Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer cell growth through a miR-7-RASSF2-PAR-4 axis in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 27901488
- PMCID: PMC5352055
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13609
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer cell growth through a miR-7-RASSF2-PAR-4 axis in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
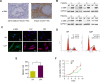
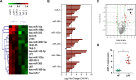
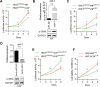
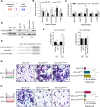
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), a major component of cancer stroma, play an important role in cancer progression but little is known about how CAFs affect tumorigenesis and development. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that can negatively regulate target mRNA expression at post-transcriptional levels. In head and neck cancer (HNC), our analysis of miRNA arrays showed that miR-7, miR-196 and miR-335 were significantly up-regulated in CAFs when compared with their paired normal fibroblasts (NFs). FAP, α-SMA and FSP, specific markers of CAFs, were significantly expressed in CAFs. Functionally, exogenous expression of miR-7 in NFs induced a functional conversion of NFs into CAFs. In contrast, inhibition of miR-7 expression in CAFs could induce a functional conversion of CAFs into NFs. Our study demonstrated that overexpression of miR-7 in NFs significantly increased the migration activity and growth rates of cancer cells in co-culture experiments. Mechanistically, we confirmed that the RASSF2-PAR-4 axis was mainly responsible for miR-7 functions in CAFs using bioinformatics methods. Overexpression of miR-7 in CAFs led to down-regulation of RASSF2, which dramatically decreased the secretion of PAR-4 from CAFs and then enhanced the proliferation and migration of the co-cultured cancer cells. Thus, these results reveal that the inactivation of the RASSF2-PAR-4 axis controlled by miR-7 may be a novel strategy for gene therapy in HNCs.
Keywords: RASSF2; cancer microenvironment; cancer-associated fibroblasts; head and neck cancer; miR-7.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deregulated MicroRNAs in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Front Tumor Tissues of Lung Adenocarcinoma as Potential Predictors of Tumor Promotion.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018 Oct;246(2):107-120. doi: 10.1620/tjem.246.107. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 30369556
-
Downregulation of miRNA-214 in cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through targeting FGF9 and inducing EMT.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 15;38(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0995-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30646925 Free PMC article.
-
[Dectection and analysis of miRNA expression in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;30(10):1071-5. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25270211 Chinese.
-
Small role with big impact: miRNAs as communicators in the cross-talk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Feb 25;13(3):339-348. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.17680. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28367098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNAs in cell signaling of cancer associated fibroblasts.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;101:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.05.015. Epub 2018 May 25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29807095 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of CAF-Derived MicroRNA on Tumor Biology and Clinical Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;13(13):3160. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133160. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling and Functional Analysis of microRNA Deregulation in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Depicts an Anti-Invasive Role of microRNA-204 via Regulation of Their Motility.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 4;22(21):11960. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111960. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769388 Free PMC article.
-
Using picoliter droplet deposition to track clonal competition in adherent and organoid cancer cell cultures.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):18832. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42849-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37914743 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor C-RASSF proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 May;75(10):1773-1787. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2756-5. Epub 2018 Jan 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29353317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jun 10;6(1):218. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00641-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34108441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Polanska H, Raudenska M, Gumulec J, Sztalmachova M, Adam V, Kizek R, Masarik M. Clinical significance of head and neck squamous cell cancer biomarkers. Oral Oncol. 2014;50:168–177. - PubMed
-
- Polyak K, Haviv I, Campbell IG. Co-evolution of tumor cells and their microenvironment. Trends Genet. 2009;25:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Wang Y, Li D, Jing S. Notch and TGF-beta/Smad3 pathways are involved in the interaction between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:379–385. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

