The hide and seek of Plasmodium vivax in West Africa: report from a large-scale study in Beninese asymptomatic subjects
- PMID: 27887647
- PMCID: PMC5123334
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-016-1620-z
The hide and seek of Plasmodium vivax in West Africa: report from a large-scale study in Beninese asymptomatic subjects
Abstract
Background: Plasmodium vivax is considered to be absent from western Africa, where the prevalence of Duffy-negative red blood cell phenotype proves to be high. Several studies have, however, detected P. vivax infection cases in this part of Africa, raising the question of what is the actual prevalence of P. vivax in local populations.
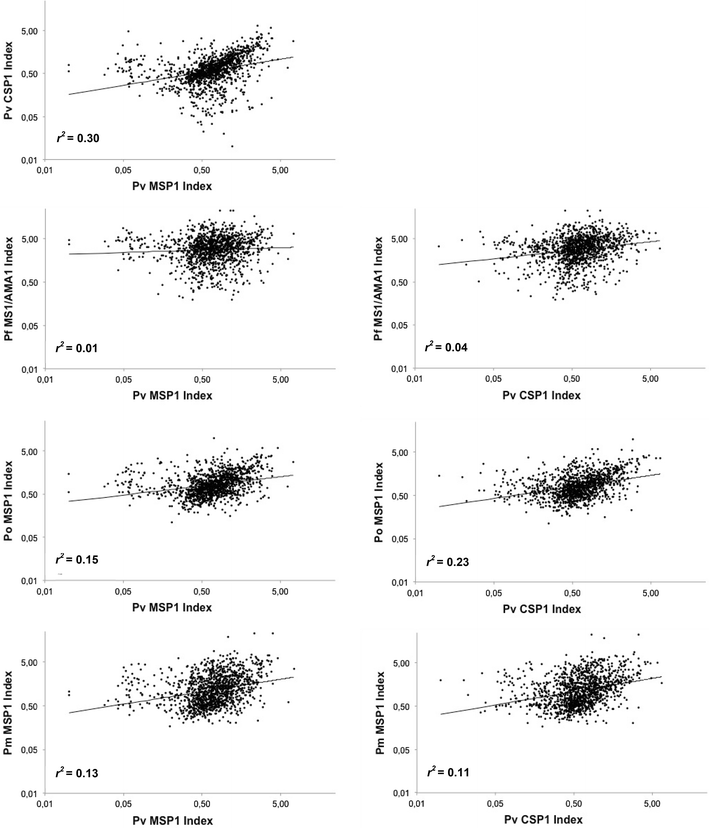
Methods: The presence of P. vivax was investigated in a large population of healthy blood donors in Benin using microscopy, serology and molecular detection. The seroprevalence was measured with species-specific ELISA using two recombinant P. vivax proteins, namely rPvMSP1 and rPvCSP1. Specific molecular diagnosis of P. vivax infection was carried out using nested-PCR. The performances and cut-off values of both rPvCSP1 and rPvMSP1 ELISA were first assessed using sera from P. vivax-infected patients and from non-exposed subjects.
Results: Among 1234 Beninese blood donors, no parasites were detected when using microscopy, whereas 28.7% (354/1234) of patients exhibited had antibodies against rPvMSP1, 21.6% (266/1234) against rPvCSP1, and 15.2% (187/1234) against both. Eighty-four samples were selected for nested-PCR analyses, of which 13 were positive for P. vivax nested-PCR and all Duffy negative.
Conclusion: The results of the present study highlight an unexpectedly high exposure of Beninese subjects to P. vivax, resulting in sub-microscopic infections. This suggests a probably underestimated and insidious parasite presence in western Africa. While the vaccination campaigns and therapeutic efforts are all focused on Plasmodium falciparum, it is also essential to consider the epidemiological impact of P. vivax.
Keywords: Benin; Blood donors; CSP1; ELISA; MSP1; Malaria; Plasmodium vivax; Western Africa.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. World Malaria report. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2015. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs094/en/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources