Pancreaticoduodenectomy for pediatric and adolescent pancreatic malignancy: A single-center retrospective analysis
- PMID: 27894759
- PMCID: PMC5253309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.11.025
Pancreaticoduodenectomy for pediatric and adolescent pancreatic malignancy: A single-center retrospective analysis
Abstract
Purpose: While pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) has been extensively studied in adults, there are few data pertaining specifically to pediatric patients. We retrospectively analyzed PD-associated morbidity and mortality in pediatric patients.
Methods: Our analytic cohort included all consecutive patients ≤18years of age treated at our institution from 1993 to 2015 who underwent PD. Patient data (demographics, disease characteristics, surgical and adjuvant treatment, length of hospital stay, and postoperative course) were extracted from the medical records.
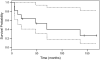
Results: We identified 12 children with a median age of 9years (7 female, 5 male). Final diagnoses were pancreatoblastoma (n=3), solid pseudopapillary tumor (n=3), neuroblastoma (n=2), rhabdomyosarcoma (n=2), and neuroendocrine carcinoma (n=2). Four patients underwent PD for resection of recurrent disease. 75% (9/12 patients) received neoadjuvant therapy. The median operative time was approximately 7hours with a mean blood loss of 590cm3. The distal pancreas was invaginated into the posterior stomach (n=3) or into the jejunum (n=5) or was directly sewn to the jejunal mucosa (n=4). There were no operative deaths. There were 4 patients (34%) with grade II complications, 1 with a grade IIIb complication (chest tube), and 1 with a grade IV complication (reexploration). The most common long-term morbidity was pancreas exocrine supplementation (n=10; 83%). Five patients (42%) diagnosed with either solid pseudopapillary tumor or rhabdomyosarcoma are currently alive with a mean survival of 77.4months.
Conclusion: Pancreaticoduodenectomy is a feasible management strategy for pediatric pancreatic malignancies and is associated with acceptable morbidity and overall survival. Long-term outcome is mostly dependent on histology of the tumor.
Level of evidence: Level IV; retrospective study with no comparison group.
Keywords: Pancreatic tumor; Pancreaticoduodenectomy; Pancreatoblastoma; Solid pseudopapillary tumor; Whipple procedure.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy for the treatment of pancreatic neoplasms in children: A Pediatric Surgical Oncology Research Collaborative study.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020 Sep;67(9):e28425. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28425. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32658372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pancreatic masses in children: a single-center experience over two decades.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Oct;183(10):4467-4476. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05731-z. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39145888
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy for malignancies in children.J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Apr;49(4):534-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.09.010. J Pediatr Surg. 2014. PMID: 24726107
-
Outcome of pancreaticoduodenectomy in octogenarians: Single institution's experience and review of the literature.J Visc Surg. 2015 Nov;152(5):279-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Visc Surg. 2015. PMID: 26117303 Review.
-
Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a single-institution 20-year series of pediatric patients.J Pediatr Surg. 2012 Jun;47(6):1217-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.03.026. J Pediatr Surg. 2012. PMID: 22703796 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy for the treatment of pancreatic neoplasms in children: A Pediatric Surgical Oncology Research Collaborative study.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020 Sep;67(9):e28425. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28425. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32658372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pediatric pancreatic teratoma: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Nov;98(46):e18001. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018001. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31725669 Free PMC article.
-
Successful management of a pancreatic mature cystic teratoma with Whipple procedure: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Dec;125:110504. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110504. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39461133 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective analysis of pancreas operations in children.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jul 25;6:39. doi: 10.21037/tgh-20-260. eCollection 2021. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34423160 Free PMC article.
-
Living donor liver transplantation with total pancreatectomy and portal vein homograft replacement in a pediatric patient with advanced pancreatoblastoma.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2020 Feb;24(1):78-84. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.1.78. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2020. PMID: 32181434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Senthilnathan P, Patel N, Nalankilli VP, et al. Laparoscopic pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy in paediatric age for solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of head of the pancreas - case report. Pancreatology. 2014;14:550–552. - PubMed
-
- d'Ambrosio G, del Prete L, Grimaldi C, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for malignancies in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2014;49:534–538. - PubMed
-
- Donahue TR, Reber HA. Surgical management of pancreatic cancer--pancreaticoduodenectomy. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:98–109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials