Structural Mechanism for Cargo Recognition by the Retromer Complex
- PMID: 27889239
- PMCID: PMC5147500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.056
Structural Mechanism for Cargo Recognition by the Retromer Complex
Abstract
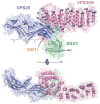
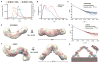
Retromer is a multi-protein complex that recycles transmembrane cargo from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane. Defects in retromer impair various cellular processes and underlie some forms of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Although retromer was discovered over 15 years ago, the mechanisms for cargo recognition and recruitment to endosomes have remained elusive. Here, we present an X-ray crystallographic analysis of a four-component complex comprising the VPS26 and VPS35 subunits of retromer, the sorting nexin SNX3, and a recycling signal from the divalent cation transporter DMT1-II. This analysis identifies a binding site for canonical recycling signals at the interface between VPS26 and SNX3. In addition, the structure highlights a network of cooperative interactions among the VPS subunits, SNX3, and cargo that couple signal-recognition to membrane recruitment.
Keywords: cargo recognition; endocytic recycling; endosomes; membrane recruitment; membrane tubules; protein coats; retrograde transport; retromer; sorting nexins; sorting signals.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

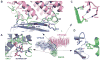



Comment in
-
Retromer Sets a Trap for Endosomal Cargo Sorting.Cell. 2016 Dec 1;167(6):1452-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.026. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27912055
References
-
- Canuel M, Lefrancois S, Zeng J, Morales CR. AP-1 and retromer play opposite roles in the trafficking of sortilin between the Golgi apparatus and the lysosomes. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2008;366:724–730. - PubMed
-
- Carlton J, Bujny M, Peter BJ, Oorschot VM, Rutherford A, Mellor H, Klumperman J, McMahon HT, Cullen PJ. Sorting nexin-1 mediates tubular endosome-to-TGN transport through coincidence sensing of high-curvature membranes and 3-phosphoinositides. Current biology : CB. 2004;14:1791–1800. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

