Comparable Effectiveness of First Week Treatment with Anti-Staphylococcal Penicillin versus Cephalosporin in Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: A Propensity-Score Adjusted Retrospective Study
- PMID: 27898714
- PMCID: PMC5127580
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167112
Comparable Effectiveness of First Week Treatment with Anti-Staphylococcal Penicillin versus Cephalosporin in Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: A Propensity-Score Adjusted Retrospective Study
Abstract
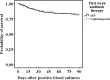
The objective was to compare the prognostic impact of first week treatment with anti-staphylococcal penicillin (ASP) versus cephalosporin in methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (MS-SAB). Altogether 580 patients were retrospectively followed and categorized according to first week treatment; 84% (488) received ASP (cloxacillin) and 16% (92) cephalosporin (cefuroxime or ceftriaxone). SAB management was optimized with formal bedside infectious disease specialist consultation in 88%, deep infection foci diagnosed in 77% and adjunctive rifampicin therapy given to 61% of patients. The total case fatality in 580 patients was 12% at 28 days and 18% at 90 days. When comparing effectiveness of first week ASP versus cephalosporin treatment there were no significant differences in 28-days (11% vs. 12%, OR; 1.05, 95% CI, 0.53-2.09) or 90-days (17% vs. 21% OR; 1.25, 95% CI, 0.72-2.19) outcome. In univariate analysis no prognostic impact of either first week ASP or cephalosporin treatment was observed for 28-days (OR; 0.96, 95% CI, 0.48-1.90 and OR; 1.05, 95% CI, 0.53-2.09) or 90-days (OR; 0.80, 95% CI, 0.46-1.39 and OR; 1.25, 95% CI, 0.72-2.19) outcome. Propensity-score adjusted Cox proportional regression analysis for first week treatment with cephalosporin demonstrated no significant prognostic impact at 28-days (HR 1.54, 95% CI 0.72-3.23) or 90-days (HR 1.56, 95% CI 0.88-2.86).
In conclusion: There is a comparable effectiveness with respect to 28- and 90-days outcome for first week treatment with ASP versus cephalosporin in MS-SAB. The results indicate that the difference in prognostic impact between first week ASP and cephalosporin may be non-significant in patient cohorts with SAB management optimized by infectious disease specialist consultation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of patient characteristics, clinical management, infectious specialist consultation, and outcome in men and women with methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a propensity-score adjusted retrospective study.Infection. 2018 Dec;46(6):837-845. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-1216-3. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Infection. 2018. PMID: 30194636
-
Relative efficacy of cefuroxime versus dicloxacillin as definitive antimicrobial therapy in methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a propensity-score adjusted retrospective cohort study.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Feb;69(2):506-14. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt375. Epub 2013 Sep 26. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24078468
-
Effectiveness of penicillin, dicloxacillin and cefuroxime for penicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a retrospective, propensity-score-adjusted case-control and cohort analysis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Aug;68(8):1894-900. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt108. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23599360
-
Meta-analysis of trials comparing cefazolin to antistaphylococcal penicillins in the treatment of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;84(6):1258-1266. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13554. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29600576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cefazolin versus anti-staphylococcal penicillins for the treatment of patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Jul;25(7):818-827. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.03.010. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 30928559
Cited by
-
The Cefazolin Inoculum Effect Is Associated With Increased Mortality in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018 May 23;5(6):ofy123. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy123. eCollection 2018 Jun 1. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29977970 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ceftaroline against Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Exhibiting the Cefazolin High-Inoculum Effect in a Rat Model of Endocarditis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jun 27;61(7):e00324-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00324-17. Print 2017 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28483961 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Exclusive Exposure to Nafcillin or Oxacillin, Cefazolin, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, and Fluoroquinolones Among a National Cohort of Veterans With Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 6;6(7):ofz270. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofz270. eCollection 2019 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31281864 Free PMC article.
-
Comparable Effectiveness of Cefuroxime and Piperacillin-Tazobactam as Empirical Therapy for Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0153021. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01530-21. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35438533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forsblom E, Ruotsalainen E, Mölkänen T, Ollgren J, Lyytikäinen O, Järvinen A. Predisposing factors, disease progression and outcome in 430 prospectively followed patients of healthcare- and communityassociated Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J Hosp Infect 2011; 78:102–07. 10.1016/j.jhin.2011.03.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

