Phylogenomic analysis of the family Peptostreptococcaceae (Clostridium cluster XI) and proposal for reclassification of Clostridium litorale (Fendrich et al. 1991) and Eubacterium acidaminophilum (Zindel et al. 1989) as Peptoclostridium litorale gen. nov. comb. nov. and Peptoclostridium acidaminophilum comb. nov
- PMID: 27902180
- PMCID: PMC5244501
- DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001548
Phylogenomic analysis of the family Peptostreptococcaceae (Clostridium cluster XI) and proposal for reclassification of Clostridium litorale (Fendrich et al. 1991) and Eubacterium acidaminophilum (Zindel et al. 1989) as Peptoclostridium litorale gen. nov. comb. nov. and Peptoclostridium acidaminophilum comb. nov
Abstract
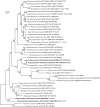
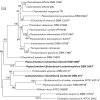
In 1994, analyses of clostridial 16S rRNA gene sequences led to the assignment of 18 species to Clostridium cluster XI, separating them from Clostridium sensu stricto (Clostridium cluster I). Subsequently, most cluster XI species have been assigned to the family Peptostreptococcaceae with some species being reassigned to new genera. However, several misclassified Clostridium species remained, creating a taxonomic conundrum and confusion regarding their status. Here, we have re-examined the phylogeny of cluster XI species by comparing the 16S rRNA gene-based trees with protein- and genome-based trees, where available. The resulting phylogeny of the Peptostreptococcaceae was consistent with the recent proposals on creating seven new genera within this family. This analysis also revealed a tight clustering of Clostridium litorale and Eubacterium acidaminophilum. Based on these data, we propose reassigning these two organisms to the new genus Peptoclostridium as Peptoclostridium litorale gen. nov. comb. nov. (the type species of the genus) and Peptoclostridium acidaminophilum comb. nov., respectively. As correctly noted in the original publications, the genera Acetoanaerobium and Proteocatella also fall within cluster XI, and can be assigned to the Peptostreptococcaceae. Clostridium sticklandii, which falls within radiation of genus Acetoanaerobium, is proposed to be reclassified as Acetoanaerobium sticklandii comb. nov. The remaining misnamed members of the Peptostreptococcaceae, [Clostridium] hiranonis, [Clostridium] paradoxum and [Clostridium] thermoalcaliphilum, still remain to be properly classified.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proposal for the reclassification of obligately purine-fermenting bacteria Clostridium acidurici (Barker 1938) and Clostridium purinilyticum (Dürre et al. 1981) as Gottschalkia acidurici gen. nov. comb. nov. and Gottschalkiapurinilytica comb. nov. and of Eubacterium angustum (Beuscher and Andreesen 1985) as Andreesenia angusta gen. nov. comb. nov. in the family Gottschalkiaceae fam. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017 Aug;67(8):2711-2719. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002008. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28853681 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic relationships of three amino-acid-utilizing anaerobes, Selenomonas acidaminovorans, 'Selenomonas acidaminophila' and Eubacterium acidaminophilum, as inferred from partial 16S rDNA nucleotide sequences and proposal of Thermanaerovibrio acidaminovorans gen. nov., comb. nov. and Anaeromusa acidaminophila gen. nov., comb. nov.Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999 Jul;49 Pt 3:969-74. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-3-969. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10425752
-
Robust demarcation of the family Peptostreptococcaceae and its main genera based on phylogenomic studies and taxon-specific molecular markers.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024 Feb;74(2). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006247. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38319314
-
Review of the genus Methylobacterium and closely related organisms: a proposal that some Methylobacterium species be reclassified into a new genus, Methylorubrum gen. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018 Sep;68(9):2727-2748. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002856. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30024371 Review.
-
Porphyromonas levii - A Boon for Periodontists?J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Apr;16(Suppl 2):S1051-S1054. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1106_23. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 38882857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A diet high in sugar and fat influences neurotransmitter metabolism and then affects brain function by altering the gut microbiota.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 May 27;11(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01443-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34045460 Free PMC article.
-
Using meta-analysis to understand the impacts of dietary protein and fat content on the composition of fecal microbiota of domestic dogs (Canis lupus familiaris): A pilot study.Microbiologyopen. 2024 Apr;13(2):e1404. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1404. Microbiologyopen. 2024. PMID: 38515236 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on the Novel Genera and Species and Revised Taxonomic Status of Bacterial Organisms Described in 2016 and 2017.J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Jan 30;57(2):e01181-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01181-18. Print 2019 Feb. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30257907 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and Evolution of the Sporulation Gene Set in Diverse Members of the Firmicutes.J Bacteriol. 2022 Jun 21;204(6):e0007922. doi: 10.1128/jb.00079-22. Epub 2022 May 31. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35638784 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional electroactive microbial biofilms and the role of biogenic sulfur in charge storage and release.iScience. 2021 Jul 7;24(8):102822. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102822. eCollection 2021 Aug 20. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34337365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baena S., Fardeau M. L., Woo T. H., Ollivier B., Labat M., Patel B. K.(1999). Phylogenetic relationships of three amino-acid-utilizing anaerobes, Selenomonas acidaminovorans, ‘Selenomonas acidaminophila’ and Eubacterium acidaminophilum, as inferred from partial 16S rDNA nucleotide sequences and proposal of Thermanaerovibrio acidaminovorans gen. nov., comb. nov. and Anaeromusa acidaminophila gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49969–974.10.1099/00207713-49-3-969 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bes M., Merrouch M., Joseph M., Quéméneur M., Payri C., Pelletier B., Ollivier B., Fardeau M. L., Erauso G., Postec A.(2015). Acetoanaerobium pronyense sp. nov., an anaerobic alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a carbonate chimney of the Prony Hydrothermal Field (New Caledonia). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 652574–2580.10.1099/ijs.0.000307 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brisbarre N., Fardeau M. L., Cueff V., Cayol J. L., Barbier G., Cilia V., Ravot G., Thomas P., Garcia J. L., Ollivier B.(2003). Clostridium caminithermale sp. nov., a slightly halophilic and moderately thermophilic bacterium isolated from an Atlantic deep-sea hydrothermal chimney. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 531043–1049.10.1099/ijs.0.02471-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Collins M. D., Lawson P. A., Willems A., Cordoba J. J., Fernandez-Garayzabal J., Garcia P., Cai J., Hippe H., Farrow J. A.(1994). The phylogeny of the genus Clostridium: proposal of five new genera and eleven new species combinations. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44812–826.10.1099/00207713-44-4-812 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

