Cell membrane modulation as adjuvant in cancer therapy
- PMID: 27889637
- PMCID: PMC5195909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.10.008
Cell membrane modulation as adjuvant in cancer therapy
Abstract
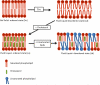
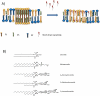
Cancer is a complex disease involving numerous biological processes, which can exist in parallel, can be complementary, or are engaged when needed and as such can replace each other. This redundancy in possibilities cancer cells have, are fundamental to failure of therapy. However, intrinsic features of tumor cells and tumors as a whole provide also opportunities for therapy. Here we discuss the unique and specific makeup and arrangement of cell membranes of tumor cells and how these may help treatment. Interestingly, knowledge on cell membranes and associated structures is present already for decades, while application of membrane modification and manipulation as part of cancer therapy is lagging. Recent developments of scientific tools concerning lipids and lipid metabolism, opened new and previously unknown aspects of tumor cells and indicate possible differences in lipid composition and membrane function of tumor cells compared to healthy cells. This field, coined Lipidomics, demonstrates the importance of lipid components in cell membrane in several illnesses. Important alterations in cancer, and specially in resistant cancer cells compared to normal cells, opened the door to new therapeutic strategies. Moreover, the ability to modulate membrane components and/or properties has become a reality. Here, developments in cancer-related Lipidomics and strategies to interfere specifically with cancer cell membranes and how these affect cancer treatment are discussed. We hypothesize that combination of lipid or membrane targeted strategies with available care to improve chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy will bring the much needed change in treatment in the years to come.
Keywords: Cancer adjuvant; Cell membrane; Lipid modulation; Lipidomics.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Nicolson GL. The Fluid-Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure: still relevant to understanding the structure, function and dynamics of biological membranes after more than 40 years. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838(6):1451–66. - PubMed
-
- Bagatolli LA, et al. An outlook on organization of lipids in membranes: searching for a realistic connection with the organization of biological membranes. Prog Lipid Res. 2010;49(4):378–89. - PubMed
-
- Singer SJ, Nicolson GL. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972;175(4023):720–31. - PubMed
-
- Goni FM. The basic structure and dynamics of cell membranes: an update of the Singer-Nicolson model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838(6):1467–76. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson K, Mouritsen OG, Anderson RG. Lipid rafts: at a crossroad between cell biology and physics. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(1):7–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

