Uterine rupture in pregnancies following myomectomy: A multicenter case series
- PMID: 27896247
- PMCID: PMC5120064
- DOI: 10.5468/ogs.2016.59.6.454
Uterine rupture in pregnancies following myomectomy: A multicenter case series
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this case series was to retrospectively examine records of cases with uterine rupture in pregnancies following myomectomy and to describe the clinical features and pregnancy outcomes.
Methods: This study was conducted as a multicenter case series. The patient databases at 7 tertiary hospitals were queried. Records of patients with a diagnosis of uterine rupture in the pregnancy following myomectomy between January 2012 and December 2014 were retrospectively collected. The uterine rupture cases enrolled in this study were defined as follows: through-and-through uterine rupture or tear of the uterine muscle and serosa, occurrence from 24+0 to 41+6 weeks' gestation, singleton pregnancy, and previous laparoscopic myomectomy (LSM) or laparotomic myomectomy (LTM) status.
Results: Fourteen pregnant women experienced uterine rupture during their pregnancy after LSM or LTM. Preterm delivery of less than 34 weeks' gestation occurred in 5 cases, while intrauterine fetal death occurred in 3, and 3 cases had fetal distress. Of the 14 uterine rupture cases, none occurred during labor. All mothers survived and had no sequelae, unlike the perinatal outcomes, although they were receiving blood transfusion or treatment for uterine artery embolization because of uterine atony or massive hemorrhage.
Conclusion: In women of childbearing age who are scheduled to undergo LTM or LSM, the potential risk of uterine rupture on subsequent pregnancy should be explained before surgery. Pregnancy in women after myomectomy should be carefully observed, and they should be adequately counseled during this period.
Keywords: Myomectomy; Pregnancy outcome; Uterine rupture.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
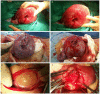
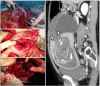
References
-
- Buttram VC, Jr, Reiter RC. Uterine leiomyomata: etiology, symptomatology, and management. Fertil Steril. 1981;36:433–445. - PubMed
-
- Carlson KJ, Miller BA, Fowler FJ., Jr The maine women’s health study: I. outcomes of hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:556–565. - PubMed
-
- Eldar-Geva T, Meagher S, Healy DL, MacLachlan V, Breheny S, Wood C. Effect of intramural, subserosal, and submucosal uterine fibroids on the outcome of assisted reproductive technology treatment. Fertil Steril. 1998;70:687–691. - PubMed
-
- Brady PC, Stanic AK, Styer AK. Uterine fibroids and subfertility: an update on the role of myomectomy. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;25:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Parazzini F, Tozzi L, Bianchi S. Pregnancy outcome and uterine fibroids. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;34:74–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

