Cytotoxic effects of ergone, a compound isolated from Fulviformes fastuosus
- PMID: 27887609
- PMCID: PMC5124230
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1471-8
Cytotoxic effects of ergone, a compound isolated from Fulviformes fastuosus
Abstract
Background: Mushrooms inspired the cuisines of many cultures and conventional medicaments for cancer. However, a substantial number of mushroom species are yet unexplored, possessing an unknown chemical, biological and pharmacological profiles. Fulviformes fastuosus is a terrestrial mushroom, which is commonly found in Sri Lankan woodlands. The current study was aimed at isolation and characterization of a potent cytotoxic compound from F. fastuosus and investigating the apoptotic effect induced by the active principle against cancer and normal cell lines.
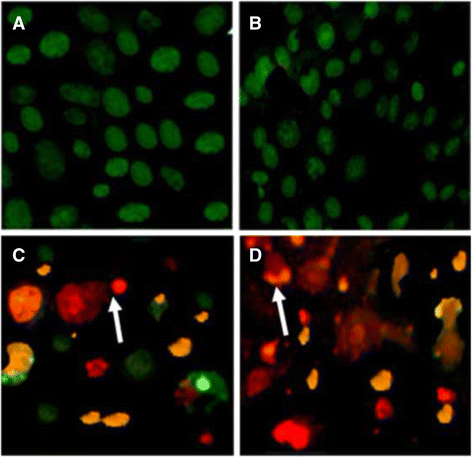
Methods: Bioactivity guided isolation of active principles from the methanol extract of F. fastuosus was performed by a rapid extraction and isolation method using different chromatographic techniques. Potential cytotoxic compound was identified using one and two dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Isolated compound was screened for in vitro cytotoxicity against Hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG-2), Muscle rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) and Rat Wistar liver normal (CC-1) cell lines using 3 4, 5-(dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2-5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) cell viability assay. Apoptotic features of cells were observed via microscopic examination and ethidium bromide/acridine orange fluorescent staining.
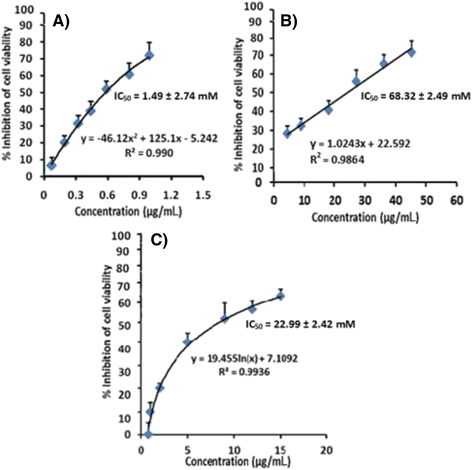
Results: The interpretation of spectral data resulted in the identification of the chemical structure as ergosta-4,6,8 (14),22-tetraen-3-one (ergone). Ergone exhibited promising cytotoxic properties against RD cells with less cytotoxicity effect on CC-1 cells. In addition, ergone also possesses a strong cytotoxic effect against HepG-2 cells showing low toxic level for CC-1 cells. Apoptotic features of treated cells were detected via morphological characterization and ethidium bromide/acridine orange staining.
Conclusion: The present study elaborates the isolation of a potent cytotoxic compound; ergone, from F. fastuosus via a rapid and efficient isolation method. Importantly, ergone has exhibited greater cytotoxic activity against RD cells with high selectivity index compared to cytotoxicity against HepG-2 cells. Ergone can be used in the development of therapeutic strategies for curbing rhabdomyosarcoma.
Keywords: Cytotoxic activity; Ergone; Fulviformes fastuosus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Isolation method; Mushrooms; Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Apr;1810(4):384-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.12.005. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21241775
-
Cytotoxicity of Anchusa arvensis Against HepG-2 Cell Lines: Mechanistic and Computational Approaches.Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;19(30):2805-2813. doi: 10.2174/1568026619666191105103801. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31702502
-
Antioxidant potential, in vitro cytotoxicity and apoptotic effect induced by crude organic extract of Anthracophyllum lateritium against RD sarcoma cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Nov 6;15:398. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0924-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26546450 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and determination of ergosta-4,6,8 (14),22-tetraen-3-one].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;39(20):3905-9. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25751937 Review. Chinese.
-
Ergostanes from the mushroom Trametes versicolor and their cancer cell inhibition: In vitro and in silico evaluation.Steroids. 2024 Dec;212:109511. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2024.109511. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Steroids. 2024. PMID: 39303896 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study on the therapeutic potential of aqueous extracts from commercially cultivated Agaricus bisporus and Lentinula edodes in Sri Lanka: antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, and antibacterial properties.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04984-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40611248 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Aqueous Extracts from Hymenochaetaceae Fungi Associated with Endemic Chilean Sclerophyll Forest Trees.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5877. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125877. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565340 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing and Mobility Inhibition of Pathogenic Bacteria by Fulvifomes mexicanus sp. nov.Molecules. 2025 May 22;30(11):2278. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112278. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509166 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Biological Activity of Ergostane-Type Steroids from Fungi.Molecules. 2022 Mar 24;27(7):2103. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072103. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keles A, Koca I, Gençcelep H. Antioxidant properties of wild edible mushrooms. J Food Process Technol. 2011;2:1–6.
-
- Wang DH, Weng XC. Antitumor activity of extracts of Ganoderma lucidum and their protective effects on damaged HL-7702 cells induced by radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006;31(19):1618–22. - PubMed
-
- World Cancer Report - 2014. World Health Organization. 2014; pp. Chapter 1.1. ISBN 9283204298.
-
- Bhanot A, Sharma R, Noolvi MN. Natural sources as potential anti-cancer agents: a review. J Phytomed. 2011;3:09–26.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

