Negative feedback between TAp63 and Mir-133b mediates colorectal cancer suppression
- PMID: 27894087
- PMCID: PMC5349978
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13515
Negative feedback between TAp63 and Mir-133b mediates colorectal cancer suppression
Abstract
Background: TAp63 is known as the most potent transcription activator and tumor suppressor. microRNAs (miRNAs) are increasingly recognized as essential components of the p63 pathway, mediating downstream post-transcriptional gene repression. The aim of present study was to investigate a negative feedback loop between TAp63 and miR-133b.
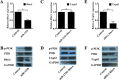
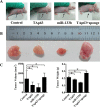
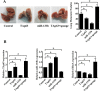
Results: Overexpression of TAp63 inhibited HCT-116 cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion via miR-133b. Accordingly, miR-133b inhibited TAp63 expression through RhoA and its downstream pathways. Moreover, we demonstrated that TAp63/miR-133b could inhibit colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis in vivo and vitro.
Materials and methods: We evaluated the correlation between TAp63 and miR-133b in HCT-116 cells and investigated the roles of the TAp63/miR-133b feedback loop in cell proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis via MTT, flow cytometry, Transwell, and nude mouse xenograft experiments. The expression of TAp63, miR-133b, RhoA, α-tubulin and Akt was assessed via qRT-PCR, western blot and immunofluorescence analyses. miR-133b target genes were identified through luciferase reporter assays.
Conclusions: miR-133b plays an important role in the anti-tumor effects of TAp63 in colorectal cancer. miR-133b may represent a tiemolecule between TAp63 and RhoA, forming a TAp63/miR-133b/RhoA negative feedback loop, which could significantly inhibit proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis.
Keywords: TAp63; metastasis; miR-133b; negative feedback; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

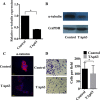
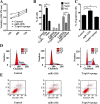
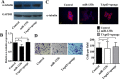
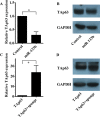
References
-
- Moll UM, Slade N. p63 and p73: roles in development and tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2:371–386. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

