Circadian Homeostasis of Liver Metabolism Suppresses Hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 27889186
- PMCID: PMC5695235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.007
Circadian Homeostasis of Liver Metabolism Suppresses Hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
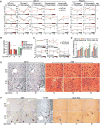
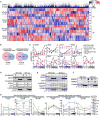
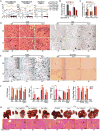
Chronic jet lag induces spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in wild-type mice following a mechanism very similar to that observed in obese humans. The process initiates with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that progresses to steatohepatitis and fibrosis before HCC detection. This pathophysiological pathway is driven by jet-lag-induced genome-wide gene deregulation and global liver metabolic dysfunction, with nuclear receptor-controlled cholesterol/bile acid and xenobiotic metabolism among the top deregulated pathways. Ablation of farnesoid X receptor dramatically increases enterohepatic bile acid levels and jet-lag-induced HCC, while loss of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), a well-known liver tumor promoter that mediates toxic bile acid signaling, inhibits NAFLD-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Circadian disruption activates CAR by promoting cholestasis, peripheral clock disruption, and sympathetic dysfunction.
Keywords: cholestasis; chronic circadian disruption; constitutive androstane receptor (CAR); farnesoid X receptor (FXR); fibrosis; hepatocarcinogenesis; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; social jet lag; sympathetic dysfunction.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Comment in
-
Timing Is Everything.Cell Metab. 2017 Jan 10;25(1):2-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.015. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 28076761
-
Synchrony between suprachiasmatic nucleus-driven signals and the light/dark cycle is essential for liver homeostasis.Hepatology. 2017 Jun;65(6):2110-2112. doi: 10.1002/hep.29124. Epub 2017 May 4. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28198033 No abstract available.
References
-
- Audard V, Grimber G, Elie C, Radenen B, Audebourg A, Letourneur F, Soubrane O, Vacher-Lavenu MC, Perret C, Cavard C, Terris B. Cholestasis is a marker for hepatocellular carcinomas displaying beta-catenin mutations. The Journal of pathology. 2007;212:345–352. - PubMed
-
- Diwan BA, Rice JM, Ward JM. Strain-dependent effects of phenobarbital on liver tumor promotion in inbred mice. Progress in clinical and biological research. 1990;331:69–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

