Complete morphometric analysis of jugular foramen and its clinical implications
- PMID: 27891036
- PMCID: PMC5111328
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8237.193268
Complete morphometric analysis of jugular foramen and its clinical implications
Abstract
Introduction: Tumors affecting structures in the vicinity of jugular foramen such as glomus jugulare require microsurgical approach to access this region. These tumors tend to alter the normal architecture of the jugular foramen by invading it. Therefore, it is not feasible to have correct anatomic visualization of the foramen in the presence of such pathologies. Hence, a comprehensive knowledge of the jugular foramen is needed by all the neurosurgeons while doing surgery in this region.
Aim: Due to the inadequate knowledge of the accurate morphology of the jugular foramen in different sexes, the aim of this osteological study was to provide a complete morphometry including gender differences and describe some morphological characteristics of the jugular foramen in an adult Indian population.
Materials and methods: The study was done on 114 adult human dry skulls (63 males and 51 females) collected from the osteology museum in the department. Various dimensions of both endo- and exocranial aspect of jugular foramen were measured. Presence and absence of domed bony roof of jugular fossa and compartmentalization of jugular foramen were also noticed. Statistical analysis was done using Chi-square test and Student's t-test in SPSS version 23.
Results: All the parameters of right jugular foramen were greater than the left side, except the distance of stylomastoid foramen from lateral margin of jugular foramen (SMJF) which was greater on the left side. Gender differences between various measurements of jugular foramen, presence of dome of jugular fossa, and compartmentalization patterns were reported.
Conclusion: This study gives knowledge about the various parameters, anatomical variations of jugular foramen in both sexes of an adult Indian population, and its clinical impact on the surgeries of this region.
Keywords: Glomus jugulare; internal jugular vein; jugular foramen; morphometry.
Figures
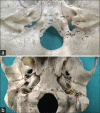
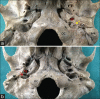

Similar articles
-
A morphological and morphometric study of jugular foramen in dry skulls with its clinical implications.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2014 Jul;5(3):118-21. doi: 10.4103/0974-8237.142305. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2014. PMID: 25336833 Free PMC article.
-
A Morphometric Study of Stylomastoid Foramen with Its Clinical Applications.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2020 Oct 12;83(1):33-36. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1716674. eCollection 2022 Feb. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2020. PMID: 35155067 Free PMC article.
-
Jugular foramen: microscopic anatomic features and implications for neural preservation with reference to glomus tumors involving the temporal bone.Neurosurgery. 2001 Apr;48(4):838-47; discussion 847-8. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200104000-00029. Neurosurgery. 2001. PMID: 11322444
-
Microsurgical Anatomy of the Jugular Foramen Applied to Surgery of Glomus Jugulare via Craniocervical Approach.Front Surg. 2020 May 15;7:27. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2020.00027. eCollection 2020. Front Surg. 2020. PMID: 32500078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiologic evaluation of the jugular foramen. Anatomy, vascular variants, anomalies, and tumors.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1994 Aug;4(3):579-98. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1994. PMID: 7952957 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological variability of the jugular foramen: a comprehensive anatomical-imaging study emphasizing its compartmentalization.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Jun 24;48(1):527. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03681-0. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40550932 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical Variations of the Jugular Foramen Region in Patients with Pulsatile Tinnitus.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021 Jan 14;83(3):248-253. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1722670. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021. PMID: 35769801 Free PMC article.
-
The investigation of cranial fossae in the intracranial cavity of fixed cadaveric skull bases: associations with sex, laterality, and clinical significance.Surg Radiol Anat. 2024 Aug;46(8):1305-1329. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03408-8. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Surg Radiol Anat. 2024. PMID: 38858315
-
Morphological analysis of the jugular foramen in dry human skulls in northeastern Brazil.Anat Cell Biol. 2024 Jun 30;57(2):213-220. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.218. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Anat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38449076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy. The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 40th ed. Edinburg: Churchill & Livingstone; 2008. pp. 423–34.
-
- Vlajkovic S, Vasovic L, Dakovic-Bjelakovic M, Stankovic S, Popovic J, Cukuranovic R. Human bony jugular foramen: Some additional morphological and morphometric features. Med Sci Monit. 2010;16:BR140–6. - PubMed
-
- Kotgirwar S, Athavale S. Morphometric study of jugular foramen in adult South Indian skulls. J Anat Soc India. 2013;62:166–9.
-
- Idowu OE. The jugular foramen – A morphometric study. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 2004;63:419–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

