Antiviral activity of hemolymph of Podalia against rubella virus
- PMID: 27896559
- PMCID: PMC5264621
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-016-0035-6
Antiviral activity of hemolymph of Podalia against rubella virus
Abstract
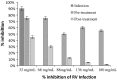
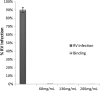
Many active principles produced by animals, plants and microorganisms have been employed in the development of new drugs for the treatment of human diseases. Among animals known to produce pharmacologically active molecules that interfere in human cell physiology. Rubella virus (genus Rubivirus, family Togaviridae) is a single stranded RNA virus of positive genome polarity. Rubella virus infection of susceptible women during the first trimester of pregnancy often results in long-term virus persistence in the fetus causing multiple organ abnormalities. Potent antiviral activity against rubella virus (RV) has been observed in the hemolymph of Podalia sp. (Lepidoptera: Megalopygidae). This study evaluated the effect of hemolymph on RV infected Statens Serum Institute Rabbit Cornea (SIRC) cells. Results of cell viability and cell proliferation assays indicated that hemolymph was not toxic to cultured SIRC cells. Viral binding assay, antiviral assay, PCR, real-time PCR, and transmission electron microscopy were used to demonstrate that hemolymph in post-treatment could inhibit the production of infectious RV particles. Specifically, hemolymph was found to inhibit RV adsorption to the SIRC cells.
Keywords: Antiviral; Congenital Rubella Syndrome; Hemolymph; Rubella virus.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[The life cycle of Rubella Virus].Uirusu. 2014;64(2):137-46. doi: 10.2222/jsv.64.137. Uirusu. 2014. PMID: 26437836 Review. Japanese.
-
A study of rubella virus infection during pregnancy.Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2002 Jul;37(7):391-4. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12411033
-
[Rubella (German measles)--still a major infectious disease].Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2012 Jan;35(1):14-22; quiz 23-4. Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22332308 Review. German.
-
Molecular analysis of rubella virus in travelers suspected of measles infection in São Paulo, Brazil.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2012 Sep-Oct;58(5):527-31. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2012. PMID: 23090221
-
Isolation of infectious Zika virus from a urine sample cultured in SIRC cells from a patient suspected of having rubella virus.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2018;60:e15. doi: 10.1590/s1678-9946201860015. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2018. PMID: 29557985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abernathy E, Cabezas C, Sun H, Jin L, Brown D, Komase K, Mori Y, Xu W, Zhu Z. Confirmation of rubella within 4 days of rash onset: comparison of rubella virus RNA detection in oral fluid with immunoglobulin M detection in serum or oral fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:182–188. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01231-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carmo AC, Yamasaki LH, Figueiredo CA, da Silva Giovanni DN, de Oliveira MI, Dos Santos FC, Curti SP, Rahal P, Mendonça RZ. Discovery of a new antiviral protein isolated Lonomia obliqua analysed by bioinformatics and real-time approaches. Cytotechnology. 2015;67:1011–1022. doi: 10.1007/s10616-014-9740-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

