Liposomal delivery systems for intestinal lymphatic drug transport
- PMID: 27895934
- PMCID: PMC5120490
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-016-0083-1
Liposomal delivery systems for intestinal lymphatic drug transport
Abstract
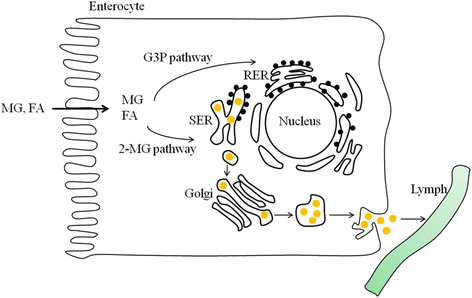
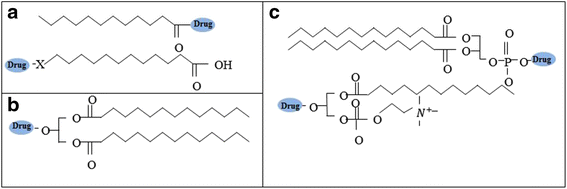
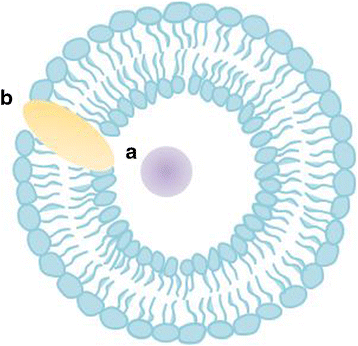
Intestinal lymphatic drug delivery has been widely studied because drugs can bypass the first-pass metabolism in the liver via the lymphatic route, which increases oral bioavailability. Various lipid-based nanoparticles have been used to deliver hydrophobic drugs to the lymphatic pathway. This review focuses on the liposomal delivery systems used for intestinal lymphatic drug transport. Liposomal formulations have attracted particular attention because they can stimulate the production of chylomicrons and the incorporated drugs readily associate with enterocyte-derived chylomicrons, enhancing lymphatic drug transport. We believe that a full understanding of their contribution to intestinal drug translocation will lead to effective oral delivery with liposomal formulations.
Keywords: Chylomicron; First-pass metabolism; Intestinal lymphatic transport; Lipid; Liposome.
Figures


References
-
- Charman WNA, Stella VJ. Estimating the maximum potential for intestinal lymphatic transport of lipophilic drug molecules. Int J Pharm. 1986;34:175–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(86)90027-X. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

