Connectivity map of bipolar cells and photoreceptors in the mouse retina
- PMID: 27885985
- PMCID: PMC5148610
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.20041
Connectivity map of bipolar cells and photoreceptors in the mouse retina
Abstract
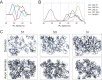
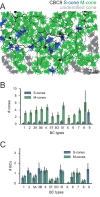
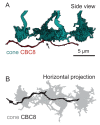
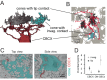
In the mouse retina, three different types of photoreceptors provide input to 14 bipolar cell (BC) types. Classically, most BC types are thought to contact all cones within their dendritic field; ON-BCs would contact cones exclusively via so-called invaginating synapses, while OFF-BCs would form basal synapses. By mining publically available electron microscopy data, we discovered interesting violations of these rules of outer retinal connectivity: ON-BC type X contacted only ~20% of the cones in its dendritic field and made mostly atypical non-invaginating contacts. Types 5T, 5O and 8 also contacted fewer cones than expected. In addition, we found that rod BCs received input from cones, providing anatomical evidence that rod and cone pathways are interconnected in both directions. This suggests that the organization of the outer plexiform layer is more complex than classically thought.
Keywords: bipolar cell; computational biology; connectivity; connectomics; mouse; neural circuit; neuroscience; photoreceptor; retina; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Bishop CM. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York: Springer; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

