Biological Markers for Pulpal Inflammation: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 27898727
- PMCID: PMC5127562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167289
Biological Markers for Pulpal Inflammation: A Systematic Review
Abstract
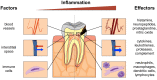
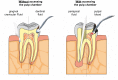
Background and objective: Pulpitis is mainly caused by an opportunistic infection of the pulp space with commensal oral microorganisms. Depending on the state of inflammation, different treatment regimes are currently advocated. Predictable vital pulp therapy depends on accurate determination of the pulpal status that will allow repair to occur. The role of several players of the host response in pulpitis is well documented: cytokines, proteases, inflammatory mediators, growth factors, antimicrobial peptides and others contribute to pulpal defense mechanisms; these factors may serve as biomarkers that indicate the status of the pulp. Therefore, the aim of this systematic review was to evaluate the presence of biomarkers in pulpitis.
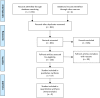
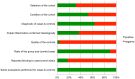
Methods: The electronic databases of MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus and other sources were searched for English and non-English articles published through February 2015. Two independent reviewers extracted information regarding study design, tissue or analyte used, outcome measures, results and conclusions for each article. The quality of the included studies was assessed using a modification of the Newcastle-Ottawa-Scale.
Results and conclusions: From the initial 847 publications evaluated, a total of 57 articles were included in this review. In general, irreversible pulpitis was associated with different expression of various biomarkers compared to normal controls. These biomarkers were significantly expressed not only in pulp tissue, but also in gingival crevicular fluid that can be collected non-invasively, and in dentin fluid that can be analyzed without extirpating the entire pulpal tissue. Such data may then be used to accurately differentiate diseased from healthy pulp tissue. The interplay of pulpal biomarkers and their potential use for a more accurate and biologically based diagnostic tool in endodontics is envisaged.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Effectiveness of diagnosing pulpitis: A systematic review.Int Endod J. 2023 Oct;56 Suppl 3:296-325. doi: 10.1111/iej.13762. Epub 2022 May 25. Int Endod J. 2023. PMID: 35536159
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Histology-based profile of inflammatory mediators in experimentally induced pulpitis in a rat model: screening for possible biomarkers.Int Endod J. 2021 Aug;54(8):1328-1341. doi: 10.1111/iej.13514. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Int Endod J. 2021. PMID: 33715185 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Pulp Repair after BiodentineTM Full Pulpotomy in a Rat Molar Model of Pulpitis.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 6;9(7):784. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070784. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356848 Free PMC article.
-
Biodentine but not MTA induce DSPP expression of dental pulp cells with different severity of LPS-induced inflammation.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Mar;27(3):1207-1214. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04734-0. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 36208328
-
ARMCX3 regulates ROS signaling, affects neural differentiation and inflammatory microenvironment in dental pulp stem cells.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 28;10(17):e37079. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37079. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296219 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Inflammatory and Homeostasis Biomarkers after Selective Removal of Carious Dentin-An In Vivo Feasibility Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 2;10(5):1003. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051003. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33801317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith AJ. Pulpal responses to caries and dental repair. Caries Res. 2002;36: 223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

