Co-infusion of haplo-identical CD19-chimeric antigen receptor T cells and stem cells achieved full donor engraftment in refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 27887660
- PMCID: PMC5124292
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-016-0357-z
Co-infusion of haplo-identical CD19-chimeric antigen receptor T cells and stem cells achieved full donor engraftment in refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Background: Elderly patients with relapsed and refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have poor prognosis. Autologous CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-modified T (CAR-T) cells have potentials to cure patients with B cell ALL; however, safety and efficacy of allogeneic CD19 CAR-T cells are still undetermined.
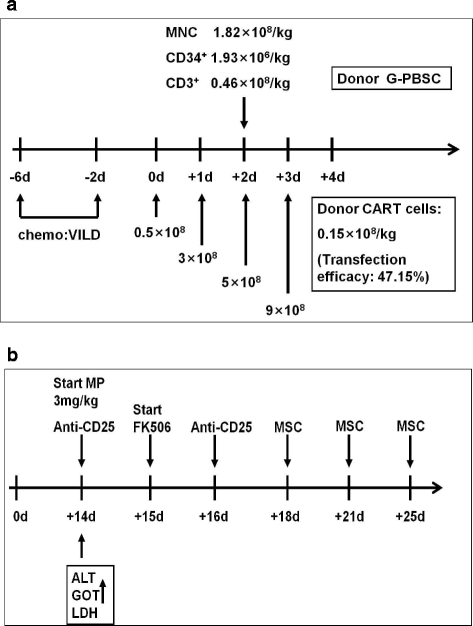
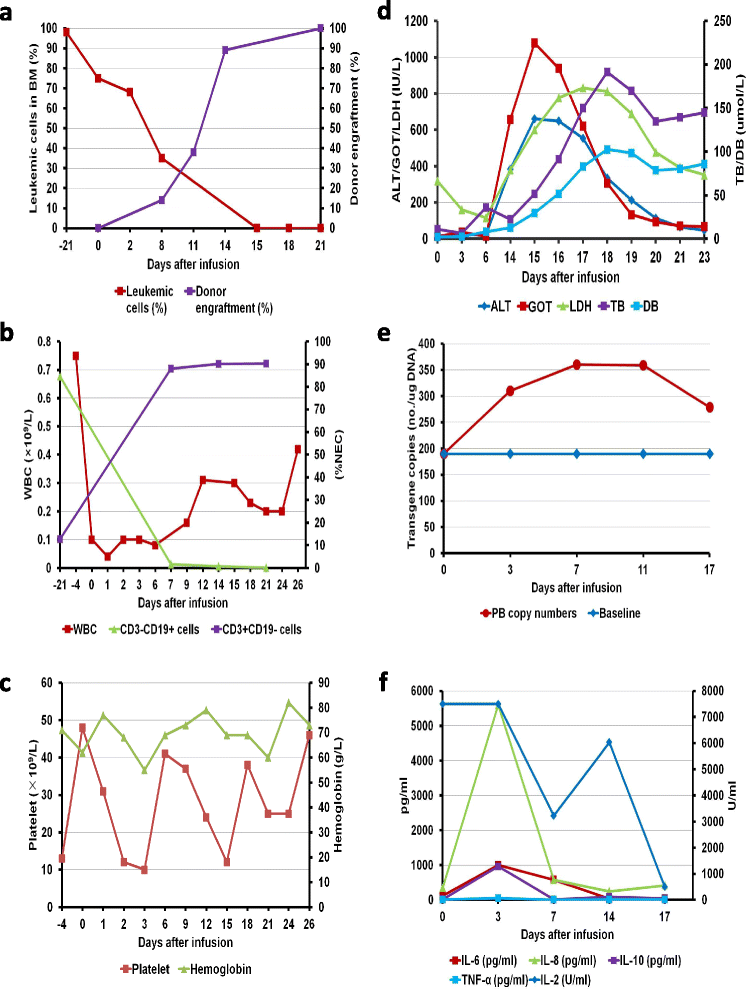
Case presentation: We treated a 71-year-old female with relapsed and refractory ALL who received co-infusion of haplo-identical donor-derived CD19-directed CAR-T cells and mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC) following induction chemotherapy. Undetectable minimal residual disease by flow cytometry was achieved, and full donor cell engraftment was established. The transient release of cytokines and mild fever were detected. Significantly elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase, alanine transaminase, bilirubin and glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase were observed from days 14 to 18, all of which were reversible after immunosuppressive therapy.
Conclusions: Our preliminary results suggest that co-infusion of haplo-identical donor-derived CAR-T cells and mobilized PBSCs may induce full donor engraftment in relapsed and refractory ALL including elderly patients, but complications related to donor cell infusions should still be cautioned.
Trial registration: Allogeneic CART-19 for Elderly Relapsed/Refractory CD19+ ALL. NCT02799550.
Keywords: Allogeneic anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells; B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL); Case report; Haplo-identical mobilized peripheral blood stem cell infusion; Relapsed and refractory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Donor-derived CD19-targeted T cell infusion induces minimal residual disease-negative remission in relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with no response to donor lymphocyte infusions after haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Br J Haematol. 2017 Nov;179(4):598-605. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14923. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Br J Haematol. 2017. PMID: 29076142
-
Donor-derived CAR-T Cells Serve as a Reduced-intensity Conditioning Regimen for Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation in Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Case Report and Review of the Literature.J Immunother. 2018 Jul/Aug;41(6):306-311. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000233. J Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29864079 Review.
-
[Maintenance therapy following CD19 CAR-T treatment for relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Jun 14;41(6):495-501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.06.011. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32654464 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell therapy bridging to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: An open-label pragmatic clinical trial.Am J Hematol. 2019 Oct;94(10):1113-1122. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25582. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Am J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31321805 Clinical Trial.
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy for Pediatric B-ALL: Narrowing the Gap Between Early and Long-Term Outcomes.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 11;11:1985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01985. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I CAR-T Clinical Trials Review.Anticancer Res. 2022 Dec;42(12):5673-5684. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16076. Anticancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36456127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity related to CAR-T cell therapy.Biomark Res. 2018 Jan 22;6:4. doi: 10.1186/s40364-018-0116-0. eCollection 2018. Biomark Res. 2018. PMID: 29387417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming the tumor microenvironment by genome editing for precision cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 11;21(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01561-5. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35410257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to Combine the Two Landmark Treatment Methods-Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Together to Cure High-Risk B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia?Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 15;11:611710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.611710. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33384696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syk inhibitors in clinical development for hematological malignancies.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jul 28;10(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0512-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28754125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee DW, Kochenderfer JN, Stetler-Stevenson M, Cui YK, Delbrook C, Feldman SA, et al. T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children and young adults: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 2015;385:517–528. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61403-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qasim W, Amrolia PJ, Samarasinghe S, Ghorashian S, Zhan H, Stafford S, et al. First clinical application of talen engineered universal CAR19 T cells in B-ALL. Blood. 2015;126:2046.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

