Genetic and epigenetic silencing of mircoRNA-506-3p enhances COTL1 oncogene expression to foster non-small lung cancer progression
- PMID: 27893417
- PMCID: PMC5352185
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13501
Genetic and epigenetic silencing of mircoRNA-506-3p enhances COTL1 oncogene expression to foster non-small lung cancer progression
Abstract
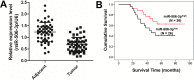
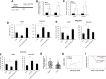
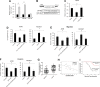
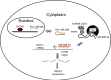
Although previous studies suggested that microRNA-506-3p (miR-506-3p) was frequently downregulated, and functioned as a tumor suppressor in several cancers, the biological role and intrinsic regulatory mechanisms of miR-506-3p in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remain elusive. The present study found miR-506-3p expression was downregulated in advanced NSCLC tissues and cell lines. The expression of miR-506-3p in NSCLC was inversely correlated with larger tumor size, advanced TNM stage and lymph node metastasis. In addition, we also found patients with lower expression of miR-506-3p had a poor prognosis than those patients with higher expression of miR-506-3p. Function studies demonstrated that aberrant miR-506-3p expression modulates tumor cell growth, cell mobility, cell migration and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistic investigations manifested that coactosin-like protein 1 (COTL1) was a direct downstream target of miR-506-3p. Knockdown of COTL1 mimicked the tumor-suppressive effects of miR-506-3p overexpression in A549 cells, whereas COTL1 overexpression enhanced the tumorigenic function in HCC827 cells. Importantly, we also found GATA3 transcriptionally actives miR-506-3p expression, and the long non-coding RNA urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 (UCA1) exerts oncogenic function in NSCLC by competitively 'sponging' miRNA-506. Together, our combined results elucidated genetic and epigenetic silencing of miR-506-3p enhances COTL1 oncogene expression to foster NSCLC progression.
Keywords: COTL1; LncRNA; UCA1; miR-506-3p; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LncRNA-UCA1 exerts oncogenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-193a-3p.Cancer Lett. 2016 Feb 1;371(1):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.024. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26655272
-
Upregulated lncRNA SNHG1 contributes to progression of non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of miR-101-3p and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 14;8(11):17785-17794. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14854. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28147312 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-361-3p suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting SH2B1 in NSCLC.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 May 10;35:76. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0357-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27164951 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of miR-200 family members in lung cancer: more than tumor suppressors.Future Oncol. 2018 Nov;14(27):2875-2886. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0155. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30208739 Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 in Breast Cancer: Epigenetic Mechanisms and Biological Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6810. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136810. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The long non-coding RNA, urothelial carcinoma associated 1, promotes cell growth, invasion, migration, and chemo-resistance in glioma through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Oct 8;11(19):8239-8253. doi: 10.18632/aging.102317. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31596734 Free PMC article.
-
A Systemic and Integrated Analysis of p63-Driven Regulatory Networks in Mouse Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;15(2):446. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020446. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672394 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of artificial skin membrane on the expression of miR-155 and miR-506-3p in patients with second-degree burns.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24564. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24564. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35949047 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA LAMTOR5-AS1 Interference Affects MicroRNA-506-3p/E2F6-Mediated Behavior of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2022 Jan 31;28(9):945-959. doi: 10.3727/096504021X16328213967104. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 34588094 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between long noncoding RNA and microRNA in Cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Aug;46(4):885-908. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00806-9. Epub 2023 May 28. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 37245177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, Le Chevalier T, Lim E, Nicholson AG, Shepherd FA. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2011;378:1727–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

