Prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of antibodies against carbamylated proteins in a monocentric cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 27887639
- PMCID: PMC5124308
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1173-0
Prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of antibodies against carbamylated proteins in a monocentric cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of antibodies against carbamylated proteins in a monocentric cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Dec 16;18(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1205-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27986080 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Antibodies against carbamylated proteins (anti-CarP) have been recently identified in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of the study was to evaluate the prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of anti-CarP compared to anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF), replicating the existing data in a large cohort of Italian patients with RA and extending the evaluation to other autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs).
Methods: Serum samples (n = 607) from 309 patients with RA, 200 disease controls and 98 normal healthy subjects (NHS) were evaluated. Anti-CarP were detected using carbamylated fetal calf serum as the antigen. ACPAs were detected using second-generation ELISA and IgM RF was assessed as part of routine analysis.
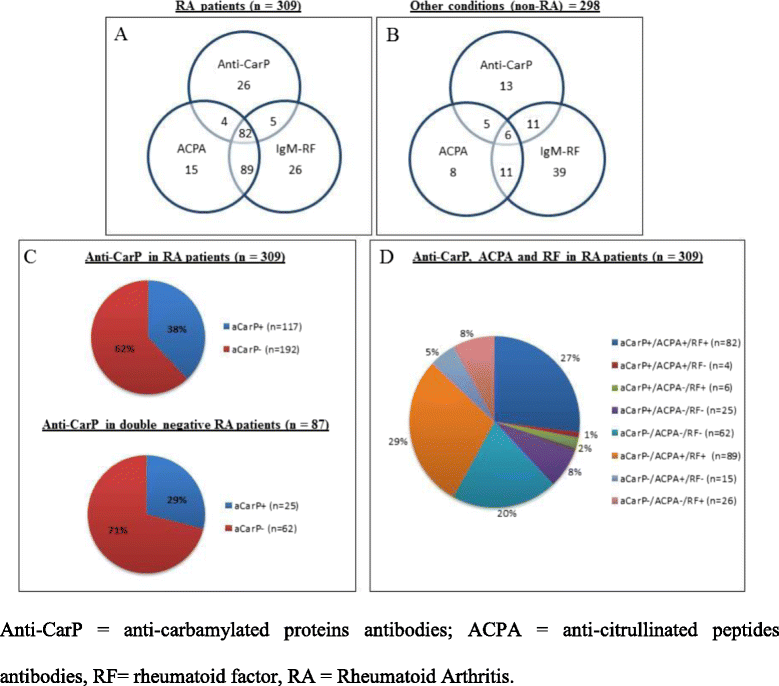
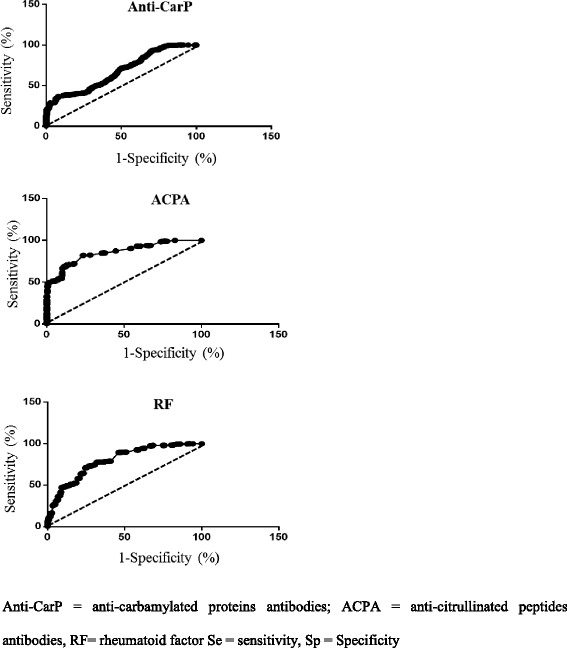
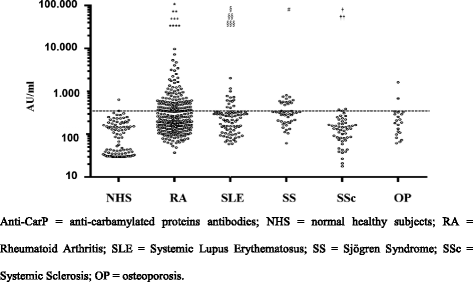
Results: Anti-CarP antibodies were detected in 117 patients with RA (34.4%), ACPA in 190 patients (61.4%) and RF in 202 patients (65.3%). Two (2.04%) of the NHS were positive for anti-CarP, one NHS (1.02%) was positive for ACPA and three NHS were positive for RF (3.06%). Among disease controls, anti-CarP antibodies were detected in 33 patients (16.5%), ACPA in 29 patients (14.5%) and RF in 64 patients (32%). In particular, 16.8% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and 31.1% of patients with Sjögren syndrome were positive for anti-CarP. The sensitivity of anti-CarP, ACPA and RF was 46.8%, 61.8% and 64.4%, respectively and specificity was 91.95%, 89.93% and 76.51%, respectively.
Conclusions: The present study extends the knowledge of anti-CarP antibodies, confirming previous data on the diagnostic accuracy of anti-CarP in RA in a large cohort of Italian patients. Anti-CarP antibodies demonstrated relatively low sensitivity and slightly higher specificity compared to ACPA and RF. Even if predominantly present in RA, anti-CarP was detected in a variable percentage of patients with other autoimmune rheumatic diseases and their generation could be attributed to the inflammatory status; the clinical relevance of anti-CarP antibodies in these latter patients should be further determined.
Keywords: Anti-carbamylated proteins antibodies; Anti-citrullinated peptides antibodies; Autoimmune rheumatic diseases; Rheumatoid arthritis; Rheumatoid factor; Sjögren syndrome post-translational modifications; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

