Radiology as the Point of Cancer Patient and Care Team Engagement: Applying the 4R Model at a Patient's Breast Cancer Care Initiation
- PMID: 27888945
- PMCID: PMC5127438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.008
Radiology as the Point of Cancer Patient and Care Team Engagement: Applying the 4R Model at a Patient's Breast Cancer Care Initiation
Abstract
Radiologists aspire to improve patient experience and engagement, as part of the Triple Aim of health reform. Patient engagement requires active partnerships among health providers and patients, and rigorous teamwork provides a mechanism for this. Patient and care team engagement are crucial at the time of cancer diagnosis and care initiation but are complicated by the necessity to orchestrate many interdependent consultations and care events in a short time. Radiology often serves as the patient entry point into the cancer care system, especially for breast cancer. It is uniquely positioned to play the value-adding role of facilitating patient and team engagement during cancer care initiation. The 4R approach (Right Information and Right Care to the Right Patient at the Right Time), previously proposed for optimizing teamwork and care delivery during cancer treatment, could be applied at the time of diagnosis. The 4R approach considers care for every patient with cancer as a project, using project management to plan and manage care interdependencies, assign clear responsibilities, and designate a quarterback function. The authors propose that radiology assume the quarterback function during breast cancer care initiation, developing the care initiation sequence, as a project care plan for newly diagnosed patients, and engaging patients and their care teams in timely, coordinated activities. After initial consultations and treatment plan development, the quarterback function is transitioned to surgery or medical oncology. This model provides radiologists with opportunities to offer value-added services and solidifies radiology's relevance in the evolving health care environment. To implement 4R at cancer care initiation, it will be necessary to change the radiology practice model to incorporate patient interaction and teamwork, develop 4R content and local adaption approaches, and enrich radiology training with relevant clinical knowledge, patient interaction competence, and teamwork skill set.
Keywords: Cancer; breast cancer; breast cancer diagnosis; models of care; patient engagement; radiology care delivery; team-based care; teamwork.
Copyright © 2016 American College of Radiology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
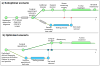
 Insurance eligibility and network verification issues and other delays PCP – Primary Care Physician Diagram is not to the actual time scale
Insurance eligibility and network verification issues and other delays PCP – Primary Care Physician Diagram is not to the actual time scale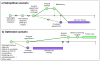
 Patient delays due to childcare and work schedule issues (present in scenario a, but resolved in scenario b) PCP – Primary Care Physician Diagram is not to the actual time scale
Patient delays due to childcare and work schedule issues (present in scenario a, but resolved in scenario b) PCP – Primary Care Physician Diagram is not to the actual time scale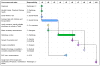
Similar articles
-
Focusing on the "Person" in Personalized Medicine: The Future of Patient-Centered Care in Radiation Oncology.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Dec;13(12 Pt B):1571-1578. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.012. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27888944 Review.
-
Using Quality Improvement Methods to Improve Patient Experience.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Dec;13(12 Pt B):1550-1554. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.005. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27888940 Review.
-
Patient- and Family-Centered Care: A Primer.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Dec;13(12 Pt B):1544-1549. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.003. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27888939 Review.
-
Lessons Learned From Two Decades of Patient- and Family-Centered Care in Radiology, Part 2: Building a Culture.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Dec;13(12 Pt B):1560-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.011. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27888942 Review.
-
Lessons Learned From Two Decades of Patient- and Family-Centered Care in Radiology, Part 1: Getting Started.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Dec;13(12 Pt B):1555-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.09.010. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27888941 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Patient Navigation Strategies to Scale Breast Cancer Disparity Reduction by Improved Cancer Prevention and Care Delivery Processes.JCO Oncol Pract. 2020 Dec;16(12):e1462-e1470. doi: 10.1200/JOP.19.00314. Epub 2020 Jun 23. JCO Oncol Pract. 2020. PMID: 32574137 Free PMC article.
-
Capacity for Cancer Care Delivery Research in National Cancer Institute Community Oncology Research Program Community Practices: Availability of Radiology and Primary Care Research Partners.J Am Coll Radiol. 2017 Dec;14(12):1530-1537. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Oct 19. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017. PMID: 29055605 Free PMC article.
-
Advance Directives for Patients With Breast Cancer: Applying the Right Info/Right Care/Right Patient/Right Time Oncology Model.Perm J. 2023 Sep 15;27(3):30-36. doi: 10.7812/TPP/22.177. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Perm J. 2023. PMID: 37255340 Free PMC article.
-
Fostering a High-Functioning Team in Cancer Care Using the 4R Oncology Model: Assessment in a Large Health System and a Blueprint for Other Institutions.JCO Oncol Pract. 2023 Jan;19(1):e125-e137. doi: 10.1200/OP.22.00287. Epub 2022 Sep 30. JCO Oncol Pract. 2023. PMID: 36178937 Free PMC article.
-
Timeliness of Breast Diagnostic Imaging and Biopsy in Practice: 15 Years of Collecting, Comparing, and Defining Quality Breast Cancer Care.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Oct;30(10):6070-6078. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-13905-6. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37528305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berwick DM, Nolan TW, Whittington J. The triple aim: care, health, and cost. Health Aff (Millwood) 2008;27:759–69. - PubMed
-
- Allen B., Jr Improving our patients’ experience in their radiological care. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12:767–8. - PubMed
-
- Mayo RC, 3rd, Parikh JR. Breast Imaging: The Face of Imaging 3.0. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Swan JS, Pandharipande PV, Salazar GM. Developing a Patient-Centered Radiology Process Model. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016;13:510–6. - PubMed
-
- Chhor CM, Mercado CL. Integrating Customer Intimacy Into Radiology to Improve the Patient Perspective: The Case of Breast Cancer Screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;206:265–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

