FDG PET-CT imaging of therapeutic response in granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
- PMID: 27896807
- PMCID: PMC5167039
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12856
FDG PET-CT imaging of therapeutic response in granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
Abstract
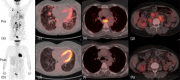
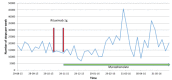
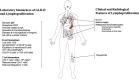
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is the most common severe adult primary immunodeficiency and is characterized by a failure to produce antibodies leading to recurrent predominantly sinopulmonary infections. Improvements in the prevention and treatment of infection with immunoglobulin replacement and antibiotics have resulted in malignancy, autoimmune, inflammatory and lymphoproliferative disorders emerging as major clinical challenges in the management of patients who have CVID. In a proportion of CVID patients, inflammation manifests as granulomas that frequently involve the lungs, lymph nodes, spleen and liver and may affect almost any organ. Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) is associated with a worse outcome. Its underlying pathogenic mechanisms are poorly understood and there is limited evidence to inform how best to monitor, treat or select patients to treat. We describe the use of combined 2-[(18)F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography (FDG PET-CT) scanning for the assessment and monitoring of response to treatment in a patient with GLILD. This enabled a synergistic combination of functional and anatomical imaging in GLILD and demonstrated a widespread and high level of metabolic activity in the lungs and lymph nodes. Following treatment with rituximab and mycophenolate there was almost complete resolution of the previously identified high metabolic activity alongside significant normalization in lymph node size and lung architecture. The results support the view that GLILD represents one facet of a multi-systemic metabolically highly active lymphoproliferative disorder and suggests potential utility of this imaging modality in this subset of patients with CVID.
Keywords: common variable immunodeficiency; fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography; granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease; rituximab.
© 2016 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Granulomatous-Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease in Common Variable Immunodeficiency-Features of CT and 18F-FDG Positron Emission Tomography/CT in Clinically Progressive Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 26;11:617985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617985. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33584710 Free PMC article.
-
Granulomatous-Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease in a Patient With Common Variable Immunodeficiency.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2018 Jul-Aug;47(4):282-284. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28583689
-
Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease as the first manifestation of common variable immunodeficiency.Clin Respir J. 2018 Jan;12(1):337-343. doi: 10.1111/crj.12511. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 27243233
-
Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).Clin Immunol. 2010 Feb;134(2):97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.10.002. Epub 2009 Nov 8. Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19900842 Review.
-
Sarcoidosis and common variable immunodeficiency: similarities and differences.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun;35(3):330-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1376862. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25007085 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosuppressive therapy with rituximab in common variable immunodeficiency.Clin Mol Allergy. 2019 May 6;17:9. doi: 10.1186/s12948-019-0113-3. eCollection 2019. Clin Mol Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31080365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When to initiate immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IGRT) in antibody deficiency: a practical approach.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Jun;188(3):333-341. doi: 10.1111/cei.12915. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28000208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoidosis versus Granulomatous and Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease in Common Variable Immunodeficiency: A Comparative Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 6;12(7):1503. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071503. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic testing for interstitial lung disease in common variable immunodeficiency: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2023 May 8;14:1190235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190235. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37223103 Free PMC article.
-
The biological basis for current treatment strategies for granulomatous disease in common variable immunodeficiency.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Dec 1;24(6):479-487. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000001032. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39431514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jolles S. The variable in common variable immunodeficiency: a disease of complex phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2013; 1:545–56. - PubMed
-
- Chapel H, Lucas M, Lee M et al Common variable immunodeficiency disorders: division into distinct clinical phenotypes. Blood 2008; 112:277–86. - PubMed
-
- Prasse A, Kayser G, Warnatz K. Common variable immunodeficiency‐associated granulomatous and interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2013; 19:503–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

