn skin to skin contact on postpartum blues [Persian]. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 2011;13(3):60‐5.
Salariya 1978 {published data only}
-
- Salariya EM, Easton PM, Cater JI. Duration of breastfeeding after early initiation and frequent feeding. Lancet 1978;2:1141‐3. - PubMed
Seeman 2015 {published data only}
-
- Seeman J, Griifin J, Amoura J. Maternal outcomes associated with skin‐to‐skin contact after cesarean section. Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(Suppl 1):S‐18.
Sloan 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed S, Mitra SN, Chowdhury AM, Camacho LL, Winikoff B, Sloan NL. Community Kangaroo Mother Care: implementation and potential for neonatal survival and health in very low‐income settings. Journal of Perinatology 2011;31(5):361‐7. - PubMed
-
- Sloan NL, Ahmed S, Chowdhury N, Mitra S, Chowdhury M, Rob U. Community‐based kangaroo mother care to prevent neonatal mortality [abstract]. Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting; 2006 April 29‐May 2; San Francisco, CA, USA. 2006.
-
- Sloan NL, Ahmed S, Mitra SN, Choudhury N, Chowdhury M, Rob U, et al. Community‐based kangaroo mother care to prevent neonatal and infant mortality: a randomized, controlled cluster trial. Pediatrics 2008;121(5):e1047‐59. - PubMed
Suman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Suman Rao PN, Udani R, Nanavati R. Kangaroo mother care for low birth weight infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatrics 2008;45(1):17‐23. - PubMed
Svensson 2013 {published data only}
Taylor 1979 {published data only}
-
- Taylor PM, Campbell SBG, Taylor FH, Maloni J, Dickey D, Rubenstein G. Short‐term effects of extra mother‐first born contact. Pediatric Research 1979;13:338.
Taylor 1985 {published data only}
-
- Taylor PM, Maloni JA, Taylor FH, Campbell SB. Extra early mother‐infant contact and duration of breastfeeding. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica Supplement 1985;316:15‐22. - PubMed
-
- Taylor PM, Taylor FH, Campbell SB, Maloni JA, Cannon M. Extra early physical contact and aspects of the early mother‐infant relationship. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica Supplement 1985;316:3‐14. - PubMed
Taylor 1986 {published data only}
-
- Taylor PM, Maloni JA, Brown DR. Early sucking and prolonged breastfeeding. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1986;140:151‐4. - PubMed
Tessier 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tessier R, Charpak N, Giron M, Cristo M, Calume ZF, Ruiz‐Pelaez JG. Kangaroo Mother Care, home environment and father involvement in the first year of life: a randomized controlled study. Acta Paediatrica 2009;98(9):1444‐50. - PubMed
Thukral 2010 {published data only}
-
- Thukral A, Sankar J, Agarwal R, Deorari A, Paul V. Effect of early skin to skin (STS) contact on breastfeeding behavior in term neonates: a randomized trial. Pediatric Academic Societies 2010 Annual Meeting; 2010 May 1‐4; Vancouver, Canada. 2010.
Velandia 2010 {published data only}
-
- Velandia M, Matthisen AS, Uvnas‐Moberg K, Nissen E. Onset of vocal interaction between parents and newborns in skin‐to‐skin contact immediately after elective caesarean section. Birth 2010;37(3):192‐201. - PubMed
-
- Velandia M, Uvnas‐Moberg K, Nissen E. Sex differences in newborn interaction with mother or father during skin‐to‐skin contact after Caesarean section. Acta Paediatrica 2012;101(4):360‐7. - PubMed
Vendivel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vendivel EF, Gatcheco F. A randomized controlled trial on the effect of maternal skin‐to‐skin contact versus paternal skin‐to‐skin contact on the prefeeding behaviors, crying, and temperature of newborns delivered via cesarean section. Pediatric Academic Societies and Asian Society for Pediatric Research Joint Meeting; 2011 April 30‐May 3; Denver, Colorado, USA. 2011:1453.598.
Vesel 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vesel L, Asbroek AH, Manu A, Soremekun S, Tawiah Agyemang C, Okyere E, et al. Promoting skin‐to‐skin care for low birthweight babies: findings from the Ghana Newhints cluster‐randomised trial. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2013;18(8):952‐61. - PubMed
Wimmer‐Puchinger 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wimmer‐Puchinger B, Nagel M. The importance of attitudes during pregnancy and early mother‐child contact for breastfeeding behavior: an empirical study. In: Prill HJ, Stauber M editor(s). Advances in Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer‐Verlag, 1982:482‐4.
Worku 2005 {published data only}
-
- Worku B, Kassie A. Kangaroo mother care: a randomized controlled trial on effectiveness of early kangaroo mother care for the low birthweight infants in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2005;51(2):93‐7. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ramani 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ramani M, Choe EA, Major M, Newton R, Carlo W. Randomized trial of skin‐to‐skin contact to prevent hypothermia in term neonates. Journal of Investigative Medicine 2015;63(2):418.
Rosas 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rosas BS, Rodriguez J, Vargas G, Lozano F, Canfield H. Effect of skin to skin care on the success of breastfeeding exclusivity: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Academic Socieities Annual Meeting; 2015 April 25‐28; San Diego, California, USA. 2015.
Tateoka 2014 {published data only}
-
- Tateoka Y, Katori Y, Takahashi M. Effect of early mother‐child contact immediately after birth on delivery stress state. International Confederation of Midwives 30th Triennial Congress. Midwives: Improving Women’s Health; 2014 June 1‐4; Prague, Czech Republic. 2014:P188.
References to ongoing studies
Keshavarz 2010b {published data only}
-
- Keshavarz M. Comparison the effect of skin to skin contact and music during skin to skin contact on maternal state anxiety in cesarean section unit. IRCT Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (www.irct.ir) (accessed 6 December 2010) 2010.
Additional references
Adamkin 2011
-
- Adamkin DH. Postnatal glucose homeostasis in late‐preterm and term infants. Pediatrics 2011;127(3):575‐9. - PubMed
Affonso 1989
-
- Affonso D, Wahlberg V, Persson B. Exploration of mother's reactions to the kangaroo method of prematurity care. Neonatal Network 1989;7(6):43‐51. - PubMed
Alberts 1994
-
- Alberts JR. Learning as adaptation of the infant. Acta Paediatrica Supplement 1994;397:77‐85. - PubMed
Anderson 1995
-
- Anderson GC, Chang H‐P, Behnke M, Conlon M, Eyler FD. Self‐regulatory mothering (SR) postbirth: effect on, and correlation between, infant crying and salivary cortisol. Pediatric Research 1995;37(4 Pt 2):12A.
Anderson 2004a
-
- Anderson GC, Chiu SH, Morrison B, Burkhammer M, Ludington‐Hoe S. Skin‐to‐skin care for breastfeeding difficulties postbirth. In: Field T editor(s). Touch and Massage Therapy in Early Development. New Brunswick: Johnson & Johnson Pediatric Institute, 2004:115‐36.
Anderson 2004b
-
- Anderson GC, Radjenovic D, Chiu SH, Conlon M, Lane AE. Development of an observational instrument to measure mother‐infant separation post birth. Journal of Nursing Measurement 2004;12(3):215‐34. - PubMed
Arabadzisz 2010
-
- Arabadzisz D, Diaz‐Heijtz R, Knuesel I, Weber E, Pilloud S, Dettling AC, et al. Primate early life stress leads to long‐term mild hippocampal decreases in corticosteroid receptor expression. Biological Psychiatry 2010;67:1106‐9. - PubMed
Baby‐Friendly USA
-
- Baby‐Friendly USA. Guidelines and Evaluation Criteria for Facilities Seeking Baby‐Friendly Designation. Albany, NY: Baby‐Friendly USA, 2016.
Barbero 2013
-
- Barbero P, Madamangalam AS, Shields A. Skin to skin after cesarean birth. Journal of Human Lactation 2013;29(4):446‐8. - PubMed
Bartocci 2000
-
- Bartocci M, Winberg J, Ruggiero C, Bergqvist LL, Serra G, Lagercrantz H. Activation of olfactory cortex in newborn infants after odor stimulation: A functional near‐infrared spectroscopy study. Pediatric Research 2000;48:18‐23. - PubMed
Bernard‐Bonnin 1989
-
- Bernard‐Bonnin AC, Stachtchenko S, Girard G, Rousseau E. Hospital practices and breast‐feeding duration: a meta‐analysis of controlled trials. Birth 1989;16:64‐6. - PubMed
Brady 2014
Bramson 2010
-
- Bramson L, Lee JW, Moore E, Montgomery S, Neish C, Bahjri K. Effect of early skin‐to‐skin mother‐infant contact during the first 3 hours following birth on exclusive breastfeeding during the maternity hospital stay. Journal of Human Lactation 2010;26(2):130‐7. - PubMed
Bystrova 2007a
-
- Bystrova K, Matthiesen AS, Widstrom AM, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Welles‐Nystrom B, Vorontsov I, et al. The effect of Russian maternity home routines on breastfeeding and neonatal weight loss with special reference to swaddling. Early Human Development 2007;83(1):29‐39. - PubMed
Bystrova 2007b
-
- Bystrova K, Widstrom AM, Matthiesen AS, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Welles‐Nystrom B, Vorontsov I, et al. Early lactation performance in primiparous and multiparous women in relation to different maternity home practices. A randomised trial in St. Petersburg. International Breastfeeding Journal 2007;2(1):9. - PMC - PubMed
Bystrova 2007c
-
- Bystrova K, Matthiesen AS, Vorontsov I, Widstrom AM, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Uvnas‐Moberg K. Maternal axillar and breast temperature after giving birth: effects of delivery ward practices and relation to infant temperature. Birth 2007;34(4):291‐300. - PubMed
Bystrova 2009
-
- Bystrova K, Ivanova V, Edhborg M, Matthiesen AS, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Mukhamedrakhimov R, et al. Early contact versus separation: effects on mother‐infant interaction one year later. Birth 2009;36(2):97‐109. - PubMed
CDC 2013
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC National Survey of Maternity Care Practices in Infant Nutrition and Care (mPINC). United States Department of Health and Human Services, 2013. [http://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/data/mpinc/results‐tables.htm]
Chiu 2009
Christidis 2003
-
- Christidis I, Zotter H, Rosegger H, Engele H, Kurz R, Kerbl R. Infrared thermography in newborns: the first hour after birth. Gynakologisch Geburtschilfliche Rundschau 2003; Vol. 43:31‐5. - PubMed
Clark 1985
-
- Clark R. The parent‐child early relational assessment: instrument and manual. Madison, Wisconsin: Department of Psychiatry, University of Wisconsin Medical School, 1985.
Clark 1999
-
- Clark R. The parent‐child early relational assessment: a factorial validity study. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1999;59(5):821‐46.
Conde‐Agudelo 2014
Conlon 1990
-
- Conlon M, Anderson GC. Three methods of random assignment: Comparison of balance achieved on potentially confounding variables. Nursing Research 1990;39:376‐9. - PubMed
Crenshaw 2012
-
- Crenshaw JT, Cadwell K, Brimdyr K, Widstrom AM, Svensson K, Champion JD, et al. Use of a video‐ethnographic intervention (PRECESS Immersion Method) to improve skin‐to‐skin care and breastfeeding rates. Breastfeed Medicine 2012;7(2):69‐78. - PubMed
Dageville 2008
-
- Dageville C, Pignol J, Smet S. Very early neonatal apparent life‐threatening events and sudden unexpected deaths: incidence and risk factors. Acta Paediatrica 2008; Vol. 97:866‐9. - PubMed
Davanzo 2015
-
- Davanzo R, De CA, Paviotti G, Travan L, Inglese S, Brovedani P, et al. Making the first days of life safer: preventing sudden unexpected postnatal collapse while promoting breastfeeding. Journal of Human Lactation 2015;31(1):47‐52. - PubMed
De Carvalho 1983
-
- Carvalho M, Robertson S, Friedman A, Klaus M. Effect of frequent breast‐feeding on early milk production and infant weight gain. Pediatrics 1983;72:307‐11. - PubMed
Dennis 1999
-
- Dennis C. Theoretical underpinnings of breast‐feeding confidence: a self‐efficacy framework. Journal of Human Lactation 1999;15:195‐201. - PubMed
Dewey 2003
-
- Dewey KG, Nommsen‐Rivers LA, Heinig MJ, Cohen RJ. Risk factors for suboptimal infant breastfeeding behavior, delayed onset of lactation, and excess neonatal weight loss. Pediatrics 2003;112(3 Pt 1):607‐19. - PubMed
Dordevic 2008
-
- Dordevic G, Jovanovic B, Dordevic M. An early contact with the baby ‐ benefit for the mother. Medicina Preglio 2008;61(11‐12):576‐9. - PubMed
Fischer 1998
-
- Fischer CB, Sontheimer D, Scheffer F, Bauer J, Linderkamp O. Cardiorespiratory stability of premature boys and girls during kangaroo care. Early Human Development 1998;52(2):145‐53. - PubMed
Fleming 2012
-
- Fleming P. Unexpected collapse of apparently healthy newborn infants: the benefits and potential risks of skin‐to‐skin contact. Archives of Disease in Childhood Fetal & Neonatal Edition 2012;97(1):F2‐F3. - PubMed
Francis 1999
-
- Francis D, Diorio J, Liu D, Meaney MJ. Nongenomic transmission across generations of maternal behavior and stress responses in the rat. Science 1999;286:1155‐8. - PubMed
Geddes 2008
-
- Geddes DT, Langton DB, Gollow I, Jacobs LA, Hartmann PE, Simmer K. Frenulotomy for breastfeeding infants with ankyloglossia: Effect on milk removal and sucking mechanism as imaged by ultrasound. Pediatrics 2008;122(1):e188‐e194. - PubMed
Gibaud‐Wallston 1977
-
- Gibaud‐Wallston J. Self‐esteem and situational stress: Factors related to sense of competence in new parents. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. George Peabody College. Nashville TN 1977.
Gluckman 2005
-
- Gluckman P, Hanson M. The Fetal Matrix Evolution, Development and Disease. The Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 2005.
Gomez 1998
-
- Gomez P, Baiges Nogues MT, Batiste Fernandez MT, Marca Gutierrez MM, Nieto Jurado A, Closa Monasterolo R. Kangaroo method in delivery room for full‐term babies [Metodo canguro en sala de partos en recien nacidos a termino]. Anales Espanoles De Pediatria 1998;48(6):631‐3. - PubMed
Graeff 1994
-
- Graeff FG. Neuroanatomy and neurotransmitter regulation of defensive behaviors and related emotions in mammals. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 1994;27:811‐29. - PubMed
Grassley 2014
-
- Grassley JS, Jones J. Implementing skin‐to‐skin contact in the operating room following cesarean birth. Worldviews of Evidence Based Nursing 2014;11(6):414‐6. - PubMed
Grummer‐Strawn 2008
-
- Grummer‐Strawn LM, Scanlon KS, Fein SB. Infant feeding and feeding transitions during the first year of life. Pediatrics 2008; Vol. 122:S36‐S42. - PubMed
Guyatt 2013
Hagnevik 1984
-
- Hagnevik K, Faxelius G, Irestedt L, Lagercrantz H, Lundell B, Persson B. Catecholamine surge and metabolic adaptation in the newborn after vaginal delivery and caesarean section. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1984;73(5):602‐9. - PubMed
Hake‐Brooks 2008
-
- Hake‐Brooks SJ, Anderson GC. Kangaroo care and breastfeeding of mother‐preterm infant dyads 0‐18 months: a randomized, controlled trial. Neonatal Network 2008;27(3):151‐9. - PubMed
Handlin 2009
-
- Handlin L, Jonas W, Petersson M, Ejdeback M, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Nissen E, et al. Effects of sucking and skin‐to‐skin contact on maternal ACTH and cortisol levels during the second day postpartum‐influence of epidural analgesia and oxytocin in the perinatal period. Breastfeeding Medicine 2009; Vol. 4, issue 4:207‐20. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hill 1994
-
- Hill P, Humenick SS. The occurrence of breast engorgement. Journal of Human Lactation 1994;10:79‐86. - PubMed
Hill 1996
-
- Hill PD, Humenick SS. Development of the H&H Lactation Scale. Nursing Research 1996;45:136‐40. - PubMed
Hill 2007
-
- Hill PD, Johnson TS. Assessment of breastfeeding and infant growth. Journal of Midwifery and Womens Health 2007;52(6):571‐8. - PubMed
Hochberg 2011
Hofer 2006
-
- Hofer MA. Psychobiological roots of early attachment. Current Directions in Psychological Science 2006;15(2):84‐8.
Hung 2011
-
- Hung KJ, Berg O. Early skin‐to‐skin after cesarean to improve breastfeeding. MCN American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing 2011;36(5):318‐24. - PubMed
Inch 1989
-
- Inch S, Garforth S. Establishing and maintaining breast‐feeding. In: Chalmers I, Enkin M, Keirse M editor(s). Effective Care in Pregnancy and Childbirth. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989:1359‐74.
Jansson 1995
-
- Jansson UM, Mustafa T, Khan MA, Lindblad BS, Widstrom AM. The effects of medically‐oriented labour ward routines on prefeeding behaviour and body temperature in newborn infants. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1995;41:360‐3. - PubMed
Johnston 2014
Labbok 1990
-
- Labbok M, Krasovec K. Toward consistency in breastfeeding definitions. Studies in Family Planning 1990;21:226‐30. - PubMed
Lawn 2010
Liu 1997
-
- Liu D, Diorio JC, Tannenbaum B, Caldji C, Francis D, Freedman A, et al. Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor expression and hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenal responses to stress. Science 1997;277:1659‐62. - PubMed
Liu 2000
-
- Liu D, Diorio J, Day JC, Francis DD, Meaney MJ. Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nature Neuroscience 2000;3:799‐806. - PubMed
Ludington‐Hoe 2014
-
- Ludington‐Hoe SM, Morgan K. Infant assessment and reduction of sudden unexpected postnatal collapse risk during skin‐to‐skin contact. Newborn & Infant Nursing Reviews 2014;14:28‐33.
Mangan 2012
-
- Mangan S, Mosher S. Challenges to skin‐to‐skin kangaroo care: cesarean delivery and critically ill NICU patients. Neonatal Network 2012;31(4):259‐61. - PubMed
Matthews 1988
-
- Matthews MK. Developing an instrument to assess infant breastfeeding behaviour in the early neonatal period. Midwifery 1988;4(4):154‐65. - PubMed
Matthews 1991
-
- Matthews MK. Mothers' satisfaction with their neonates' breastfeeding behaviors. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1991;20(1):49‐55. - PubMed
McEwen 1998
-
- McEwen BS. Stress, adaptation, and disease. Allostasis and allostatic load. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 1998;840:33‐44. - PubMed
McGowan 2009
Meaney 2005
-
- Meaney MJ, Szyf M. Maternal care as a model for experience‐dependent chromatin plasticity?. Trends in Neurosciences 2005;28(9):456‐63. - PubMed
Michelsson 1996
-
- Michelsson K, Christensson K, Rothganger H, Winberg J. Crying in separated and non‐separated newborns: sound spectrographic analysis. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85:471‐5. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schultz KF, Altman DA. The Consort statement: Revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
Moher 2010
Mori 2010
-
- Mori R, Khanna R, Pledge D, Nakayama T. Meta‐analysis of physiological effects of skin‐to‐skin contact for newborns and mothers. Pediatrics International 2010; Vol. 52:161‐70. - PubMed
O'Campo 1992
-
- O'Campo P, Faden R, Gielen A, Wang M. Prenatal factors associated with breast‐feeding duration: recommendations for prenatal interventions. Birth 1992;19:195‐201. - PubMed
Odent 2001
-
- Odent M. New reasons and new ways to study birth physiology. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2001;75 Suppl 1:S39‐S45. - PubMed
Pagel 2011
-
- Pagel C, Prost A, Lewycka S, Das S, Colbourn T, Mahapatra R, et al. Intracluster correlation coefficients and coefficients of variation for perinatal outcomes from five cluster‐randomised controlled trials in low and middle‐income countries: results and methodological implications. Trials 2011;12:151‐62. - PMC - PubMed
Pejovic 2013
Perez‐Escamilla 1994
Plotsky 2005
-
- Plotsky PM, Thrivikraman KV, Nemeroff CB, Caldji C, Sharma S, Meaney MJ. Long‐term consequences of neonatal rearing on central corticotropin‐releasing factor systems in adult male rat offspring. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005;30:2192‐204. - PubMed
Pocock 1975
-
- Pocock SJ, Simon R. Sequential treatment assignment with balancing for prognostic factors in the controlled clinical trial. Biometrics 1975;31:103‐13. - PubMed
Poets 2011
-
- Poets A, Steinfeldt R, Poets CF. Sudden deaths and severe apparent life‐threatening events in term infants within 24 hours of birth. Pediatrics 2011;127(4):e869‐e873. - PubMed
Polit 2011
-
- Polit DF, Gillespie BM, Griffin R. Deliberate ignorance: a systematic review of blinding in nursing clinical trials. Nursing Research 2011;60(1):9‐16. - PubMed
Porges 2007
Porter 1999
-
- Porter RH, Winberg J. Unique salience of maternal breast odors for newborn infants. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 1999;23:439‐49. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Righard 1990
-
- Righard L, Alade MO. Effect of delivery room routines on success of first breast‐feed. Lancet 1990;336:1105‐7. - PubMed
Riordan 1997
-
- Riordan JM. Reliability and validity testing of three breastfeeding assessment tools. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1997;26:181‐7. - PubMed
Rogers 1997
-
- Rogers IS, Emmett PM, Golding J. The incidence and duration of breast‐feeding. Early Human Development 1997;49:S45‐S74. - PubMed
Sabatini 2007
Schorn 2015
-
- Schorn MN, Moore E, Spetalnick BM, Morad A. Implementing Family‐Centered Cesarean Birth. Journal of Midwifery & Womens Health 2015;60(6):682‐90. - PubMed
Shannon 2007
-
- Shannon M, King TL, Kennedy HP. Allostasis: a theoretical framework for understanding and evaluating perinatal health outcomes. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 2007;36(2):125‐34. - PubMed
Sloan 2010
Smith 2008
Spielberger 1970
-
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE. STAI Manual for the State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1970.
Strathearn 2011
Uvnas‐Moberg 1996
-
- Uvnas‐Moberg K, Eriksson M. Breastfeeding: physiological, endocrine and behavioural adaptations caused by oxytocin and local neurogenic activity in the nipple and mammary gland. Acta Paediatrica 1996; Vol. 85:525‐30. - PubMed
Uvnas‐Moberg 1998
-
- Uvnas‐Moberg K. Oxytocin may mediate the benefits of positive social interactions and emotions. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998;23:819‐35. - PubMed
Uvnas‐Moberg 2005
-
- Uvnas‐Moberg K, Arn I, Magnusson D. The psychobiology of emotion: the role of the oxytocinergic system. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2005; Vol. 12, issue 2:59‐65. - PubMed
Varendi 1994
-
- Varendi H, Porter RH, Winberg J. Does the newborn baby find the nipple by smell?. Lancet 1994;344:989‐90. - PubMed
Varendi 1997
-
- Varendi H, Porter RH, Winberg J. Natural odor preferences of newborn infants change over time. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86:985‐90. - PubMed
Varendi 1998
-
- Varendi H, Christensson K, Porter RH, Winberg J. Soothing effect of amniotic fluid smell in newborn infants. Early Human Development 1998;51:47‐55. - PubMed
Velandia 2012
-
- Velandia M, Uvnas‐Moberg K, Nissen E. Sex differences in newborn interaction with mother or father during skin‐to‐skin contact after caesarean section. Acta Paediatrica 2012;101(4):360‐7. - PubMed
WHO 2015
-
- World Health Organization. WHO recommendations on interventions to improve preterm birth outcomes. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal_perinatal_he... 2015. - PubMed
Widstrom 1987
-
- Widstrom AM, Ransjo‐Arvidson AB, Christensson K, Matthiesen AS, Winberg J, Uvnas‐Moberg K. Gastric suction in healthy newborn infants: effects on circulation and developing feeding behavior. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1987;76:566‐72. - PubMed
Widstrom 1990
-
- Widstrom AM, Wahlberg V, Matthiesen AS, Eneroth P, Uvnas‐Moberg K, Werner S, et al. Short‐term effects of early suckling and touch of the nipple on maternal behavior. Early Human Development 1990;21:153‐63. - PubMed
Widstrom 2011
-
- Widstrom AM, Lilja G, Aaltomaa‐Michalias P, Dahllof A, Lintula M, Nissen E. Newborn behaviour to locate the breast when skin‐to‐skin: a possible method for enabling early self‐regulation. Acta Paediatrica 2011; Vol. 100:79‐85. - PubMed
Wight 2014
Winberg 1995
-
- Winberg J. Examining breast‐feeding performance: forgotten influencing factors. Acta Paediatrica 1995;84:465‐7. - PubMed
Winberg 2005
-
- Winberg J. Mother and newborn baby: mutual regulation of physiology and behavior‐‐a selective review. Developmental Psychobiology 2005;47(3):217‐29. - PubMed
Zeller 1997
-
- Zeller R, Good M, Anderson GC, Zeller DL. Strengthening experimental design by balancing potentially confounding variables across treatment groups. Nursing Research 1997;46:345‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Anderson 2003
Moore 2007
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

