Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 27888803
- PMCID: PMC5356757
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13465
Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer
Abstract
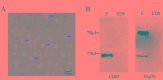
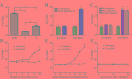
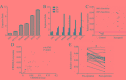
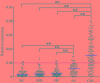
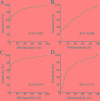
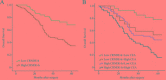
Cancer-secreted long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging mediators of cancer-host cross talk. The aim of our study was to illustrate the clinical significance of the lncRNA CRNDE-h in exosomes purified from the serum of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). The study was divided into four parts: (1) The exosome isolated methods and lncRNA detected methods which accurately and reproducibly measure CRC-related exosomal CRNDE-h in serum were optimized in preliminary pilot stage; (2) The stability of exosomal CRNDE-h was evaluated systematically; (3) The origin of exosomal CRNDE-h was explorated in vitro and in vivo; (4) The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosomal CRNDE-h for CRC were validated in 468 patients. In pilot study, our results indicated that exosomal CRNDE-h was detectable and stable in serum of CRC patients, and derived from tumor cells. Then, the increased expression of exosomal CRNDE-h was successfully validated in 148 CRC patients when compared with colorectal benign disease patients and healthy donors. Exosomal CRNDE-h level significantly correlated with CRC regional lymph node metastasis (P = 0.019) and distant metastasis (P = 0.003). Moreover, at the cut-off value of 0.020 exosomal CRNDE-h level of serum, the area under ROC curve distinguishing CRC from colorectal benign disease patients and healthy donors was 0.892, with 70.3% sensitivity and 94.4% specificity, which was superior to carcinoembryogenic antigen. In addition, high exosomal CRNDE-h level has a lower overall survival rates than that for low groups (34.6% vs. 68.2%, P < 0.001). In conclusion, detection of lncRNA CRNDE-h in exosome shed a light on utilizing exosomal CRNDE-h as a noninvasive serum-based tumor marker for diagnosis and prognosis of CRC.
Keywords: CRNDE-h; biomarker; colorectal cancer; exosome; long noncoding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
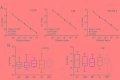
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BK, Noone AM, Mariotto AB, Simard EP, Boscoe FP, Henley SJ, Jemal A, Cho H, Anderson RN, Kohler BA, Eheman CR, Ward EM. Annual Report to the Nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2010, featuring prevalence of comorbidity and impact on survival among persons with lung, colorectal, breast, or prostate cancer. Cancer. 2014;120:1290–1314. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nissan A, Stojadinovic A, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S, Halle D, Grinbaum R, Roistacher M, Bochem A, Dayanc BE, Ritter G, Gomceli I, Bostanci EB, Akoglu M, Chen YT, Old LJ, Gure AO. Colon cancer associated transcript-1: a novel RNA expressed in malignant and pre-malignant human tissues. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:1598–1606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

