In Vitro and In Vivo Activities of Sulfur-Containing Linear Bisphosphonates against Apicomplexan Parasites
- PMID: 27895021
- PMCID: PMC5278718
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01590-16
In Vitro and In Vivo Activities of Sulfur-Containing Linear Bisphosphonates against Apicomplexan Parasites
Abstract
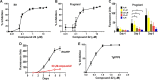
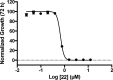
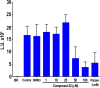
We tested a series of sulfur-containing linear bisphosphonates against Toxoplasma gondii, the etiologic agent of toxoplasmosis. The most potent compound (compound 22; 1-[(n-decylsulfonyl)ethyl]-1,1-bisphosphonic acid) is a sulfone-containing compound, which had a 50% effective concentration (EC50) of 0.11 ± 0.02 μM against intracellular tachyzoites. The compound showed low toxicity when tested in tissue culture with a selectivity index of >2,000. Compound 22 also showed high activity in vivo in a toxoplasmosis mouse model. The compound inhibited the Toxoplasma farnesyl diphosphate synthase (TgFPPS), but the concentration needed to inhibit 50% of the enzymatic activity (IC50) was higher than the concentration that inhibited 50% of growth. We tested compound 22 against two other apicomplexan parasites, Plasmodium falciparum (EC50 of 0.6 ± 0.01 μM), the agent of malaria, and Cryptosporidium parvum (EC50 of ∼65 μM), the agent of cryptosporidiosis. Our results suggest that compound 22 is an excellent novel compound that could lead to the development of potent agents against apicomplexan parasites.
Keywords: Cryptosporidium parvum; Plasmodium falciparum; Toxoplasma gondii; bisphosphonates; farnesyl diphosphate synthase; isoprenoids.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Luft BJ, Hafner R, Korzun AH, Leport C, Antoniskis D, Bosler EM, Bourland DD III, Uttamchandani R, Fuhrer J, Jacobson J, ACTG 077p/ANRS 009 Study Team. 1993. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 329:995–1000. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309303291403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland GN. 2004. Ocular toxoplasmosis: a global reassessment. Part II: disease manifestations and management. Am J Ophthalmol 137:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

