Neural mechanisms underlying visual attention to health warnings on branded and plain cigarette packs
- PMID: 27886656
- PMCID: PMC5347953
- DOI: 10.1111/add.13699
Neural mechanisms underlying visual attention to health warnings on branded and plain cigarette packs
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Addiction. 2017 Jul;112(7):1317. doi: 10.1111/add.13852. Addiction. 2017. PMID: 28586552 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: To (1) test if activation in brain regions related to reward (nucleus accumbens) and emotion (amygdala) differ when branded and plain packs of cigarettes are viewed, (2) test whether these activation patterns differ by smoking status and (3) examine whether activation patterns differ as a function of visual attention to health warning labels on cigarette packs.
Design: Cross-sectional observational study combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) with eye-tracking. Non-smokers, weekly smokers and daily smokers performed a memory task on branded and plain cigarette packs with pictorial health warnings presented in an event-related design.
Setting: Clinical Research and Imaging Centre, University of Bristol, UK.
Participants: Non-smokers, weekly smokers and daily smokers (n = 72) were tested. After exclusions, data from 19 non-smokers, 19 weekly smokers and 20 daily smokers were analysed.
Measurements: Brain activity was assessed in whole brain analyses and in pre-specified masked analyses in the amygdala and nucleus accumbens. On-line eye-tracking during scanning recorded visual attention to health warnings.
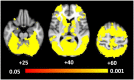
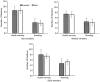
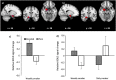
Findings: There was no evidence for a main effect of pack type or smoking status in either the nucleus accumbens or amygdala, and this was unchanged when taking account of visual attention to health warnings. However, there was evidence for an interaction, such that we observed increased activation in the right amygdala when viewing branded as compared with plain packs among weekly smokers (P = 0.003). When taking into account visual attention to health warnings, we observed higher levels of activation in the visual cortex in response to plain packaging compared with branded packaging of cigarettes (P = 0.020).
Conclusions: Based on functional magnetic resonance imaging and eye-tracking data, health warnings appear to be more salient on 'plain' cigarette packs than branded packs.
Keywords: Attention; eye-tracking; fMRI; health warnings; plain packaging; policy; smoking; standardised packaging; tobacco; tobacco control.
© 2016 The Authors. Addiction published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures



References
-
- Maynard O. M., Munafò M. R., Leonards U. Visual attention to health warnings on plain tobacco packaging in adolescent smokers and non‐smokers. Addiction 2013; 108: 413–419. - PubMed
-
- Munafò M. R., Roberts N., Bauld L., Leonards U. Plain packaging increases visual attention to health warnings on cigarette packs in non‐smokers and weekly smokers but not daily smokers. Addiction 2011; 106: 1505–1510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

