GWAS study using DNA pooling strategy identifies association of variant rs4910623 in OR52B4 gene with anti-VEGF treatment response in age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 27892514
- PMCID: PMC5124940
- DOI: 10.1038/srep37924
GWAS study using DNA pooling strategy identifies association of variant rs4910623 in OR52B4 gene with anti-VEGF treatment response in age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
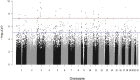
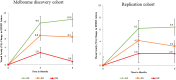
Pooled DNA based GWAS to determine genetic association of SNPs with visual acuity (VA) outcome in anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) treated neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) patients. We performed pooled DNA based GWAS on 285 anti-VEGF treated nAMD patients using high density Illumina 4.3 M array. Primary outcome was change in VA in Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) letters after 6 months of anti-VEGF treatment (patients who lost ≥5 ETDRS letters classified as non-responders and all remaining classified as responders). GWAS analysis identified 44 SNPs of interest: 37 with strong evidence of association (p < 9 × 10-8), 2 in drug resistance genes (p < 5 × 10-6) and 5 nonsynonymous changes (p < 1 × 10-4). In the validation phase, individual genotyping of 44 variants showed three SNPs (rs4910623 p = 5.6 × 10-5, rs323085 p = 6.5 × 10-4 and rs10198937 p = 1.30 × 10-3) remained associated with VA response at 6 months. SNP rs4910623 also associated with treatment response at 3 months (p = 1.5 × 10-3). Replication of these three SNPs in 376 patients revealed association of rs4910623 with poor VA response after 3 and 6 months of treatment (p = 2.4 × 10-3 and p = 3.5 × 10-2, respectively). Meta-analysis of both cohorts (673 samples) confirmed association of rs4910623 with poor VA response after 3 months (p = 1.2 × 10-5) and 6 months (p = 9.3 × 10-6) of treatment in nAMD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: molecular and biological aspects. Current topics in microbiology and immunology 237, 1–30 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

