A novel approach for evaluating the performance of real time quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based methods
- PMID: 27896139
- PMCID: PMC5121211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bdq.2014.11.001
A novel approach for evaluating the performance of real time quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based methods
Abstract
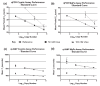
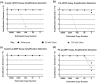
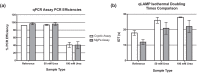
Molecular diagnostic measurements are currently underpinned by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). There are also a number of alternative nucleic acid amplification technologies, which unlike PCR, work at a single temperature. These 'isothermal' methods, reportedly offer potential advantages over PCR such as simplicity, speed and resistance to inhibitors and could also be used for quantitative molecular analysis. However there are currently limited mechanisms to evaluate their quantitative performance, which would assist assay development and study comparisons. This study uses a sexually transmitted infection diagnostic model in combination with an adapted metric termed isothermal doubling time (IDT), akin to PCR efficiency, to compare quantitative PCR and quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification (qLAMP) assays, and to quantify the impact of matrix interference. The performance metric described here facilitates the comparison of qLAMP assays that could assist assay development and validation activities.
Keywords: Cq, quantification cycle; Diagnostics; IDT, isothermal doubling time; Isothermal nucleic acid amplification; MIQE, minimum information for the publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments; NAA, nucleic acid amplification; Quantitative LAMP; Quantitative real time PCR; Standardisation; Tt, threshold time; qLAMP, quantitative loop-mediated amplification; qPCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; td, doubling time.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative study of sensitivity, linearity, and resistance to inhibition of digital and nondigital polymerase chain reaction and loop mediated isothermal amplification assays for quantification of human cytomegalovirus.Anal Chem. 2014 May 6;86(9):4387-94. doi: 10.1021/ac500208w. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24684191
-
Highly sensitive detection of gluten-containing cereals in food samples by real-time Loop-mediated isothermal AMPlification (qLAMP) and real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).Food Chem. 2018 Apr 25;246:156-163. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29291834
-
Comparison of fluorescent intercalating dyes for quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification (qLAMP).Biotechniques. 2016 Jul 1;61(1):20-5. doi: 10.2144/000114432. eCollection 2016. Biotechniques. 2016. PMID: 27401670
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA (LAMP): a new diagnostic tool lights the world of diagnosis of animal and human pathogens: a review.Pak J Biol Sci. 2014 Jan 15;17(2):151-66. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2014.151.166. Pak J Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24783797 Review.
-
Recent advances in molecular diagnostics of hepatitis B virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 28;20(40):14615-25. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14615. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25356025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Portable real-time colorimetric LAMP-device for rapid quantitative detection of nucleic acids in crude samples.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 8;12(1):3775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06632-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35260588 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Application of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assays for Rapid Diagnosis of the Bat White-Nose Disease Fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans.Mycopathologia. 2022 Dec;187(5-6):547-565. doi: 10.1007/s11046-022-00650-9. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Mycopathologia. 2022. PMID: 35931867 Free PMC article.
-
RT-LAMP: A Cheaper, Simpler and Faster Alternative for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater.Food Environ Virol. 2021 Dec;13(4):447-456. doi: 10.1007/s12560-021-09489-7. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Food Environ Virol. 2021. PMID: 34308531 Free PMC article.
-
Development of PCR, LAMP and qPCR Assays for the Detection of Aflatoxigenic Strains of Aspergillusflavus and A. parasiticus in Hazelnut.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 30;12(12):757. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120757. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33266343 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of Multiple DNA Dyes Based on Inhibition Effects on Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): Prospect for Point of Care Setting.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 15;10:2234. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02234. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31681184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. - PubMed
-
- Millar B.C., Xu J., Moore J.E. Molecular diagnostics of medically important bacterial infections. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2007;9(1):21–39. - PubMed
-
- Josko D. Molecular diagnostics in the public health laboratories. Clin Lab Sci. 2010;23(4):242–247. - PubMed
-
- Kim J., Easley C.J. Isothermal DNA amplification in bioanalysis: strategies and applications. Bioanalysis. 2011;3(2):227–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
