Migrating fish bone piercing the common carotid artery, thyroid gland and causing deep neck abscess
- PMID: 27900327
- PMCID: PMC5112358
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i11.375
Migrating fish bone piercing the common carotid artery, thyroid gland and causing deep neck abscess
Abstract
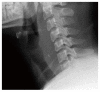
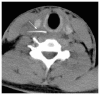
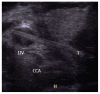
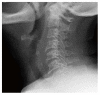
Foreign body (FB) ingestion is very common in Malaysian population. The most commonly ingested FB is fish bone. Common presenting symptoms include FB sensation, odynophagia and or sharp pricking pain during swallowing. A careful history and physical examination is very important. Despite negative laryngoscopy and rigid esophagoscopy, persistent symptoms warrants further radiographic imaging studies. The FB can migrate extraluminally and involve other important adjacent structures of the neck and along the digestive tract. We report 3 cases of extraluminal migration of fish bone and their complications, which were successfully managed. One case with vascular complication which involve common carotid artery and the other two cases with neck abscess formation involving thyroid gland, retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess.
Keywords: Abscess; Carotid artery; Complication; Foreign body; Migrating; Thyroid gland.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no conflict of interest in this case study.
Figures
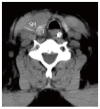

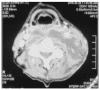
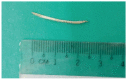
References
-
- Jha SK, Kumar SP, Somu L, Ravikumar A. Missing fish bone: case report and literature review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012;33:623–626. - PubMed
-
- Thomas AM, Nadeem B, Badaridatta HC. Migrated foreign body neck. J Case Rep Med. 2012;1:1–3.
-
- Yang SW, Chen TM, Chen TA. Migrating fish bone complicating a deep neck abscess. Chang Gung Med J. 2005;28:872–875. - PubMed
-
- Chee LW, Sethi DS. Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to migrating foreign bodies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999;108:177–180. - PubMed
-
- Shanmugam R, Shanmugam VU, Mariappan R, Swaminathan B, Nandipati S, Ghosh P, Ramya CV. Migrating foreign body in the neck penetrating the neck muscle. Sch J Med Case Rep. 2015;3:393–395.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

