Age-Dependent Hepatic UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Gene Expression and Activity in Children
- PMID: 27899892
- PMCID: PMC5110524
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00437
Age-Dependent Hepatic UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Gene Expression and Activity in Children
Abstract
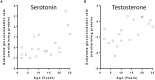
UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) are important phase II drug metabolism enzymes. The aim of this study was to explore the relationship between age and changes in mRNA expression and activity of major human hepatic UGTs, as well as to understand the potential regulatory mechanism underlying this relationship. Using previously generated data, we investigated age-dependent mRNA expression levels of 11 hepatic UGTs (UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A5, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B4, UGT2B7, UGT2B10, UGT2B15, and UGT2B17) and 16 transcription factors (AHR, AR, CAR, ESR2, FXR, GCCR, HNF1a, HNF3a, HNF3b, HNF4a, PPARA, PPARG, PPARGC, PXR, SP1, and STAT3) in liver tissue of donors (n = 38) ranging from 0 to 25 years of age. We also examined the correlation between age and microsomal activities using 14 known UGT drug substrates in the liver samples (n = 19) of children donors. We found a statistically significant increase (nominal p < 0.05) in the expression of UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A5, UGT1A6, UGT2B7, and UGT2B17, as well as glucuronidation activities of serotonin, testosterone, and vorinostat during the first 25 years of life. Expression of estrogen receptor 1 and pregnane X receptor, two strong UGT transcriptional regulators, were significantly correlated with both age and UGT mRNA expression (p ≤ 0.05). These results suggest that both UGT expression and activity increase during childhood and adolescence, possibly driven in part by hormonal signaling. Our findings may help explain inter-patient variability in response to medications among children.
Keywords: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase; age; children; liver; ontogeny.
Figures

References
-
- Burchell B., Coughtrie M., Jackson M., Harding D., Fournel-Gigleux S., Leakey J., et al. (1989). Development of human liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Dev. Pharmacol. Ther. 13 70–77. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

