Bibliometric analysis of publications on Campylobacter: (2000-2015)
- PMID: 27899145
- PMCID: PMC5129233
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-016-0076-7
Bibliometric analysis of publications on Campylobacter: (2000-2015)
Abstract
Background: Campylobacter species are widespread zoonotic pathogens. Campylobacter jejuni causes a form of gastroenteritis called campylobacteriosis. Campylobacter drug resistance is considered a serious threat. In order to better understand national and international research output on Campylobacter, we conducted this bibliometric overview of publications on Campylobacter. This study can be used to assess extent of interaction and response of researchers, food regulators, and health policy makers to global burden of campylobacateriosis.
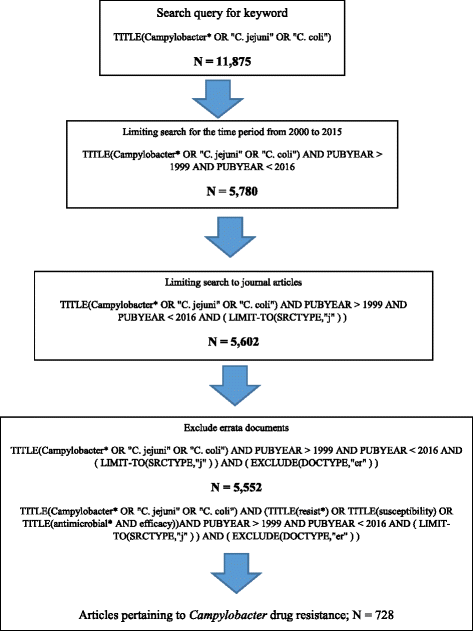
Methods: Scopus database was used to retrieve publications with the following keywords (Campylobacter/campylobacteriosis, C. jejuni, C. coli). The study period was set from 2000 to 2015. All types of journal documents, excluding errata, were considered. Bibliometric indicators such as annual growth of publications, country contribution, international collaboration, and citation analysis were presented. The quality of retrieved data was indirectly assessed by Hirsch index and impact factor of journals.
Results: A total of 5522 documents were retrieved with median (Q1-Q3) citations of 9 (2-23) and h-index of 113. Annual number of publications showed a fluctuating increase. The core leading journals were Applied and Environmental Microbiology journal and Journal of Food Protection with 246 (4.46%) publications for each. The USA (1309; 23.6%) was the most productive country while Danmarks Tekniske Universitet (150; 2.7%) was the most productive institution. Half of the top ten productive countries were European. France had the lowest percentage (33.5%) of articles with international collaboration while Netherlands (57.7%) had the highest percentage of articles with international collaboration. Approximately half (50.1%) of retrieved articles were published in journals under the subject area of "immunology/microbiology". Main themes in highly cited articles were molecular biology/genetics and public health burden of campylobacteriosis. There were 728 (13.1%) articles on campylobacter-related drug resistance, and the top cited articles focused mainly on increasing resistance to quinolones and fluoroquinolones.
Conclusions: There was a clear increase in number of publications on Campylobacter. Rational use of antimicrobials in humans, poultry, and animals is highly recommended. International collaboration is highly required particularly in implementing new diagnostic screening technologies to minimize global health burden of Campylobacter and ensure food safety.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Campylobacter.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bibliometric analysis of literature on female genital mutilation: (1930 - 2015).Reprod Health. 2016 Oct 10;13(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12978-016-0243-8. Reprod Health. 2016. PMID: 27724920 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global scientific research on carbapenem resistance (1986-2015).Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016 Sep 23;15(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12941-016-0169-6. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016. PMID: 27663999 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of literature on malaria vector resistance: (1996 - 2015).Global Health. 2016 Nov 25;12(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12992-016-0214-4. Global Health. 2016. PMID: 27884199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of literature on toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: 1940 - 2015.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 Jan 18;12(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0566-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28100272 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing and midwifery research activity in Arab countries from 1950 to 2017.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 May 28;19(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4178-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 31138250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric analysis of global migration health research in peer-reviewed literature (2000-2016).BMC Public Health. 2018 Jun 20;18(1):777. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5689-x. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29925353 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Worldwide Publications on Antimalarial Drug Resistance (2006-2015).Malar Res Treat. 2017;2017:6429410. doi: 10.1155/2017/6429410. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Malar Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28856028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global toxocariasis research trends from 1932 to 2015: a bibliometric analysis.Health Res Policy Syst. 2017 Feb 23;15(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12961-017-0178-8. Health Res Policy Syst. 2017. PMID: 28231792 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis of Mindfulness and Meditation Research from 1900 to 2021.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 13;18(24):13150. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413150. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34948760 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of medicine - related publications on refugees, asylum-seekers, and internally displaced people: 2000 - 2015.BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2017 Mar 20;17(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12914-017-0116-4. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2017. PMID: 28320410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarkar SR, Hossain MA, Paul SK, Ray NC, Sultana S, Rahman MM, et al. Campylobacteriosis—an overview. Mymensingh Med J. 2014;23(1):173–180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical