Complications and Short-Term Outcomes of Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Locking Plate for Medial Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- PMID: 27894176
- PMCID: PMC5134783
- DOI: 10.5792/ksrr.16.028
Complications and Short-Term Outcomes of Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Locking Plate for Medial Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate complications and radiologic and clinical outcomes of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy (MOWHTO) using a locking plate.
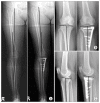
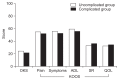
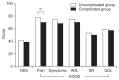
Materials and methods: This study reviewed 167 patients who were treated with MOWHTO using a locking plate from May 2012 to June 2014. Patients without complications were classified into group 1 and those with complications into group 2. Medical records, operative notes, and radiographs were retrospectively reviewed to identify complications. Clinically, Oxford Knee score and Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome score (KOOS) were evaluated.
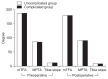
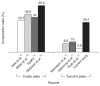
Results: Overall, complications were observed in 49 patients (29.3%). Minor complications included lateral cortex fracture (15.6%), neuropathy (3.6%), correction loss (2.4%), hematoma (2.4%), delayed union (2.4%), delayed wound healing (2.4%), postoperative stiffness (1.2%), hardware irritation (1.2%), tendinitis (1.2%), and hardware failure without associated symptoms (0.6%). Major complications included hardware failure with associated symptoms (0.6%), deep infection (0.6%), and nonunion (0.6%). At the first-year follow-up, there were no significant differences in radiologic measurements between groups 1 and 2. There were no significant differences in knee scores except for the KOOS pain score.
Conclusions: Our data showed that almost all complications of the treatment were minor and the patients recovered without any problems. Most complications did not have a significant impact on radiologic and clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Complication; Knee; Open wedge; Osteoarthritis; Osteotomy; Plate.
Figures

References
-
- Niemeyer P, Schmal H, Hauschild O, von Heyden J, SJ, Sn NP, Kostler W. Open-wedge osteotomy using an internal plate fixator in patients with medial-compartment gonarthritis and varus malalignment: 3-year results with regard to preoperative arthroscopic and radiographic findings. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1607–16. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2010.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
