Impact of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome, cancer and longevity
- PMID: 27894098
- PMCID: PMC5352455
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13553
Impact of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome, cancer and longevity
Abstract
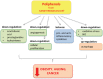
Obesity symbolizes a major public health problem. Overweight and obesity are associated to the occurrence of the metabolic syndrome and to adipose tissue dysfunction. The adipose tissue is metabolically active and an endocrine organ, whose dysregulation causes a low-grade inflammatory state and ectopic fat depositions. The Mediterranean Diet represents a possible therapy for metabolic syndrome, preventing adiposopathy or "sick fat" formation.The Mediterranean Diet exerts protective effects in elderly subjects with and without baseline of chronic diseases. Recent studies have demonstrated a relationship between cancer and obesity. In the US, diet represents amount 30-35% of death causes related to cancer. Currently, the cancer is the second cause of death after cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Furthermore, populations living in the Mediterranean area have a decreased incidence of cancer compared with populations living in Northern Europe or the US, likely due to healthier dietary habits. The bioactive food components have a potential preventive action on cancer. The aims of this review are to evaluate the impact of Mediterranean Diet on onset, progression and regression of metabolic syndrome, cancer and on longevity.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; antioxidant; cancer; obesity; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Noto D, Cefalù AB, Barbagallo CM, Ganci A, Cavera G, Fayer F, Palesano O, Spina R, Valenti V, Altieri GI, Caldarella R, Giammanco A, Termini R, et al. Baseline metabolic disturbances and the twenty-five years risk of incident cancer in a Mediterranean population. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;26:1020–5. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

