The emerging role of long non-coding RNA in gallbladder cancer pathogenesis
- PMID: 27894946
- PMCID: PMC6282167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.11.007
The emerging role of long non-coding RNA in gallbladder cancer pathogenesis
Abstract
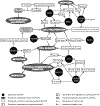
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is the most common and aggressive form of biliary tract carcinoma with an alarmingly low 5-year survival rate. Despite its high mortality rate, the underlying mechanisms of GBC pathogenesis are not completely understood. Recently, from a growing volume of literature, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as key regulators of gene expression and appear to play vital roles in many human cancers. To date, a number of lncRNAs have been implicated in GBC, but their potential roles in GBC have not been systematically examined. Thus, in this review, we critically discuss the emerging roles of lncRNAs in GBC, and the pathways involved. Specifically, we note that some lncRNAs show greater expression in T1 and T2 tumor stages compared to T3 and T4 tumor stages and that their dysregulation leads to alterations in cell cycle progression and can cause an increase in GBC cell proliferation or apoptosis. In addition, some lncRNAs control the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, while others take part in the regulation of ERK/MAPK and Ras cancer-associated signaling pathways. We also present their potential utility in diagnosis, prognosis, and/or treatment of GBC. The overall goal of this review is to stimulate interest in the role of lncRNAs in GBC, which may open new avenues in the determination of GBC pathogenesis and may lead to the development of new preventive and therapeutic strategies for GBC.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diagnostic markers; Gallbladder cancer; LncRNAs; Long non-coding RNA; Oncogenes; Prognostic markers; Tumor suppressors.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. and Société Française de Biochimie et Biologie Moléculaire (SFBBM). All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Coburn NG, Cleary SP, Tan JC, Law CH, Surgery for gallbladder cancer: a population-based analysis, J Am Coll Surg, 207 (2008) 371–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

