Widespread and dynamic translational control of red blood cell development
- PMID: 27899360
- PMCID: PMC5290990
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-741835
Widespread and dynamic translational control of red blood cell development
Abstract
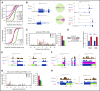
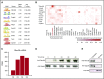
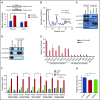
Cell development requires tight yet dynamic control of protein production. Here, we use parallel RNA and ribosome profiling to study translational regulatory dynamics during murine terminal erythropoiesis. Our results uncover pervasive translational control of protein synthesis, with widespread alternative translation initiation and termination, robust discrimination of long noncoding from micropeptide-encoding RNAs, and dynamic use of upstream open reading frames. Further, we identify hundreds of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) whose translation efficiency is dynamically controlled during erythropoiesis and that enrich for target sites of RNA-binding proteins that are specific to hematopoietic cells, thus unraveling potential regulators of erythroid translational programs. A major such program involves enhanced decoding of specific mRNAs that are depleted in terminally differentiating/enucleating cells with decreasing transcriptional capacity. We find that RBM38, an erythroid-specific RNA-binding protein previously implicated in splicing, interacts with the general translation initiation factor eIF4G and promotes translation of a subset of these irreplaceable mRNAs. Inhibition of RBM38 compromises translation in erythroblasts and impairs their maturation, highlighting a key function for this protein during erythropoiesis. These findings thus reveal critical roles for dynamic translational control in supporting specialized mammalian cell formation.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Decoding erythropoiesis.Blood. 2017 Feb 2;129(5):544-545. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-755538. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28153837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kong J, Lasko P. Translational control in cellular and developmental processes. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(6):383-394. - PubMed
-
- Baranov PV, Atkins JF, Yordanova MM. Augmented genetic decoding: global, local and temporal alterations of decoding processes and codon meaning. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16(9):517-529. - PubMed
-
- Namy O, Rousset JP, Napthine S, Brierley I. Reprogrammed genetic decoding in cellular gene expression. Mol Cell. 2004;13(2):157-168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

