Fab glycosylation of immunoglobulin G does not associate with improvement of rheumatoid arthritis during pregnancy
- PMID: 27887659
- PMCID: PMC5123206
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1172-1
Fab glycosylation of immunoglobulin G does not associate with improvement of rheumatoid arthritis during pregnancy
Abstract
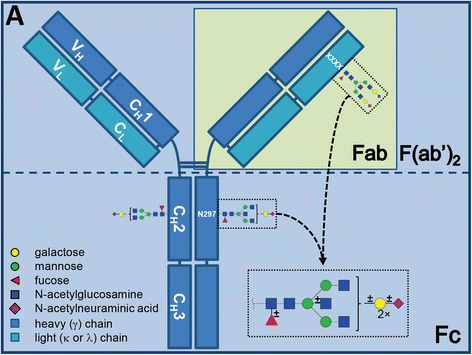
Background: Changes in immunoglobulin G (IgG) constant domain (Fc) glycosylation are associated with changes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity in response to pregnancy. Here, we sought to determine whether the same holds true for variable domain (Fab) glycosylation.
Methods: IgGs were captured from RA and control sera obtained before (RA only), during and after pregnancy, followed by Fc and Fab separation, glycan release, and mass spectrometric detection. In parallel, glycans from intact IgG were analysed. The data was used to calculate glycosylation traits, and to estimate the level of Fab glycosylation.
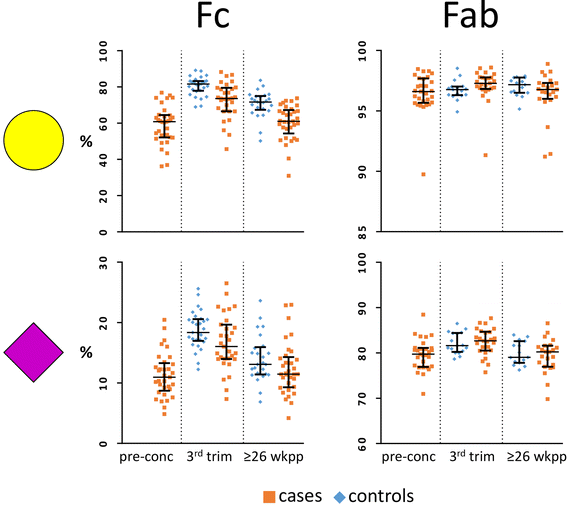
Results: The overall level of Fab glycosylation was increased in RA patients compared to controls, while no differences in Fab glycosylation patterns were found. For the Fc and intact IgG (Total) previously observed differences in galactosylation and bisection were confirmed. Furthermore, increased galactosylation of Fc and Total were associated with lower disease activity and autoantibody positivity. In addition, the change in Fc galactosylation associated with the change in disease activity during pregnancy and after delivery, while this was not the case for Fab.
Conclusions: In contrast to changes in Fc glycosylation, changes in Fab glycosylation are not associated with improvement of RA during pregnancy and arthritis flare after delivery.
Keywords: Disease activity; Inflammation; Pregnancy; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between galactosylation of immunoglobulin G and improvement of rheumatoid arthritis during pregnancy is independent of sialylation.J Proteome Res. 2013 Oct 4;12(10):4522-31. doi: 10.1021/pr400589m. Epub 2013 Sep 24. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 24016253
-
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fab glycosylation analysis using a new mass spectrometric high-throughput profiling method reveals pregnancy-associated changes.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Nov;13(11):3029-39. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.039537. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25004930 Free PMC article.
-
ACPA IgG galactosylation associates with disease activity in pregnant patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Aug;77(8):1130-1136. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-212946. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29615411
-
The Emerging Importance of IgG Fab Glycosylation in Immunity.J Immunol. 2016 Feb 15;196(4):1435-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502136. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26851295 Review.
-
Sweet but dangerous - the role of immunoglobulin G glycosylation in autoimmunity and inflammation.Lupus. 2016 Jul;25(8):934-42. doi: 10.1177/0961203316640368. Lupus. 2016. PMID: 27252272 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential antibody glycosylation in autoimmunity: sweet biomarker or modulator of disease activity?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Oct;13(10):621-630. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.146. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28905852 Review.
-
High-throughput characterization of the functional impact of IgG Fc glycan aberrancy in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Glycobiology. 2017 Dec 1;27(12):1099-1108. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwx082. Glycobiology. 2017. PMID: 28973482 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Glycosylation of Immunoglobulin G Associates With Clinical Features of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.Gastroenterology. 2018 Apr;154(5):1320-1333.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29309774 Free PMC article.
-
Raider of the lost N-glycans - Localizing rare and frequently overlooked IgG N-glycans with sulfation or bisecting LacNAc.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 9;12:1593708. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1593708. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40703705 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics in rheumatoid arthritis: Advances and review.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:961708. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.961708. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van de Geijn FE, Wuhrer M, Selman MH, et al. Immunoglobulin G galactosylation and sialylation are associated with pregnancy-induced improvement of rheumatoid arthritis and the postpartum flare: results from a large prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(6):R193. doi: 10.1186/ar2892. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

