The dynamics of GABA signaling: Revelations from the circadian pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
- PMID: 27894927
- PMCID: PMC5225159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.11.003
The dynamics of GABA signaling: Revelations from the circadian pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
Abstract
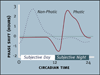
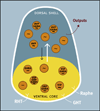
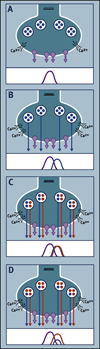
Virtually every neuron within the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) communicates via GABAergic signaling. The extracellular levels of GABA within the SCN are determined by a complex interaction of synthesis and transport, as well as synaptic and non-synaptic release. The response to GABA is mediated by GABAA receptors that respond to both phasic and tonic GABA release and that can produce excitatory as well as inhibitory cellular responses. GABA also influences circadian control through the exclusively inhibitory effects of GABAB receptors. Both GABA and neuropeptide signaling occur within the SCN, although the functional consequences of the interactions of these signals are not well understood. This review considers the role of GABA in the circadian pacemaker, in the mechanisms responsible for the generation of circadian rhythms, in the ability of non-photic stimuli to reset the phase of the pacemaker, and in the ability of the day-night cycle to entrain the pacemaker.
Keywords: Benzodiazepines; Cation chloride cotransporters; Entrainment; Ethanol; GABA vesicular transporters; GABA(A) receptors; GABA(B) receptors; Glutamic acid decarboxylase; Membrane GABA transporters; Neurosteroids.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Aguilar-Roblero R, Verduzco-Carbajal L, Rodriguez C, Mendez-Franco J, Moran J, Perez de la Mora M. Circadian rhythmicity in the GABAergic system in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1993;157:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Aioun J, Chambille I, Peytevin J, Martinet L. Neurons containing gastrin-releasing peptide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide are involved in the reception of the photic signal in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the Syrian hamster: an immunocytochemical ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1998;291:239–253. - PubMed
-
- Ajpru S, McArthur AJ, Piggins HD, Sugden D. Identification of PAC1 receptor isoform mRNAs by real-time PCR in rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002;105:29–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 NS051183/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS078220/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS082413/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH067420/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS092545/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH012956/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS009927/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM086683/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM086683/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS084683/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058789/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

