Xiphoidectomy: A Surgical Intervention for an Underdocumented Disorder
- PMID: 27900228
- PMCID: PMC5120187
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9306262
Xiphoidectomy: A Surgical Intervention for an Underdocumented Disorder
Abstract
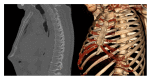
Two patients who presented with nonspecific thoracic and upper abdominal symptoms and tenderness of the xiphoid process are discussed. Both patients had undergone extensive examinations, but no source for their symptoms could be found. Plain chest radiographs revealed an anterior displacement of the xiphoid process in both patients. Physical examination confirmed this to be the primary source of discomfort. Anterior displacement of the xiphoid process may be the result of significant weight gain. Repeated trauma of the afflicted area, unaccustomed heavy lifting, exercise, and perichondritis are, amongst other causes, believed to contribute to the development of xiphodynia. Both patients were treated by performing a xiphoidectomy, resulting in disappearance of the symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources