Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27899995
- PMCID: PMC5103943
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5039
Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
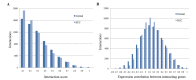
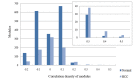
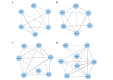
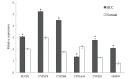
The objective of the present study is to identify significant genes and pathways associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by systematically tracking the dysregulated modules of re-weighted protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. Firstly, normal and HCC PPI networks were inferred and re-weighted based on Pearson correlation coefficient. Next, modules in the PPI networks were explored by a clique-merging algorithm, and disrupted modules were identified utilizing a maximum weight bipartite matching in non-increasing order. Then, the gene compositions of the disrupted modules were studied and compared with differentially expressed (DE) genes, and pathway enrichment analysis for these genes was performed based on Expression Analysis Systematic Explorer. Finally, validations of significant genes in HCC were conducted using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis. The present study evaluated 394 disrupted module pairs, which comprised 236 dysregulated genes. When the dysregulated genes were compared with 211 DE genes, a total of 26 common genes [including phospholipase C beta 1, cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 and CYP2B6] were obtained. Furthermore, 6 of these 26 common genes were validated by RT-qPCR. Pathway enrichment analysis of dysregulated genes demonstrated that neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, purine and drug metabolism, and metabolism of xenobiotics mediated by CYP were significantly disrupted pathways. In conclusion, the present study greatly improved the understanding of HCC in a systematic manner and provided potential biomarkers for early detection and novel therapeutic methods.
Keywords: dysregulated gene; hepatocellular carcinoma; modules; pathway; protein-protein interaction network; reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
References
-
- Kaseb AO, Xiao L, Hassan MM, Chae YK, Lee JS, Vauthey JN, Krishnan S, Cheung S, Hassabo HM, Aloia T, et al. Development and validation of a scoring system using insulin-like growth factor to assess hepatic reserve in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106 doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju088. pii: dju088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Kokudo N, Matsuyama Y, Izumi N, Ichida T, Kudo M, Ku Y, Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, Matsui O, et al. Prognostic impact of spontaneous tumor rupture in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of 1160 cases from a nationwide survey. Ann Surg. 2014;259:532–542. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828846de. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
