Effect Of α2-Adrenergic Agonists And Antagonists On Cytokine Release From Human Lung Macrophages Cultured In Vitro
- PMID: 27896229
- PMCID: PMC5120752
Effect Of α2-Adrenergic Agonists And Antagonists On Cytokine Release From Human Lung Macrophages Cultured In Vitro
Abstract
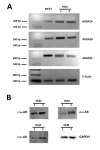
The most trusted hypothesis to explain how α2-adrenergic agonists may preserve pulmonary functions in critically ill patients is that they directly act on macrophages by interfering with an autocrine/paracrine adrenergic system that controls cytokine release through locally synthetized noradrenaline and α1- and α2-adrenoreceptors. We tested this hypothesis in primary cultures of resident macrophages from human lung (HLMs). HLMs were isolated by centrifugation on percoll gradients from macroscopically healthy human lung tissue obtained from four different patients at the time of lung resection for cancer. HLMs from these patients showed a significant expression of α2A, α2B and α2C adrenoreceptors both at the mRNA and at the protein level. To evaluate whether α2 adrenoreceptors controlled cytokine release from HMLs, we measured IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α concentrations in the culture medium in basal conditions and after preincubation with several α2-adrenergic agonists or antagonists. Neither the pretreatment with the α2-adrenergic agonists clonidine, medetomidine or dexdemetomidine or with the α2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine caused significant changes in the response of any of these cytokines to LPS. These results show that, different from what reported in rodents, clonidine and dexdemetomidine do not directly suppress cytokine release from human pulmonary macrophages. This suggests that alternative mechanisms such as effects on immune cells activation or the modulation of autonomic neurotransmission could be responsible for the beneficial effects of these drugs on lung function in critical patients.
Keywords: clonidine; cytokines; dexmedetomidine; macrophages; medetomidine; yohimbine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study of presynaptic alpha2-autoreceptors in alpha2A/D-, alpha2B- and alpha2C-adrenoceptor-deficient mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;364(2):117-30. doi: 10.1007/s002100100423. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11534851
-
Effects of imidazoline and nonimidazoline α-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists, including xylazine, medetomidine, dexmedetomidine, yohimbine, and atipamezole, on aggregation of feline platelets.Am J Vet Res. 2020 Feb;81(2):159-171. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.81.2.159. Am J Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 31985287
-
The anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of alpha2-adrenoreceptor agonists are mediated by distinct populations of alpha2A-adrenoreceptors.Neuroscience. 2004;126(3):795-803. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.04.030. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15183527
-
Application of α2 -adrenergic agonists combined with anesthetics and their implication in pulmonary intravascular macrophages-insulted pulmonary edema and hypoxemia in ruminants.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul;44(4):478-502. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12960. Epub 2021 Mar 12. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33709435 Review.
-
Alpha2-Adrenergic Agonists for the Reduction or Discontinuation of Opioids or Opioid Substitution Therapy: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018 Feb 23. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018 Feb 23. PMID: 30379508 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of dexmedetomidine on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial killing and phagocytosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110327. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110327. Epub 2023 May 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37201408 Free PMC article.
-
The immunomodulatory mechanism of dexmedetomidine.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Aug;97:107709. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107709. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33933842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity: a neuroimmunometabolic perspective.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Jan;16(1):30-43. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0283-6. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31776456 Review.
-
Narrative review of systemic inflammatory response mechanisms in cardiac surgery and immunomodulatory role of anesthetic agents.Ann Card Anaesth. 2023 Apr-Jun;26(2):133-142. doi: 10.4103/aca.aca_147_22. Ann Card Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 37706376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cAMP metabolism controls caspase-11 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in sepsis.Sci Adv. 2019 May 22;5(5):eaav5562. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav5562. eCollection 2019 May. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31131320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Practice of Anaesthesia. London, United Kingdom: Elsevier Health Sciences; 1997.
-
- Conti G, Ranieri VM, Costa R, Garratt C, Wighton A, Spinazzola G, Urbino R, Mascia L, Ferrone G, Pohjanjousi P, Ferreyra G, Antonelli M. Effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol on patient-ventilator interaction in difficult-to-wean, mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective, open-label, randomised, multicentre study. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):206. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
