EZH1 and EZH2 promote skeletal growth by repressing inhibitors of chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy
- PMID: 27897169
- PMCID: PMC5477487
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13685
EZH1 and EZH2 promote skeletal growth by repressing inhibitors of chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy
Abstract
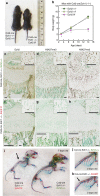
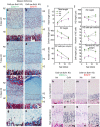
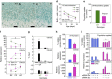
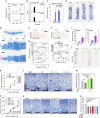
Histone methyltransferases EZH1 and EZH2 catalyse the trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27), which serves as an epigenetic signal for chromatin condensation and transcriptional repression. Genome-wide associated studies have implicated EZH2 in the control of height and mutations in EZH2 cause Weaver syndrome, which includes skeletal overgrowth. Here we show that the combined loss of Ezh1 and Ezh2 in chondrocytes severely impairs skeletal growth in mice. Both of the principal processes underlying growth plate chondrogenesis, chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy, are compromised. The decrease in chondrocyte proliferation is due in part to derepression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors Ink4a/b, while ineffective chondrocyte hypertrophy is due to the suppression of IGF signalling by the increased expression of IGF-binding proteins. Collectively, our findings reveal a critical role for H3K27 methylation in the regulation of chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy in the growth plate, which are the central determinants of skeletal growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 depletion induces cellular senescence via histone demethylation along the INK4/ARF locus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Aug;65:104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.05.011. Epub 2015 May 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26004298
-
EZH1 and EZH2 cogovern histone H3K27 trimethylation and are essential for hair follicle homeostasis and wound repair.Genes Dev. 2011 Mar 1;25(5):485-98. doi: 10.1101/gad.2019811. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21317239 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Proteins EZH1 and EZH2 Regulate Timing of Postnatal Hepatocyte Maturation and Fibrosis by Repressing Genes With Euchromatic Promoters in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2019 May;156(6):1834-1848. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.041. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30689973 Free PMC article.
-
The polycomb proteins EZH1 and EZH2 co-regulate chromatin accessibility and nephron progenitor cell lifespan in mice.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 14;295(33):11542-11558. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013348. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32554463 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrations of EZH2 in cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 May 1;17(9):2613-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2156. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21367748 Review.
Cited by
-
A critical bioenergetic switch is regulated by IGF2 during murine cartilage development.Commun Biol. 2022 Nov 11;5(1):1230. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04156-4. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36369360 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Modifications and Chondrocyte Fate: Regulation and Therapeutic Implications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 16;9:626708. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.626708. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33937229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH1 Is Associated with TCP-Induced Bone Regeneration through Macrophage Polarization.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Aug 30;2018:6310560. doi: 10.1155/2018/6310560. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30228822 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide CRISPR screening of chondrocyte maturation newly implicates genes in skeletal growth and height-associated GWAS loci.Cell Genom. 2023 Apr 14;3(5):100299. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100299. eCollection 2023 May 10. Cell Genom. 2023. PMID: 37228756 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Heart Diseases.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 30;26(7):38696. doi: 10.31083/RCM38696. eCollection 2025 Jul. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40776938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kurotaki N. et al.. Haploinsufficiency of NSD1 causes Sotos syndrome. Nat. Genet. 30, 365–366 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Luscan A. et al.. Mutations in SETD2 cause a novel overgrowth condition. J. Med. Genet. 51, 512–517 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Cao R. et al.. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298, 1039–1043 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

