Small cell lung cancer transformation and the T790M mutation: A case report of two acquired mechanisms of TKI resistance detected in a tumor rebiopsy and plasma sample of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 27895763
- PMCID: PMC5104225
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5193
Small cell lung cancer transformation and the T790M mutation: A case report of two acquired mechanisms of TKI resistance detected in a tumor rebiopsy and plasma sample of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
The present study describes the case of a 45-year-old man diagnosed with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma, which harbored a deletion within exon 19 of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene. The patient was subsequently treated with gefitinib (250 mg/day orally from May 2013 to March 2014), but developed acquired resistance to the drug following 11 months of treatment. Tumor burden molecular analysis was performed on a tumor rebiopsy and plasma sample, and histological analysis was also performed on the tumor rebiopsy. A small cell transformation retaining the original EGFR mutation was detected in the tumor rebiopsy, while the T790M mutation together with the activating ex19del mutation were identified only in the plasma sample. The patient was treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy (off-label schedule with epirubicin 80 mg/mq and paclitaxel 160 mg/mq every 21 days for 6 cycles) and radiation (50.4 Gy administered in 28 fractions of 1.8 Gy once daily for 5.5 weeks) specific for small cell lung cancer, and may also have benefitted from treatment with a third generation T790M-specific EGFR-TKI. To better describe the mechanisms of resistance to TKI inhibitors and to optimize therapeutic regimens, the simultaneous analysis of tumor biopsies and circulating tumor DNA should be considered.
Keywords: circulating free tumor DNA; epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation; epidermal growth factor receptor/tyrosine kinase inhibitor-acquired resistance; lung adenocarcinoma; small cell carcinoma transformation.
Figures
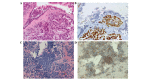
Similar articles
-
Picoliter-Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Analysis of Cell-Free Plasma DNA to Assess EGFR Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma That Confer Resistance to Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitors.Oncologist. 2016 Feb;21(2):156-64. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0288. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 26768482 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of Bronchoscopic Rebiopsy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Acquired Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor.J Cancer. 2018 Mar 2;9(6):1113-1120. doi: 10.7150/jca.21650. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29581791 Free PMC article.
-
The emergence of T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients having a history of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI: focus on rebiopsy timing and long-term existence of T790M.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48059-48069. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10351. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384480 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancers: an update for recent advances in therapeutics.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016 Jun;22(3):461-76. doi: 10.1177/1078155215577810. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016. PMID: 25855240 Review.
-
Optimal management of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with disease progression on first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy.Lung Cancer. 2017 Aug;110:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.05.009. Epub 2017 May 11. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28676222 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of liquid biopsy and pharmacogenomics for precision therapy of EGFR mutant and resistant lung cancers.Mol Cancer. 2022 Feb 24;21(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01534-8. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35209919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic changes of acquired T790M mutation and small cell lung cancer transformation in a patient with EGFR-mutant adenocarcinoma after first- and third-generation EGFR-TKIs: a case report.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(1):139-143. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2020.01.07. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32206560 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential occurrence of small cell and non-small lung cancer in a male patient: Is it a transformation?Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Dec 2;18(12):940-943. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1394546. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 29157085 Free PMC article.
-
mAb MDR1-modified chitosan nanoparticles overcome acquired EGFR-TKI resistance through two potential therapeutic targets modulation of MDR1 and autophagy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2017 Oct 4;15(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0302-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2017. PMID: 28978341 Free PMC article.
-
Histological transformation after acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Int J Clin Oncol. 2018 Apr;23(2):235-242. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1211-1. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29110101 Review.
References
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:2240–2247. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Jänne PA, Skokan M, Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Ligorio C, Zucali PA, Terracciano L, Toschi L, Toschi L, et al. MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:298–304. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn635. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takezawa K, Parazzoli V, Arcila ME, Nebhan CA, Song X, de Stanchina E, Ohashi K, Janjigian YY, Spitzler PJ, Melnick MA, et al. HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers that lack the second-site EGFR T790M mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:922–933. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
